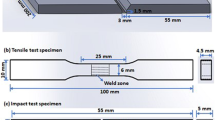
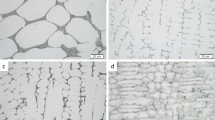
Abstract
In this study, gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) was used to weld AA6082-T651 plates using ER5335 and ER4340 filler metals. Significant softening of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) was observed in the as-welded condition. An attempt was made to recover the softening by applying an appropriate heat treatment after welding. The thermal process consisted of solution annealing and then aging at 160 °C for 18 h. The HAZ properties were characterized in the as-welded and post-weld heat-treated (PWHT) conditions using field emission scanning and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, microhardness testing, thermal simulation, and differential scanning calorimetry techniques. The HAZ hardness profile revealed four distinct regions: partially melted zone (PMZ), partial solution, over-aged zone, and partial transformation. A PMZ with a hardness of about 90 Vickers was detected adjacent to the fusion line, which had been exposed to a sufficient temperature to dissolve the Mg2Si phases completely. Accordingly, natural aging increased the hardness of PMZ after welding. The minimum HAZ hardness was found at a distance of about 7–9 mm from the fusion line, where the temperature was in the range of β-Mg2Si formation and resulted in over-aging. In addition, dislocation density was reduced compared to the as-received base metal. The hardness after PWHT exhibited full recovery and improved to values higher than the as-received base metal. The hardness recovery was attributed to the uniformly distributed fine coherent needle-shaped βꞌꞌ-Mg2Si after PWHT. There were also coarse Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2 intermetallic and submicron spherical Mn-rich dispersoids in all conditions.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. George, D.S. Totten, Mackenzie, Handbook of Aluminum: Vol. 1: Physical Metallurgy and Processes (CRC Press, New York, 2003)
J.W. Bray, Aluminum mill and engineered wrought products, in Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, vol. 2 (ASM International, Materials Park, 1990). https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v02.9781627081627
J.R. Kissell, R.L. Ferry, Aluminum Structures: A Guide to Their Specifications and Design, 2nd edn. (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, 2002)
N.H. Alharthi, Evaluation and prediction of microstructure evolution in deformed aluminum alloys, M.S. Thesis, Lehigh University (2011)
L. Zhang, R. Lu, J. Tang, F. Jiang, D. Fu, H. Zhang, J. Teng, Met. Mater. Int. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-022-01353-y
C. Vargel, Corrosion of Aluminium, 1st edn. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2004)
E.R. Imam Fauzi, M.S. Che Jamil, Z. Samad, P. Muangjunburee, J. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 27, 17 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60003-7
A. Bandi, S.R. Bakshi, Met. Mater. Int. 28, 1678 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-021-01039-x
S.R. Chikhale, K.P. Kolhe, A review on prediction of heat affected Zone of Al-6061 alloy. Int. J. Eng. Res. Special Issue, 54 (2015)
W.A. Monteiro, Light Metal Alloys Applications, 1st edn. (IntechOpen, Rijeka, 2014)
M. Hakem, S. Lebaili, S. Mathieu, D. Miroud, A. Lebaili, B. Cheniti, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 102, 2907 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03401-1
EN 1999, Eurocode 9: Design of aluminium structures, European Standard (2007)
G. Mathers, The Welding of Aluminium and Its Alloys (Woodhead Publishing, Abington, 2002)
T. Anderson, Welding Aluminum-Questions and Answers, 2nd edn. (American Welding Society, Miami, 2010)
W. Ma, B. Wang, J. Lin, X. Tang, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 27, 2454 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60272-3
N.E. Nanninga, High Cycle Fatigue of AA6082 and AA6063 Aluminum Extrusions, Ph.D. Thesis, Michigan Technological University (2008)
C.D. Marioara, S.J. Andersen, J. Jansen, H.W. Zandbergen, Acta Mater. 51, 789 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00470-6
W. Chrominski, M. Lewandowska, Acta Mater. 103, 547 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.10.030
X. He, Q. Pan, H. Li, Z. Huang, S. Liu, K. Li, X. Li, Metals 9, 173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/met9020173
O.R. Myhr, Ã. Grong, H.G. Fjær, C.D. Marioara, Acta Mater. 52, 4997 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2004.07.002
S. Missori, A Sili, Mechanical behaviour of 6082-T6 aluminium alloy welds. Metall. Res. Technol. 18(1), 12 (2000)
S. Baskutis, J. Baskutiene, R. Bendikiene, A. Ciuplys, J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 33, 765 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-0131-6
