Abstract
Striking a balance between economic development and environmental sustainability has evolved into an important primary goal for international organizations, governments and the globe. In the modern era, world economies, particularly develo** ones such as South Asian economies, aim to achieve economic growth while simultaneously improving the reduction of ecological footprint (EFP). Against this backdrop, this study explores the impact of economic growth, biocapacity, renewable energy use, natural resource rent, agricultural value-added, green finance and information and communication technology on the ecological footprint. The scope of the relationship among the variables is examined within the environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) framework with a dataset from 1990 to 2017. The cross-sectional-augmented autoregressive distributed lag (CS-ARDL) approach was applied to estimate the variable's short and long-term interaction. The results indicated the existence of the EKC hypothesis in this region. In addition, agriculture value-added, natural resources, and biocapacity increase EFP. Further, renewable energy use, green finance, and ICT mitigate EFP. The Dumitrescu and Hurlin (D-H) causality test reflected a unidirectional causality association flowing from economic growth, renewable energy use, green finance, and agricultural value-added to EFP. Lastly, there exists a bidirectional nexus between natural resource rent, biocapacity, ICT, and EFP. The present research adds to the existing literature on the factors contributing to environmental pollution by presenting new insights from South Asian economies. This study also provides a reference point for policymakers and government entities in these regions to invest in cleaner technologies, ICT, and green finance to mitigate environmental pollution.

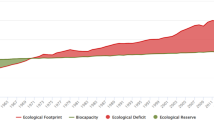
(Source: Author's own)








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Abbreviations
- COP 26:
-
Conference of the parties 26
- UNFCCC:
-
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change conference
- SSE:
-
South Asian economies
- EFP:
-
Ecological footprint
- BIO:
-
Biocapacity
- EGC:
-
Economic growth
- GDP:
-
Gross domestic product
- REU:
-
Renewable energy use
- GFN:
-
Green finance
- NRR:
-
Natural resource rent
- ICT:
-
Information and communication technology
- AGRIC-VA:
-
Agriculture value-added
- EKC:
-
Environmental Kuznets curve
- CS-ARDL:
-
Cross-sectional-augmented autoregressive distributed lag
- CC-MG:
-
Common correlated effect means group estimator
- AMG:
-
Augmented mean group
- D-H:
-
Dumitrescu–Hurlin
- SHT:
-
Slope homogeneity test
- VIF:
-
Variance inflation factor
- CSD:
-
Cross-sectional dependency
- CADF:
-
Cross-sectional augmented Dickey–Fuller
- CIPS:
-
I'm Pesaran and Shin
- STIRPAT:
-
Stochastic impacts by regression on population, affluence, and technology
- WID:
-
World development indicator
- OECD:
-
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development
References
Abid M (2016) Impact of economic, financial, and institutional factors on CO 2 emissions : evidence from Sub-Saharan Africa economies. Utilities Policy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jup.2016.06.009
Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D, Adeshola I, Oluwajana D, Akinsola GD, Osemeahon OS (2021) Coal consumption and environmental sustainability in South Africa: the role of financial development and globalization. Int J Renew Energy Dev 10(3):527–536. https://doi.org/10.14710/ijred.0.34982
Agbede EA, Bani Y, Azman-Saini WNW, Naseem NAM (2021) The impact of energy consumption on environmental quality: empirical evidence from the MINT countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(38):54117–54136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14407-2
Ahmad M, Jiang P, Majeed A, Umar M, Khan Z, Muhammad S (2020) The dynamic impact of natural resources, technological innovations and economic growth on ecological footprint : an advanced panel data estimation. Resour Policy 69(July):101817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101817
Ahmed Z, Wang Z, Mahmood F, Hafeez M, Ali N (2019) Does globalization increase the ecological footprint ? Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 18565–18582.
