Search
Search Results
-
Kainic Acid-Induced Excitotoxicity Leads to the Activation of Heat Shock Response
Heat shock response (HSR) which is regulated by heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) is the most important mechanism and the major regulator that prevents...

-
Anti-epileptic and Neuroprotective Effects of Ultra-low Dose NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor Dextromethorphan on Kainic Acid-induced Chronic Temporal Lobe Epilepsy in Rats
Neuroinflammation mediated by microglia and oxidative stress play pivotal roles in the development of chronic temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). We...

-
Anticonvulsant Effects of Royal Jelly in Kainic Acid-Induced Animal Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Through Antioxidant Activity
Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is the most common form of partial and drug-resistant epilepsy, characterized by recurrent seizures originating from...

-
Pulsed Focused Ultrasound Reduces Hippocampal Volume Loss and Improves Behavioral Performance in the Kainic Acid Rat Model of Epilepsy
Focused ultrasound (FUS) has the potential to modulate regional brain excitability and possibly aid seizure control; however, effects on behavior of...

-
Anti-Seizure and Neuronal Protective Effects of Irisin in Kainic Acid-Induced Chronic Epilepsy Model with Spontaneous Seizures
An increased level of reactive oxygen species is a key factor in neuronal apoptosis and epileptic seizures. Irisin reportedly attenuates the...

-
The Glycolysis Inhibitor 2-Deoxy-d-Glucose Exerts Different Neuronal Effects at Circuit and Cellular Levels, Partially Reverses Behavioral Alterations and does not Prevent NADPH Diaphorase Activity Reduction in the Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Temporal lobe epilepsy is the most drug-resistant type with the highest incidence among the other focal epilepsies. Metabolic manipulations are of...

-
Pulsed-Focused Ultrasound Provides Long-Term Suppression of Epileptiform Bursts in the Kainic Acid-Induced Epilepsy Rat Model
Focused ultrasound (FUS) has potential utility for modulating regional brain excitability and possibly aiding seizure control; however, the duration...

-
H19 silencing decreases kainic acid-induced hippocampus neuron injury via activating the PI3K/AKT pathway via the H19/miR-206 axis
Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is the most common type of intractable epilepsy and is refractory to medications. However, the role and mechanism of H19...

-
Chemogenetic Seizure Control with Clozapine and the Novel Ligand JHU37160 Outperforms the Effects of Levetiracetam in the Intrahippocampal Kainic Acid Mouse Model
Expression of inhibitory designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADDs) on excitatory hippocampal neurons in the hippocampus...

-
Domoic Acid as a Neurotoxin
Domoic acid (DOM) is a naturally occurring excitatory amino acid with structural similarity, and similar but not identical pharmacological profile,...
-
Melatonin Pretreatment Protects Against Status epilepticus, Glutamate Transport, and Oxidative Stress Induced by Kainic Acid in Zebrafish
Status epilepticus (SE) develops from abnormal electrical discharges, resulting in neuronal damage. Current treatments include antiepileptic drugs....

-

-
Methods for the Induction of Status Epilepticus and Temporal Lobe Epilepsy in Rodents: The Kainic Acid Model and the Pilocarpine Model
Status epilepticus (SE) and temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) models are developed to understand the pathophysiology involved, discovering novel...
-
Domoic Acid As a Neurotoxin
Domoic acid (DOM) is a naturally occurring excitatory amino acid with structural similarity, and similar but not identical pharmacological profile,...
-
Neuroprotective effects of chlorogenic acid against oxidative stress in rats subjected to lithium-pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus
Epilepsy is a condition marked by sudden, self-sustained, and recurring brain events, showcasing unique electro-clinical and neuropathological...

-
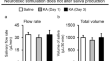
Neurotoxic stimulation alters prosaposin levels in the salivary systems of rats
Prosaposin (PSAP), a potent neurotrophic factor, is found in neuronal and non-neuronal tissues and various biological fluids. Neuropathological...
-
Astrocyte-derived SerpinA3N promotes neuroinflammation and epileptic seizures by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway in mice with temporal lobe epilepsy
Impaired activation and regulation of the extinction of inflammatory cells and molecules in injured neuronal tissues are key factors in the...

-
Role of Elevated Thrombospondin-1 in Kainic Acid-Induced Status Epilepticus
Previous studies have suggested that thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) regulates the transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1)/phosphorylated Smad2/3...

-
Quinolinic Acid and Related Excitotoxins: Mechanisms of Neurotoxicity and Disease Relevance
There are many ways in which neuronal damage can be produced in the brain, including the overactivation of depolarizing receptors, exposure to high...
-
Investigating the mechanism of antiepileptogenic effect of apigenin in kainate temporal lobe epilepsy: possible role of mTOR
Clarifying the underlying mechanisms of epileptogenesis is important in preventing the progression of chronic epilepsy. In epilepsy, the mTOR...

