Abstract
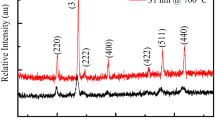
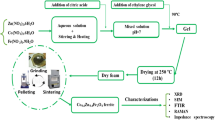
Various polycrystalline compositions Ni0.38−xCu0.15+yZn0.47+x−yFe2O4 [(x, y) = (0.00, 0.01)] are prepared through the sol–gel auto-combustion technique and sintered at 850, 950, 1050, and 1150 °C for 5 h in air. The single-phase cubic spinel structures of the compositions are confirmed by X-ray diffraction analysis. No secondary phases are observed in the X-ray diffraction patterns. The lattice constant is found to increase with do** of Zn2+ in place of Ni2+ and decrease with do** of Cu2+ in place of Ni2+. The bulk density of ferrites increases with sintering temperature up to 1050 °C, then decreases. The field emission scanning electron microscopy is used to demonstrate the surface morphology of the materials. The maximum grain size (1.97 µm) is found for the composition Ni0.38Cu0.16Zn0.46Fe2O4. The maximum bulk density (4.42 × 103 kg/m3), maximum initial permeability, and highest relative quality factor (≥ 6000) are observed for the composition Ni0.38Cu0.16Zn0.46Fe2O4 sintered at 1050 °C. The values of dielectric constants, impedance, and AC resistivity are found higher at lower frequencies but become almost constant at higher frequencies, which can be explained based on the hop** mechanism. The investigated ferrites exhibit comparatively higher permeability, lower eddy current loss, and higher resistivity, which make them suitable for wireless power transfer (WPT) applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data are a part of the ongoing studies. Partial data can be shared upon request. All the raw materials were procured from Sigma Aldrich, Germany.
References
M.V.S. Kumar, G.J. Shankar Murthy, E. Melagiriyappa, K.K. Nagaraja, H.S. Jayanna, M.P. Telenkov, Induced effects of Zn2+ on the transport and complex impedance property of Gadolinium substituted nickel-zinc nano ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 478, 12–19 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.01.058
A. Namai, M. Yoshikiyo, K. Yamada et al., Hard magnetic ferrite with a gigantic coercivity and high frequency millimeter wave rotation. Nat. Commun. 3(1035), 1–6 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2038
N.K. Gupta, Y. Ghaffari, S. Kim, Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants over MFe2O4 (M = Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) nanoparticles at neutral pH. Sci. Rep. 10, 4942 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61930-2
Y. Peng, C. **a, M. Cui, Z. Yao, X. Yi, Effect of reaction condition on microstructure and properties of (NiCuZn)Fe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized via co-precipitation with ultrasonic irradiation. Ultrason. Sonochem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105369
J. Zhao, X. Liu, X. Kan, Z. Chen, C. Liu, W. Wang, Q. Lv, J. Huang, M. Shazeda, Characterization of magnetic properties and microstructures for Co3+ ions-doped Ni-Cu-Zn ferrites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 9057–9064 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03451-2
M.H. Rashid, A.K.M. Akhter Hossain, Structural, morphological and electromagnetic properties of Sc3+ doped in Ni-Cu-Zn ferrites. Results Phys. 11, 888–895 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.10.050
S.T. Mahmud, A.K.M. Akhter Hossain, A.K.M.A. Hakim, M. Seki, T. Kawai, H. Tabata, Influence of microstructure on the complex permeability of spinel type Ni-Zn ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 305, 269–274 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.01.012
X. Wu, S. Yan, W. Liu, Z. Feng, Y. Chen, V.G. Harris, Influence of particle size on the magnetic spectrum of NiCuZn ferrites for electromagnetic shielding applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 40, 1093–1096 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.10.129
S.R. Khan, S.K. Pavuluri, M.P.Y. Desmulliez, Accurate modeling of coil inductance for near-field wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 66, 4158–4169 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2018.2854190
M. Nabil, M. Bima, A. Alsharif, W. Johnson, S. Gunukula, M. Mahmoud, M. Abdallah, Priority-based and privacy-preserving electric vehicle dynamic charging system with divisible e-payment. Smart Cities Cyber. Priv. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815032-0.00012-3