Akinsola GD, Awosusi AA, Kirikkaleli D, Umarbeyli S, Adeshola I, Adebayo TS (2022) Ecological footprint, public-private partnership investment in energy, and financial development in Brazil: a gradual shift causality approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(7):10077–10090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15791-5
Alper AE, Alper FO, Ozayturk G, Mike F (2022) Testing the long-run impact of economic growth, energy consumption, and globalization on ecological footprint: new evidence from Fourier bootstrap ARDL and Fourier bootstrap Toda-Yamamoto test results. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18610-7
Alvarado R, Ortiz C, Jiménez N, Ochoa-Jiménez D, Tillaguango B (2021) Ecological footprint, air quality and research and development: the role of agriculture and international trade. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125589
Asongu SA, Le Roux S, Biekpe N (2018) Enhancing ICT for environmental sustainability in sub-Saharan Africa. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 127:209–216
Muhammad Awais Baloch D, Danish YQ, Qiu Y (2021) Does energy innovation play a role in achieving sustainable development goals in BRICS countries? Environ Technol (united Kingdom) 2:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2021.1874542
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Osundina OA (2019a) Do agricultural activities induce carbon emissions? The BRICS experience. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(24):25218–25234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05737-3
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Gokmenoglu KK, Taspinar N, Cantos-Cantos JM (2019b) An approach to the pollution haven and pollution halo hypotheses in MINT countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(22):23010–23026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05446-x
Balsalobre-lorente D, Shahbaz M, Jose C, Jabbour C, Driha OM (2019) The role of energy innovation and corruption in carbon emissions : evidence-based on the EKC hypothesis.
Baydoun H, Aga M (2021) The effect of energy consumption and economic growth on environmental sustainability in the GCC countries: does financial development matter? Energies 14(18):21456. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14185897
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S (2019) Combustible renewables and waste consumption, agriculture, CO2 emissions and economic growth in Brazil. Carbon Manag 10(3):309–321
Ben Jebli M, Ben Youssef S, Ozturk I (2015) The role of renewable energy consumption and trade: environmental Kuznets curve analysis for Sub-Saharan Africa countries. Afr Dev Rev 27(3):288–300
Breitung J (2001) The local power of some unit root tests for panel data. Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Brenya R, Akomea-Frimpong I, Ofosu D, Adeabah D (2022) Barriers to sustainable agribusiness: a systematic review and conceptual framework. J Agribusiness Dev Emerg Econom. https://doi.org/10.1108/JADEE-08-2021-0191
Breusch T, Pagan A (1980) The lagrange multiplier test and its applications for the error components model with incomplete panels. Rev Econ Stud 47(1):239–253
Caglar AE, Mert M, Boluk G (2021) Testing the role of information and communication technologies and renewable energy consumption in ecological footprint quality: evidence from world top 10 pollutant footprint countries. J Clean Prod 298:126784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126784
Caglar AE, Yavuz E, Mert M, Kilic E (2022) The ecological footprint facing asymmetric natural resources challenges: evidence from the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(7):10521–10534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16406-9
Cai L, Kwasi Sampene A, Khan A, Oteng-Agyeman F, Tu W, Robert B (2022) Does entrepreneur moral reflectiveness matter? pursing low-carbon emission behavior among SMEs through the relationship between environmental factors, entrepreneur personal concept, and outcome expectations. Sustainability 14(2):808
Chen X, Chen Z (2021) Can green finance development reduce carbon emissions ? Empirical Evidence from 30 Chinese Provinces. 1–18.