W. Zhang, H. He, C. Xu, W. Yu, L. Li, JOM 71, 2711 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03375-1
B. Wang, S. Xue, C. Ma, J. Wang, Z. Lin, Metals 7, 463 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/met7110463
P. Wiechmann, H. Panwitt, H. Heyer, M. Reich, M. Sander, O. Kessler, Materials 11, 1396 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081396
ASTM E384-99, Standard Test Methods for Microindentation Hardness of Materials (ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 2002)
B. Wang, J. Wang, X. Liu, Q. Li, X. Liu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 858, 144090 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.144090
M.V. Kral, P.N.H. Nakashima, D.R.G. Mitchell, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 1987 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0141-8
S. Ferraro, A. Fabrizi, G. Timelli, Mater. Chem. Phys. 153, 168 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.12.050
X.D. Ren, L. Ruan, S.Q. Yuan, N.F. Ren, L.M. Zheng, Q.B. Zhan, J.Z. Zhou, H.M. Yang, Y. Wang, F.Z. Dai, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 578, 96 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.04.034
W.S. Lee, Z.C. Tang, Mater. Des. 58, 116 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.01.053
S.W. Nam, D.H. Lee, Met. Mater. 6, 13 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03026339
A.F.M. Muggerud, E.A. Mørtsell, Y. Li, R. Holmestad, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 567, 21 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.01.004
X. Qian, N. Parson, X.G. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 764, 138253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138253
A.M.F. Muggerud, Transmission electron microscopy studies of dispersoids and constituent phases in al-mn-fe-si alloys, Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (2014)
A.M.F. Muggerud, Y. Li, R. Holmestad, Acta Cryst. 70, 888 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052520614017880
Y.J. Li, A.M.F. Muggerud, A. Olsen, T. Furu, Acta Mater. 60, 1004 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.11.003
R. Vissers, M.A. van Huis, J. Jansen, H.W. Zandbergen, C.D. Marioara, S.J. Andersen, Acta Mater. 55, 3815 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.02.032
Z. Xu, H. Ma, N. Zhao, Z. Hu, Metals 10, 469 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10040469
BS EN 485-2, Aluminum and Aluminum alloys - Sheet, Strip, and Plate. Part 2: Mechanical Properties, British Standard (2016)
J.M. Sánchez-Amaya, T. Delgado, L. González-Rovira, F.J. Botana, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 9512 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.07.081
T.K. Chu, C.Y. Ho, in Thermal Conductivity 15, ed. by V.V. Mirkovich (Springer, Boston, 1978), p. 79
E. Kaschnitz, L. Kaschnitz, S. Heugenhauser, Int. J. Thermophys. 40, 27 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-019-2490-8
I. Dutta, S.M. Allen, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 10, 323 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00719697
W.F. Miao, D.E. Laughlin, Scr. Mater. 40, 873 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(99)00046-9
J. Osten, B. Milkereit, C. Schick, O. Kessler, Materials 8, 2830 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8052830
Z. Chen, K. Liu, E. Elgallad, F. Breton, X.G. Chen, Metals 10, 763 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060763
G. Asghar, L. Peng, P. Fu, L. Yuan, Y. Liu, Mater. Des. 186, 108280 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108280
J. Schällibaum, T. Burbach, C. Münch, W. Weiler, A. Wahlen, Mater. Sci. Eng. Technol. 46, 704 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/mawe.201500402
P.V. Witzendorff, S. Kaierle, O. Suttmann, L. Overmeyer, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 225, 162 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.06.007
K. Strobel, M.A. Easton, L. Sweet, M.J. Couper, J.F. Nie, Mater. Trans. 52, 914 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.L-MZ201111
S. Esmaeili, D.J. Lloyd, Mater. Sci. Forum 519-521, 169 (2006). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.519-521.169
H.W. Zandbergen, S.J. Andersen, J. Jansen, Science 277, 1221 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5330.1221
S.J. Anderson, H.W. Zandbergen, J. Jansen, C. TrÆholt, U. Tundal, O. Reiso, Acta Mater. 46, 3283 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(97)00493-X
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jula, M., Dehmolaei, R. & Ranjbar, K. Softening, Hardening, and Precipitation Evolution of the AA6082-T651 Heat-Affected Zone Caused by Thermal Cycles During and After Welding. Met. Mater. Int. 29, 3664–3678 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-023-01470-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-023-01470-2