Abstract
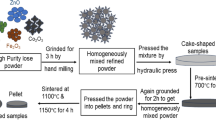
In this study, novel Ni–Cu–Zn ferrites with the chemical formula [Ni0.6Zn0.4][Cu0.2CoxFe1.8−x]O4 (x = 0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, 0.25) doped with Co2+ ions were designed and manufactured by standard solid-state reaction method. The magnetic properties, surface characteristics, and ion occupancy of ferrites were studied by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), and we explained the different mechanisms of the results and the relationship between magnetic properties and microstructures. For the obtained samples, cobalt ions entered the lattice, and all samples were characterized as spinel structures. As the do** amount of Co2+ ions increases, the lattice constant and volume of the sample also increases. With an appropriate do** level, Co2+ ions-doped Ni–Cu–Zn ferrites can maintain higher saturation magnetization, higher magnetic permeability, and lower hysteresis loss. When x ≤ 0.1, the saturation magnetization Ms increases significantly as the do** amount of Co2+ ions increases, but when x > 0.1, the value decreases. The experimental results show that the saturation magnetization value is 118.08 emu/g, the magnetic permeability value is 39.47 H/m, and the hysteresis loss is 1.192 mW/cm3 at an optimum do** amount. Therefore, the sample achieves the best magnetic properties when the do** amount is 0.1.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.L. Zhao, Q. Lv, Z.M. Shen, Fabrication and microwave absorbing properties of Ni–Zn spinel ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 480(2), 634–638 (2009)
S.J. Feng, J. Li, S.G. Huang, Magnetic hysteresis loss crossover in Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe1.95Ti0.05O4 ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 660, 398–401 (2016)
T. Nakamura, Low-temperature sintering of NiZnCu ferrite and its permeability spectra. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 168(3), 285–291 (1997)
M. Fujimoto, Inner stress induced by Cu metal precipitation at grain boundaries in low-temperature-fired Ni–Zn–Cu ferrite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 77(11), 2873–2878 (1994)
P. Yang, Z.Q. Liu, H.B. Qi, High-performance inductive couplers based on novel Ce3+ and Co2+ ions co-doped Ni–Zn ferrites. Ceram Int. 45(11), 13685–13691 (2019)
R.C. Kambale, N.R. Adhate, B.K. Chougule, Magnetic and dielectric properties of mixed spinel Ni–Zn ferrites synthesized by citrate–nitrate combustion method. J. Alloy. Compd. 491(1–2), 372–377 (2010)
T. Nakamura, Y. Okano, S. Miura, Interfacial diffusion between Ni–Zn–Cu ferrite and Ag during sintering. J. Mater. Sci. 33(4), 1091–1094 (1998)
S.E. Shirsath, R.H. Kadam, S.M. Patange, M.L. Mane, A. Ghasemi, A. Morisako, Appl. Phys. Lett 100(4), 42407 (2012)
L. Li, L. Peng, Y. Li et al., Structure and magnetic properties of Co-substituted NiZn ferrite thin films synthesized by the sol–gel process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(1), 60–62 (2012)
X. Pan, A. Sun, Y. Han, Structural and magnetic properties of Bi3+ ion doped Ni–Cu–Co nano ferrites prepared by sol–gel auto combustion method. J. Mater. Sci. 30(5), 4644–4657 (2019)
M.P. Reddy, W. Madhuri, N.R. Reddy, Influence of copper substitution on magnetic and electrical properties of MgCuZn ferrite prepared by microwave sintering method. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 30(8), 1094–1099 (2010)
H.B. Wang, J.H. Liu, W.F. Li, Structural, dynamic magnetic and dielectric properties of Ni015Cu0.2Zn0.65Fe2O4 ferrite produced by NaOH co-precipitation method. J. Alloy. Compd. 461(1), 373–377 (2008)
L. Néel, Magnetic properties of ferrites: ferrimagnetism and antiferromagnetism. Ann. Phys. 3, 137–198 (1948)
G.D. Tang, D.H. Ji, Y.X. Yao, S.P. Liu, Z.Z. Li, W.H. Qi, Q.J. Han, X. Hou, D.L. Hou, Quantum-mechanical method for estimating ion distributions in spinel ferrites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 072511 (2011)
Y.M. Kwon, M.Y. Lee, M. Mustaqima, C. Liu, B.W. Lee, Structural and magnetic properties of Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 ferrite prepared by solid state reaction and sol–gel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 19, 64–67 (2014)