Chopra R, Magazzino C, Shah MI, Sharma GD, Rao A, Shahzad U (2022) The role of renewable energy and natural resources for sustainable agriculture in ASEAN countries: do carbon emissions and deforestation affect agriculture productivity? Resour Policy 76(February):102578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.102578
Chudik A, Pesaran MH (2015) Common correlated effects estimation of heterogeneous dynamic panel data models with weakly exogenous regressors. J Econom 188(2):393–420
Danish Ulucak R, Khan SUD (2020) Determinants of the ecological footprint: role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization. Sustain Cities Soci, 54(2019), 101996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101996
Danish Wang Z (2019) Does biomass energy consumption help to control environmental pollution? Evidence from BRICS countries. Sci Total Environ 670:1075–1083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.268
Destek MA, Ulucak R, Dogan E (2018) Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve for the EU countries: the role of ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(29):29387–29396
Díaz-Roldán C, Ramos-Herrera MDC (2021) Innovations and ICT: do they favour economic growth and environmental quality? Energies 14(5):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14051431
Dogan B, Driha OM, Balsalobre Lorente D, Shahzad U (2021) The mitigating effects of economic complexity and renewable energy on carbon emissions in developed countries. Sustain Dev 29(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2125
Dong K, Sun R, Hochman G (2017) Do natural gas and renewable energy consumption lead to less CO2 emission? Empirical evidence from a panel of BRICS countries. Energy 141:1466–1478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.11.092
Dumitrescu E-I, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Model 29(4):1450–1460
Eberhardt M, Bond S (2009) Cross-section dependence in non-stationary panel models: a novel estimator. Soc Res, 17870.
Erdoğan S, Çakar ND, Ulucak R, Danish KY (2021) The role of natural resources abundance and dependence in achieving environmental sustainability: evidence from resource-based economies. Sustain Dev 29(1):143
Fryer E (2019) Does the ICT sector hamper or help reduction of carbon emissions?–friends of Europe. https://www.friendsofeurope.org/insights/does-the-ict-sector-hamper-or-help-reduction-of-carbon-emissions/
Gangwar DS, Tyagi S, Soni SK (2022) A techno-economic analysis of digital agriculture services: an ecological approach toward green growth. Int J Environ Sci Technol 19(5):3859–3870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03300-7
Global Footprint Network. (2018). Home–global footprint network. https://www.footprintnetwork.org/
Godil DI, Sharif A, Agha H, Jermsittiparsert K (2020) The dynamic nonlinear influence of ICT, financial development, and institutional quality on CO2 emission in Pakistan: new insights from QARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(19):24190–24200
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Guild J (2020) The political and institutional constraints on green finance in Indonesia. J Sustain Finance Invest 10(2):157–170
Haldar A (2021) Sethi N (2022) Environmental effects of information and communication technology–exploring the roles of renewable energy, innovation, trade and financial development. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 153:111754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111754
Hassan ST, Baloch MA, Mehmood N, Zhang J (2019) Linking economic growth and ecological footprint through human capital and biocapacity. Sustain Cities Soc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101516
Huang SZ, Chien F, Sadiq M (2021) A gateway towards a sustainable environment in emerging countries: the nexus between green energy and human capital. Econom Res-Ekonomska Istrazivanja. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2021.2012218
Huang Y, Haseeb M, Usman M (2021) Ozturk I (2022) Dynamic association between ICT, renewable energy, economic complexity and ecological footprint: Is there any difference between E-7 (develo**) and G-7 (developed) countries? Technol Soc 68:101853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101853
Ibrahim RL, Ajide KB (2021) The dynamic heterogeneous impacts of non-renewable energy, trade openness, total natural resource rents, financial development and regulatory quality on environmental quality: evidence from BRICS economies. Resour Policy 74(July):102251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2021.102251
Islam MS (2022) Does financial development cause environmental pollution? Empirical evidence from South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(3):4350–4362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16005-8
Jebli MB, Youssef SB (2017) The role of renewable energy and agriculture in reducing CO2 emissions: evidence for North Africa countries. Ecol Ind 74:295–301
Kahouli B, Nafla A, Trimeche H, Kahouli O (2022) Understanding how information and communication technologies enhance electric power consumption and break environmental damage to reach sustainable development. Energy Build 255:111662
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Econom 90(1):1–44
Kapetanios G, Pesaran MH, Yamagata T (2011) Panels with non-stationary multifactor error structures. J Econom 160(2):326–348
Khan N, Baloch MA, Saud S, Fatima T (2018) The effect of ICT on CO2 emissions in emerging economies: does the level of income matters? Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(23):22850–22860
Kongbuamai N, Bui Q, Yousaf HMAU, Liu Y (2020) The impact of tourism and natural resources on the ecological footprint: a case study of ASEAN countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(16):19251–19264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08582-x