Y. Liu, G. Sreenivasulu, P. Zhou, Converse magneto-electric effects in a core–shell multiferroic nanofiber by electric field tuning of ferromagnetic resonance. Sci. Rep. 10, 20170 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-77041-x
W. Liu, S. Yan, Y. Cheng, Q. Li, Z. Feng, X. Wang, R. Gong, Y. Nie, Monodomain design and permeability study of high-Q-factor NiCuZn ferrites for near-field communication application. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 4367–4372 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-015-3978-z
A. Gholizadeh, E. Jafari, Effect of sintering atmosphere and temperature on structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Cu-Zn ferrite nanoparticles: magnetic enhancement by a reducing atmosphere. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 422, 328–336 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.09.029
H. Su, X. Tang, H. Zhang, L. Jia, Z. Zhong, Influences of Fe deficiency on electromagnetic properties of low-temperature-fired NiCuZn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 1779–1783 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.12.029
H. Su, H. Zhang, X. Tang, Z. Zhong, F. Bai, Influences of high calcination temperature on densification and magnetic properties of low temperature-fired NiCuZn ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 47, 4328–4331 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.12.029
T. Nakamura, Snoek’s limit in high-frequency permeability of polycrystalline Ni-Zn, Mg-Zn, and Ni-Zn-Cu spinel ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 88, 348 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.373666
C.P. Wu, M.J. Tung, W.S. Ko, Y.P. Wang, S.Y. Tong, M.D. Yang, Effect of neodymium substitutions on electromagnetic properties in low temperature sintered NiCuZn ferrite. Phys. B. 476, 137–140 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2015.05.022
M. Arifuzzaman, M.B. Hossen, M. Harun-Or-Rashid, M.L. Rahman, Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni0.7-xCuxCd0.3Fe2O4 prepared through sol-gel method. J. Mater. Charact. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110810
P. Pranisisco, A. Shafie, B.H. Guan, Effect of calcination temperature on microstructure and magnetic properties of Ni-Cu-Zn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Am. Inst. Phys. 1621, 619 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4898532
S.K. Sharma, R. Kumar, S. Kumar, M. Knobel, C.T. Meneses, V.V.S. Kumar, V.R. Reddy, M. Singh, C.G. Lee, Role of interparticle interactions on the magnetic behavior of Mg-Mn ferrite nanoparticle. J. Phys: Condens. Matter. 20, 235214 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/20/23/235214
P. Lathiya, M. Kreuzer, J. Wang, RF complex permeability spectra of Ni-Cu-Zn ferrites prepared under different applied hydraulic pressures and durations for wireless power transfer (WPT) applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 499, 166273 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166273
A.K.M. Akhter Hossain, S.T. Mahmud, M. Seki, T. Kawai, H. Tabata, Structural, electrical transport, and magnetic properties of Ni1-xZnxFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 312, 210–219 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.09.030
J. **ang, X. Shen, F. Song, M. Liu, One-dimensional NiCuZn ferrite nanostructures: fabrication, structure, and magnetic properties. J. Solid State Chem. 183, 1239–1244 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2010.03.041
S.T. Assar, H.F. Abosheiasha, A.R. El Sayed, Effect of γ-rays irradiation on structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of Mg-Cu-Zn and Ni-Cu-Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 421, 355–367 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.08.028
A.B. Nawale, N.S. Kanhe, K.R. Patil, S.V. Bhoraskar, V.L. Mathe, A.K. Das, Magnetic properties of thermal plasma synthesized nanocrystalline nickel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 4404–4413 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.01.057
M. Houshiar, L. Jamilpanah, Effect of Cu dopant on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Ni-Zn ferrites. J. Mater. Res. Bull. 98, 213–218 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.10.024
S.M. Hoque, M.A. Choudhury, M.F. Islam, Characterization of Ni–Cu mixed spinel ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 251, 292–303 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00700-X
