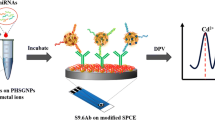
Abstract
With increase in cancer burden worldwide and poor survival rates due to delayed diagnosis, it is pertinent to develop a device for early diagnosis. We report an electrochemical biosensor for quantification of miRNA-204 (miR-204) biomarker that is dysregulated in most of the cancers. The proposed methodology uses the gold nanoparticles-modified carbon screen-printed electrode for immobilization of single-stranded DNA probe against miR-204. Colloidal gold nanoparticles were synthesized using l-glutamic acid as reducing agent. Nanoparticles were characterized by UV–visible spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Spherical gold nanoparticles were of 7–28 nm in size. Biosensor fabricated using these nanoparticles was characterized by cyclic voltammetry after spiking 0.1 fg/mL–0.1 µg/mL of miR-204 in fetal bovine serum. Response characteristics of the miR-204 biosensor displayed high sensitivity of 8.86 µA/µg/µL/cm2 with wide detection range of 15.5 aM to 15.5 nM. The low detection limit makes it suitable for early diagnosis and screening of cancer.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathur P, Sathishkumar K, Chaturvedi M, Das P, Sudarshan KL, Santhappan S, ICMR-NCDIR-NCRP Investigator Group (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020: report from national cancer registry programme, India. JCO Glob Oncol 6:1063–1075. https://doi.org/10.1200/go.20.00122
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clinicians 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Ludwig JA, Weinstein JN (2005) Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer 5(11):845–856. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1739
Ortiz-Quintero B (2016) Cell-free microRNAs in blood and other body fluids, as cancer biomarkers. Cell Prolifer 49(3):281–303. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12262
Cui M, Wang H, Yao X, Zhang D, **e Y, Cui R, Zhang X (2019) Circulating microRNAs in cancer: potential and challenge. Front Genet 10:626. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00626
Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY, How Huang K, Jen Lee M, Wang K (2010) The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem 56(11):1733–1741. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2010.147405
Rezayi M, Farjami Z, Hosseini ZS, Ebrahimi N, Abouzari-Lotf E (2018) MicroRNA-based biosensors for early detection of cancers. Curr Pharm Des 24(39):4675–4680. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612825666190111144525
**e X, Liu J, Ding M, Yang X, Peng Y, Zhao Y, Miao Y (2021) Recent development of the electrochemical sensors for miRNA detection. Int J Electrochem Sci 16(4):1–17. https://doi.org/10.20964/2021.04.35
Khalid M, Idichi T, Seki N, Wada M, Yamada Y, Fukuhisa H, Natsugoe S (2019) Gene regulation by antitumor miR-204–5p in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: the clinical significance of direct RACGAP1 regulation. Cancers 11(3):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030327
Schmeier S, Schaefer U, Essack M, Bajic VB (2011) Network analysis of microRNAs and their regulation in human ovarian cancer. BMC Syst Biol 5:183. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-5-183
Bao W, Wang HH, Tian FJ, He XY, Qiu MT, Wang JY, Wan XP (2013) A TrkB–STAT3–miR-204–5p regulatory circuitry controls proliferation and invasion of endometrial carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer 12:155. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-12-155
Li W, ** X, Zhang Q, Zhang G, Deng X, Ma L (2014) Decreased expression of miR-204 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(6):3287–3292 (PMID: 25031750; PMCID: PMC4097245)
Bussemakers MJ, Van Bokhoven A, Verhaegh GW, Smit FP, Karthaus HF, Schalken JA et al (1999) DD3: a new prostate-specific gene, highly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 59(23):5975–5979 (PMID: 10606244)
Sümbül AT, Göğebakan B, Ergün S, Yengil E, Batmacı CY, Tonyalı Ö, Yaldız M (2014) miR-204-5p expression in colorectal cancer: an autophagy-associated gene. Tumor Biol 35(12):12713–12719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2596-3
Chen X, Liu XS, Liu HY, Lu YY, Li Y (2016) Reduced expression of serum miR-204 predicts poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Genet Mol Res 15(2):15027702. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15027702
Fan X, Zou X, Liu C, Cheng W, Zhang S, Geng X, Zhu W (2021) MicroRNA expression profile in serum reveals novel diagnostic biomarkers for endometrial cancer. Biosci Rep 41(6):BSR20210111. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20210111
Zheng W, Huang W, Yu X (2021) Study on serum miR-204 expression levels in patients with severe pneumonia and patients with primary bronchial lung cancer and its diagnostic value. Evidence-Based Complement Alternat Med 2021:6034413. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6034413