Majeed MT, Mazhar M (2020) Reexamination of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: the role of biocapacity, human capital, and trade. Pak J Commerce Soc Sci 14(1):202–254. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3580586
Mohanty S, Sethi N (2021) The energy consumption-environmental quality nexus in BRICS countries: the role of outward foreign direct investment. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17180-4
Muganyi T, Yan L, Sun H (2021) Environmental science and ecotechnology green finance, fintech and environmental protection : evidence from. Environ Sci Ecotechnol 7:100107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2021.100107
Murshed M, Rahman MA, Alam MS, Ahmad P, Dagar V (2021) The nexus between environmental regulations, economic growth, and environmental sustainability: linking environmental patents to ecological footprint reduction in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(36):49967–49988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13381-z
Musah M, Kong Y, Adjei I, Kwadwo S, Mary A (2020) The connection between urbanization and carbon emissions : a panel evidence from West Africa United States of America. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01124-y
Nathaniel SP, Alam MS, Murshed M, Mahmood H, Ahmad P (2021) The roles of nuclear energy, renewable energy, and economic growth in the abatement of carbon dioxide emissions in the G7 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(35):47957–47972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13728-6
Nawaz MA, Seshadri U, Kumar P, Aqdas R, Patwary AK, Riaz M (2021) Nexus between green finance and climate change mitigation in N-11 and BRICS countries : empirical estimation through difference in differences ( DID ) approach. 6504–6519.
Nguyen KH, Kakinaka M (2019) Renewable energy consumption, carbon emissions, and development stages: some evidence from panel cointegration analysis. Renew Energy 132:1049–1057
OECD (2022). Environmental policy–patents on environmental technologies -. https://data.oecd.org/envpolicy/patents-on-environment-technologies.htm
Özpolat A (2021) How does internet use affect ecological footprint?: an empirical analysis for G7 countries. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01967-z
Paramati SR, Alam MS, Hammoudeh S, Hafeez K (2021) Long-run relationship between R&D investment and environmental sustainability: evidence from the European Union member countries. Int J Financ Econ 26(4):5775–5792
Pata UK (2021) Linking renewable energy, globalization, agriculture, CO2 emissions and ecological footprint in BRIC countries: a sustainability perspective. Renew Energy 173:197–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.03.125
Pedroni P (1999) Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):653–670
Pedroni P (2004) Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Economet Theor 20(3):597–625
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Economet 22(2):265–312
Pesaran MH, Yamagata T (2008) Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J Econ 142(1):50–93
Qiao H, Zheng F, Jiang H, Dong K (2019) The greenhouse effect of the agriculture-economic growth-renewable energy nexus: evidence from G20 countries. Sci Total Environ 671:722–731
Raheem ID, Tiwari AK, Balsalobre-lorente D, Balsalobre-lorente D (2019) The role of ICT and financial development in CO 2 emissions and economic growth.
Rahman M, Aravindakshan S, Arshadul M, Arifur M, Gulandaz A, Rahman J (2021) Environmental and Sustainability Indicators Conservation tillage ( CT ) for climate-smart sustainable intensification : Assessing the impact of CT on soil organic carbon accumulation, greenhouse gas emission and water footprint of wheat cultivation. Environ Sustain Indic 10(February):100106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indic.2021.100106
Rashid A, Irum A, Malik IA, Ashraf A, Rongqiong L, Liu G, Ullah H, Ali MU, Yousaf B (2018) Ecological footprint of Rawalpindi; Pakistan’s first footprint analysis from urbanization perspective. J Clean Prod 170:362–368
Razzaq A, Sharif A, Aziz N, Irfan M, Jermsittiparsert K (2020) Asymmetric link between environmental pollution and COVID-19 in the top ten affected states of US : a novel estimations from quantile-on-quantile approach. Environ Res 191(August):110189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110189
Ridzuan NHAM, Marwan NF, Khalid N, Ali MH, Tseng M-L (2020) Effects of agriculture, renewable energy, and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions: evidence of the environmental Kuznets curve. Resour Conserv Recycl 160:104879
Saeed Meo M, Karim MZA (2021) The role of green finance in reducing CO2 emissions: an empirical analysis. Borsa Istanbul Rev 22(1):169–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bir.2021.03.002
Sahoo M, Sethi N (2021) The intermittent effects of renewable energy on ecological footprint: evidence from develo** countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(40):56401–56417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14600-3
Salari TE, Roumiani A, Kazemzadeh E (2021) Globalization, renewable energy consumption, and agricultural production impacts on ecological footprint in emerging countries: using quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(36):49627–49641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14204-x
Samargandi N (2021) Oil exploration, biocapacity, and ecological footprint in Saudi Arabia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(39):54621–54629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14354-y
Sampene AK, Brenya R, Oteng F, Wiredu J (2022) Poverty alleviation in South Africa : the role of agriculture education and mechanization 14(2), 4–17.