W.C. Hsu, S.C. Chen, P.C. Kuo, C.T. Lie, W.S. Tsai, Preparation of NiCuZn ferrite nanoparticles from chemical co-precipitation method and the magnetic properties after sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 111, 142–149 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2004.04.009
S.M. Kabbur, U.R. Ghodake, D.Y. Nadargi, R.C. Kambale, S.S. Suryavanshi, Effect of Dy3+ substitution on structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni-Cu-Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 451, 665–675 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.12.006
M. Harun-Or-Rashid, M.N. Islam, M. Arifuzzaman, A.K.M. Akhter Hossain, Effect of sintering temperature on the structural, morphological, electrical, and magnetic properties of Ni-Cu-Zn and Ni-Cu-Zn-Sc ferrites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-05018-7
Md.D. Rahman, K.K. Nahar, M.N.I. Khan, A.K.M. Akhter Hossain, Synthesis, structural, and electromagnetic properties of Mn0.5MgxZn0.5-xFe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.1) polycrystalline ferrites. Phys. B 481, 156–164 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2015.11.008
S. Nasrin, S.M. Khan, M.A. Matin, M.N.I. Khan, A.K.M. Akhter Hossain, M.D. Rahman, Synthesis and deciphering the effects of sintering temperature on structural, elastic, dielectric, electric and magnetic properties of magnetic Ni0.25Cu0.13Zn0.62Fe2O4 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater Electron. 30, 10722–10741 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01417-7
A. Verma, T.C. Geol, R.G. Mendiratta, Frequency variation of initial permeability of NiZn ferrites prepared by the citrate precursor method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 210, 274–278 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(99)00451-5
A.K.M. Akhter Hossain, M.L. Rahman, Enhancement of microstructure and initial permeability due to Cu Substitution in Ni0.50-xCuxZn0.50Fe2O4 ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1954–1962 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.02.031
I.R. Ibrahim, K.A. Matori, I. Ismail, A study on microwave absorption properties of carbon black and Ni0.60Zn0.40Fe2O4 nanocomposites by tuning the matching-absorbing layer structures. Sci. Rep. 10, 3135 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60107-1
A.K. Sing, T.C. Goel, R.G. Mendiratta, O.P. Thakur, C. Prakash, Magnetic properties of Mn-substituted Ni-Zn ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 3872–3876 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1504493
M.D. Rahaman, M.D. Mia, M.N.I. Khan, A.K.M.A. Hossain, Study the effect of sintering temperature on structural, microstructural and electromagnetic properties of 10% Ca-doped Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 404, 238–249 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.12.029
B.C. Das, F. Alam, A.K.M. Akhter Hossain, The crystallographic, magnetic, and electrical properties of Gd3+ substituted Ni-Cu-Zn mixed ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109433
G. Umapathy, G. Senguttuvan, L.J. Berchmans, V. Sivakumar, Structural, dielectric and AC conductivity studies of Zn substituted nickel ferrites prepared by combustion technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 7062–7072 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4664-5
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the following financial support: Office of Research and Extension, Bangladesh University of Textiles, Dhaka, Bangladesh (Code-3632104, FY 2020-2021, S/N 9, BUTEX/2019/RnE/0018, 23.08.2020). We are grateful to the Solid-State Physics Laboratory of Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET), Dhaka, Bangladesh, for allowing us to do this research.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the following financial support: Office of Research and Extension, Bangladesh University of Textiles, Dhaka, Bangladesh (Code-3632104, FY 2020-2021, S/N 9, BUTEX/2019/RnE/0018, 23.08.2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harun-Or-Rashid, M., Rahman, M.M., Arifuzzaman, M. et al. Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of Ni0.38−xCu0.15+yZn0.47+x−yFe2O4 synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion technique. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 13761–13776 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05953-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05953-z