Nie D, Ma P, Chen Y, Zhao H, Liu L, **n D, Sun L (2021) MiR-204 suppresses the progression of acute myeloid leukemia through HGF/c-Met pathway. Hematology 26(1):931–939. https://doi.org/10.1080/16078454.2021.1981533
Guo W, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Shi Y, ** J, Fan H, Xu S (2015) Decreased expression of miR-204 in plasma is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Med 36(6):1720–1726. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2015.2388
Gaddam RR, Jacobsen VP, Kim YR, Gabani M, Jacobs JS, Dhuri K, Vikram A (2020) Microbiota-governed microRNA-204 impairs endothelial function and blood pressure decline during inactivity in db/db mice. Sci Rep 10(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66786-0
Cheng Y, Wang D, Wang F, Liu J, Huang B, Baker MA, Liang M (2020) Endogenous miR-204 protects the kidney against chronic injury in hypertension and diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 31(7):1539–1554. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2019101100
Chiu CC, Yeh TH, Chen RS, Chen HC, Huang YZ, Weng YH, Wang HL (2019) Upregulated expression of microRNA-204–5p leads to the death of dopaminergic cells by targeting DYRK1A-mediated apoptotic signaling cascade. Front Cell Neurosci 13:399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00399
Xu G, Thielen LA, Chen J, Grayson TB, Grimes T, Bridges SL Jr, Shalev A (2019) Serum miR-204 is an early biomarker of type 1 diabetes-associated pancreatic beta-cell loss. Am J Physiol-Endocrinol Metab 317(4):E723–E730. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00122.2019
Kurahashi R, Kadomatsu T, Baba M, Hara C, Itoh H, Miyata K, Oike Y (2019) MicroRNA-204–5p: a novel candidate urinary biomarker of Xp11. 2 translocation renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci 110(6):1897–1908. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14026
Debernardi S, Massat NJ, Radon TP, Sangaralingam A, Banissi A, Ennis DP, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T (2015) Non-invasive urinary miRNA biomarkers for early detection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Am J Cancer Res 5(11):3455–3466 (PMID: 26807325)
Tapia-Castillo A, Guanzon D, Palma C, Lai A, Barros E, Allende F, Carvajal CA (2019) Downregulation of exosomal miR-192–5p and miR-204–5p in subjects with nonclassic apparent mineralocorticoid excess. J Transl Med 17(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-019-02143-8
Hofbauer SL, de Martino M, Lucca I, Haitel A, Susani M, Shariat SF, Klatte T (2018) A urinary microRNA (miR) signature for diagnosis of bladder cancer. Urol Oncol 36(12):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.09.006
Scian MJ, Maluf DG, David KG, Archer KJ, Suh JL, Wolen AR et al (2011) MicroRNA profiles in allograft tissues and paired urines associate with chronic allograft dysfunction with IF/TA. Am J Transp 11(10):2110–2122. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03666.x
Ding M, Lin B, Li T, Liu Y, Li Y, Zhou X, Li R (2015) A dual yet opposite growth-regulating function of miR-204 and its target XRN1 in prostate adenocarcinoma cells and neuroendocrine-like prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 6(10):7686–7700. https://doi.org/10.18632/Foncotarget.3480
Lee H, Lee S, Bae H, Kang HS, Kim SJ (2016) Genome-wide identification of target genes for miR-204 and miR-211 identifies their proliferation stimulatory role in breast cancer cells. Sci Reports 6(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25287
Hong BS, Ryu HS, Kim N, Kim J, Lee E, Moon H, Moon HG (2019) Tumor suppressor miRNA-204-5p regulates growth, metastasis, and immune microenvironment remodelling in breast cancer. Can Res 79(7):1520–1534. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0891
Hoffmann A, Huang Y, Suetsugu-Maki R, Ringelberg CS, Tomlinson CR, Rio-Tsonis D, Tsonis PA (2012) Implication of the miR-184 and miR-204 competitive RNA network in control of mouse secondary cataract. Mol Med 18(3):528–538. https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2011.00463
Yin Y, Zhang B, Wang W, Fei B, Quan C, Zhang J, Huang Z (2014) miR-204-5p inhibits proliferation and invasion and enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating RAB22A. Clin Cancer Res 20(23):6187–6199. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1030
Conte I, Hadfield KD, Barbato S, Carrella S, Pizzo M, Bhat RS, Black GC (2015) MiR-204 is responsible for inherited retinal dystrophy associated with ocular coloboma. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(25):E3236–E3245. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1401464112
Qiu YH, Wei YP, Shen NJ, Wang ZC, Kan T, Yu WL et al (2013) miR-204 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting slug in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 32(5):1331–1341. https://doi.org/10.1159/000354531
Shen SQ, Huang LS, **ao XL, Zhu XF, **ong DD, Cao XM et al (2017) miR-204 regulates the biological behaviour of breast cancer MCF-7 cells by directly targeting FOXA1. Oncol Rep 38(1):368–376. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5644