Sampene A, Li C, Agyeman F, Brenya R (2021) Analysis of the BRICS countries’ pathways towards a low-carbon environment. BRICS J Econ 2(4):77–102. https://doi.org/10.3805/2712-7508-2021-4-4
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2018) Empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve and environmental sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. J Clean Prod 201:98–110
Saud S, Chen S, Haseeb A (2018) Impact of financial development and economic growth on environmental quality : an empirical analysis from Belt and Road Initiative ( BRI ) countries.
Shabani ZD, Shahnazi R (2019) Energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions, information and communications technology, and gross domestic product in Iranian economic sectors: a panel causality analysis. Energy 169:1064–1078
Sharma R, Sinha A, Kautish P (2021) Does renewable energy consumption reduce ecological footprint ? Evidence from eight develo** countries of Asia. J Clean Prod 285:124867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124867
Shen Y, Su Z-W, Malik MY, Umar M, Khan Z, Khan M (2021) Does green investment, financial development, and natural resources rent limit carbon emissions? A provincial panel analysis of China. Sci Total Environ 755:142538
Shujah-ur-Rahman, Chen S, Saud S, Saleem N, Bari MW (2019) Nexus between financial development, energy consumption, income level, and ecological footprint in CEE countries: do human capital and biocapacity matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res, 26(31), 31856–31872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06343-z
Shukla AK, Sudhakar K, Baredar P (2017) Renewable energy resources in South Asian countries: challenges, policy and recommendations. Resour-Effic Technol 3(3):342–346
Silva Ó, Cordera R, González-gonzález E, Nogués S (2022) Science of the total environment environmental impacts of autonomous vehicles : a review of the scienti fi c literature. Sci Total Environ 830:154615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154615
Smith, Z. A. (2019). Green finance for sustainable development in Pakistan. 1–34.
Sohail MT, Ullah S, Majeed MT, Usman A, Andlib Z (2021) The shadow economy in South Asia: dynamic effects on clean energy consumption and environmental pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(23):29265–29275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12690-7
Suki NM, Suki NM, Sharif A, Afshan S, Jermsittiparsert K (2022) The role of technology innovation and renewable energy in reducing environmental degradation in Malaysia: a step towards sustainable environment. Renew Energy 182:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.007
Sun H, Mohsin M, Alharthi M, Abbas Q (2020) Measuring environmental sustainability performance of South Asia. J Clean Prod 251:119519
Sunday T, Seyi A, Akadiri S, Adedapo AT, Usman N (2022) Does interaction between technological innovation and natural resource rent impact environmental degradation in newly industrialized countries? New evidence from method of moments quantile regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17631-y
Tauseef S, Awais M, Mahmood N, Zhang J (2019) Linking economic growth and ecological footprint through human capital and biocapacity. Sustain Cities Soc 47(March):101516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101516
Töbelmann D, Wendler T (2019) The impact of environmental innovation on carbon dioxide emissions. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118787
Tufail M, Song L, Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D, Khan S (2021) Do fiscal decentralization, and natural resources rent curb carbon emissions? Evidence from developed countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 1–12.