J. Jadhav, S. Biswas, A.K. Yadav, S.N. Jha, D. Bhattacharyya, Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline NiZn ferrites: in the context of cationic distribution. J. Alloys Compd. 696, 28–41 (2017)
N. Singh, A. Agarwal, S. Sanghi, Effect of magnesium substitution on dielectric and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrite. Phys. B 406(3), 687–692 (2011)
R. Kumar, H. Kumar, M. Kumar, Enhanced saturation magnetization in cobalt doped Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28(12), 3557–3564 (2015)
M. Veverka, Z. Jirak, O. Kaman, K. Knızek, M. Marysko, E. Pollert, K. Zaveta, A. Lancok, M. Dlouha, S. Vratislav, Distribution of cations in nanosize and bulk Co–Zn ferrites. Nanotechnology 22, 345701 (2011)
E.J. Choi, Y.K. Ahn, K.C. Song, D.H. An, B.G. Lee, K.U. Kang, Cation distribution and spin-canted structure in cobalt ferrite particles from a cobalt–iron hydroxide carbonate complex. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 44, 1518–1520 (2004)
M.K. Fayek, A.A. Bahgat, Y.M. Abbas, L. Moberg, Neutron diffraction and Mossbauer effect study on a cobalt substituted zinc ferrite. J. Phys. C 15, 2509–2518 (1982)
G.A. Sawatzky, F. Van Der Woude, A.H. Morrish, Mo ¨ssbauer study of several ferrimagnetic spinels. Phys. Rev. 187, 747 (1969)
A.M. Kumar, P.A. Rao, M.C. Varma, G.S. Choudary, K.H. Rao, Cation distribution in Co0.7Me0.3Fe2O4. J. Mod. Phys. 2, 1083 (2011)
J.Y. Hu, X.S. Liu, X.C. Kan, Characterization of texture and magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5TixFe2−xO4 spinel ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 489, 165411 (2019)
A.R. Das, V.S. Ananthan, D.C. Khan, Lattice parameter variation and magnetization studies on titanium-, zirconium-, and tin-substituted nickel–zinc ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 57(8), 4189–4191 (1985)
D.C. Khan, M. Misra, Magnetic, Mössbauer and electrical properties of Ti-substituted Ni0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4. Bull. Mater. Sci. 7(3–4), 253–270 (1985)
K.K. Bharathi, G. Markandeyulu, C.V. Ramana, Structural, magnetic, electrical, and magnetoelectric properties of Sm- and Ho-substituted nickel ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(2), 554–560 (2010)
D. Hu, F. Zhao, L. Miao, Magnetic properties and microstructures of a Ni–Zn ferrite ceramics co-doped with V2O5 and MnCO3. Ceram. Int. 45(8), 10028–10034 (2019)
S.S. Kim, D.H. Han, S.B. Cho, Microwave absorbing properties of sintered Ni–Zn ferrite. IEEE Trans. Magn. 30(6), 4554–4556 (1994)
F. Gen, E. Turhan, H. Kavas, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of NixZn0.9−xMn0.1Fe2O4 prepared by boron addition. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28(3), 1047–1050 (2015)
S. Modak, M. Ammar, F. Mazaleyrat, XRD, HRTEM and magnetic properties of mixed spinel nanocrystalline Ni–Zn–Cu-ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 473(1), 15–19 (2009)
P. Priyadharsini, A. Pradeep, P.S. Rao, Structural, spectroscopic and magnetic study of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 116(1), 207–213 (2009)
H. Su, X. Tang, H. Zhang, Influences of Bi2O3 additive on the microstructure, permeability, and power loss characteristics of Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321(19), 3183–3186 (2009)
S.V. Trukhanov, Magnetic and magnetotransport properties of La1−xBaxMnO3−x/2 perovskite manganites. J. Mater. Chem. 13(2), 347–352 (2003)
V.D. Doroshev, V.A. Borodin, V.I. Kamenev, Self-doped lanthanum manganites as a phase-separated system: transformation of magnetic, resonance, and transport properties with do** and hydrostatic compression. J. Appl. Phys. 104(9), 093909 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51872004, 51802002), Education Department of Anhui Province (Grant Nos. KJ2013B293, KJ2018A0039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Liu, X., Kan, X. et al. Characterization of magnetic properties and microstructures for Co2+ ions-doped Ni–Cu–Zn ferrites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 9057–9064 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03451-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03451-2