Guo J, Zhao P, Liu Z, Li Z, Yuan Y, Zhang X, **ao K (2019) MiR-204–3p inhibited the proliferation of bladder cancer cells via modulating lactate dehydrogenase-mediated glycolysis. Front Oncol 9:1242. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01242
Ying Z, Li Y, Wu J, Zhu X, Yang Y, Tian H, Li M (2013) Loss of miR-204 expression enhances glioma migration and stem cell-like phenotype. Can Res 73(2):990–999. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2895
Ryan J, Tivnan A, Fay J, Bryan K, Meehan M, Creevey L, Stallings RL (2012) MicroRNA-204 increases sensitivity of neuroblastoma cells to cisplatin and is associated with a favourable clinical outcome. Br J Cancer 107(6):967–976. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.356
Zhang L, Wang X, Chen P (2013) MiR-204 down regulates SIRT1 and reverts SIRT1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, anoikis resistance and invasion in gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer 13:290. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-290
Findlay VJ, Turner DP, Moussa O, Watson DK (2008) MicroRNA-mediated inhibition of prostate-derived Ets factor messenger RNA translation affects prostate-derived Ets factor regulatory networks in human breast cancer. Can Res 68(20):8499–8506. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0907
Sharma S, Gupta N, Srivastava S (2012) Modulating electron transfer properties of gold nanoparticles for efficient biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 37(1):30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.04.027
Kilic T, Topkaya SN, Ariksoysal DO, Ozsoz M, Ballar P, Erac Y, Gozen O (2012) Electrochemical based detection of microRNA, mir21 in breast cancer cells. Biosens Bioelectron 38(1):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.05.031
Cheng FF, Zhang JJ, He TT, Shi JJ, Abdel-Halim ES, Zhu JJ (2014) Bimetallic Pd–Pt supported graphene promoted enzymatic redox cycling for ultrasensitive electrochemical quantification of microRNA from cell lysates. Analyst 139(16):3860–3865. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AN00777H
Yang D, Cheng W, Chen X, Tang Y, Miao P (2018) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of miRNA based on DNA strand displacement polymerization and Ca 2+-dependent DNAzyme cleavage. Analyst 143(22):5352–5357. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AN01555D
Wen Y, Pei H, Shen Y, ** J, Lin M, Lu N, Fan C (2012) DNA nanostructure-based interfacial engineering for PCR-free ultrasensitive electrochemical analysis of microRNA. Sci Rep 2(1):867. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00867
Wen Y, Liu G, Pei H, Li L, Xu Q, Liang W, Fan C (2013) DNA nanostructure-based ultrasensitive electrochemical microRNA biosensor. Methods 64(3):276–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.07.035
Ge Z, Lin M, Wang P, Pei H, Yan J, Shi J, Zuo X (2014) Hybridization chain reaction amplification of microRNA detection with a tetrahedral DNA nanostructure-based electrochemical biosensor. Anal Chem 86(4):2124–2130. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4037262
Lusi EA, Passamano M, Guarascio P, Scarpa A, Schiavo L (2009) Innovative electrochemical approach for an early detection of microRNAs. Anal Chem 81(7):2819–2822. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac8026788
Wu X, Chai Y, Yuan R, Su H, Han J (2013) A novel label-free electrochemical microRNA biosensor using Pd nanoparticles as enhancer and linker. Analyst 138(4):1060–1066. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AN36506E
Cai Z, Song Y, Wu Y, Zhu Z, Yang CJ, Chen X (2013) An electrochemical sensor based on label-free functional allosteric molecular beacons for detection target DNA/miRNA. Biosens Bioelectron 41:783–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.10.002
Ma X, Xu H, Qian K, Kandawa-Schulz M, Miao W, Wang Y (2020) Electrochemical detection of microRNAs based on AuNPs/CNNS nanocomposite with Duplex-specific nuclease assisted target recycling to improve the sensitivity. Talanta 208:120441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120441
Acknowledegements
Shilpa is thankful to Jaypee Institute of Information Technology Noida, India, for providing research assistance to complete this project. The authors are also thankful to the Advanced Instrumentation and Research Facility (AIRF), Jawaharlal Nehru University, for extending the facility for transmission electron microscopy analysis.
Funding
The authors also state that there exists no financial support or funding from any sources toward this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors state that there exists no conflict of interest toward this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gundagatti, S., Srivastava, S. Development of Electrochemical Biosensor for miR204-Based Cancer Diagnosis. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 14, 596–606 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-022-00508-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-022-00508-0