Uddin GA, Salahuddin M, Alam K, Gow J (2017) Ecological footprint and real income: panel data evidence from the 27 highest emitting countries. Ecol Ind 77:166–175
Udemba EN (2020) Mediation of foreign direct investment and agriculture towards ecological footprint: a shift from single perspective to a more inclusive perspective for India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(21):26817–26834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09024-4
Ulucak R, Bilgili F (2018) A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle and low income countries. J Clean Prod 188:144–157
Unal H, Aktug M (2022) The impact of human capital and bio‑capacity on the environmental quality: evidence from G20 countries. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19122-0
Ünal H, Aktuğ M (2022) The impact of human capital and bio-capacity on the environmental quality: evidence from G20 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 1–11.
UNFCCC. (2021). the Glasgow. 28. https://ukcop26.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/COP26-Presidency-Outcomes-The-Climate-Pact.pdf
Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2021) What abates ecological footprint in BRICS-T region? Exploring the influence of renewable energy, non-renewable energy, agriculture, forest area and financial development. Renew Energy 179:12–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.07.014
Usman M, Kousar R, Makhdum MSA (2020) The role of financial development, tourism, and energy utilization in environmental deficit: evidence from 20 highest emitting economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(34):42980–42995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10197-1
Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jahanger A, Ahmad P (2022) Pollution concern during globalization mode in financially resource-rich countries: do financial development, natural resources, and renewable energy consumption matter? Renew Energy 183:90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2021.10.067
Usman M, Hammar N (2021) Dynamic relationship between technological innovations, financial development, renewable energy, and ecological footprint : fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for Asia pacific economic cooperation countries. 15519–15536.
Wackernagel M, Rees W (1998) Our ecological footprint: reducing human impact on the earth (Vol. 9). New society publishers.
Wang L, Vo XV, Shahbaz M, Ak A (2020) Globalization and carbon emissions: Is there any role of agriculture value-added, financial development, and natural resource rent in the aftermath of COP21? J Environ Manage 268:110712. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2020.110712
Wang X, Huang J, **ang Z, Huang J (2021) Nexus between green finance, energy efficiency, and carbon emission : covid-19 implications from BRICS countries. 9(December), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2021.786659
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 69(6):709–748
WID. (2022). World development indicators|databank. https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators#
**aoman W, Majeed A, Vasbieva DG, Yameogo CEW, Hussain N (2021) Natural resources abundance, economic globalization, and carbon emissions: advancing sustainable development agenda. Sustain Dev 29(5):1037–1048. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2192
Xu L, Wang X, Wang L, Zhang D (2022) Does technological advancement impede ecological footprint level ? The role of natural resources prices volatility, foreign direct investment and renewable energy in China. 76(December 2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.102559
Yang B, Jahanger A, Usman M, Khan MA (2021) The dynamic linkage between globalization, financial development, energy utilization, and environmental sustainability in GCC countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(13):16568–16588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11576-4
Yang X, Khan I (2022) Dynamics among economic growth, urbanization, and environmental sustainability in IEA countries : the role of industry value-added. 4116–4127.
Zakari A, Khan I (2022) The introduction of green finance : a curse or a benefit to environmental sustainability ? 3(2021), 1–5.
Zakaria M, Bibi S (2019) Financial development and environment in South Asia : the role of institutional quality. 7926–7937.
Zhang H (2021) Technology innovation, economic growth and carbon emissions in the context of carbon neutrality: evidence from BRICS. Sustain (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/su132011138
Acknowledgements
[1] Innovation team construction of "low carbon economy and industrial development", supported by the excellent innovation team construction project of philosophy and Social Sciences in Colleges and universities of Jiangsu Province". [2] The Humanities and Social Sciences Research Program of the Ministry of Education: Research on the Formation Mechanism and Breakthrough Path of "Low-end Capture "in the Global Value Chain of High-tech Industry (18YJA630105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Consent to Publish
All authors reviewed and approved the manuscript for publication.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Chenxi Li.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sampene, A.K., Li, C., Khan, A. et al. The dynamic nexus between biocapacity, renewable energy, green finance, and ecological footprint: evidence from South Asian economies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 8941–8962 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04471-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04471-7