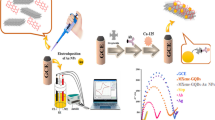
Abstract
This work describes miRNA-based electrochemical biosensor for detection of miRNA30e, a pancreatic cancer biomarker. The screen-printed gold electrode was functionalized using cysteine hydrochloride followed by immobilization of synthesized colloidal gold nanorods (10–12 nm diameter and 25–65 nm length). The gold nanorods modified electrode surface was amino functionalized for covalent attachment of single-stranded DNA probe against miRNA30e (miR30e). This platform was utilized for electrochemical measurements and response analysis of target miRNA30e. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopic measurements showed very poor sensitivity (13.51 Ω/µg/mL/cm2) using charge transfer resistance calibration plots. Cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry-based miR30e quantification showed decreasing current response with increasing concentration of miR30e with detection range of 0.1 fg/mL–0.1 µg/mL (14.9 aM–14.9 nM). The sensitivity of DPV sensing (104.4 µA/µg/mL/cm2) was found to be 1.3 times higher than that of CV-based quantification (79.6 µA/µg/mL/cm2). miRNA-based biosensors have the potential of replacing current invasive, time consuming and technically difficult diagnostic procedures. Furthermore, the lower limit of detection of 14.9 aM miRNA30e makes it a promising tool for detection of cancer at early stages and hence increasing survival rate.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaidhani RH, Balasubramaniam G (2021) An epidemiological review of pancreatic cancer with special reference to India. Indian J Med Sci 73(1):99–109. https://doi.org/10.25259/IJMS_92_2020
Rickes S, Unkrodt K, Neye H, Ocran KW, Wermke W (2002) Differentiation of pancreatic tumours by conventional ultrasound, unenhanced and echo-enhanced power Doppler sonography. Scand J Gastroenterol 37(11):1313–1320. https://doi.org/10.1080/003655202761020605
Palazzo L, Roseau G, Gayet B, Vilgrain V, Belghiti J, Fékéte F, Paolaggi JA (1993) Endoscopic ultrasonography in the diagnosis and staging of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Results of a prospective study with comparison to ultrasonography and CT scan. Endoscopy 25(2):143–150. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1010273
Sendler A, Avril N, Helmberger H, Stollfuss J, Weber W, Bengel F, Schwaiger M, Roder JD, Siewert JR (2000) Preoperative evaluation of pancreatic masses with positron emission tomography using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose: diagnostic limitations. World J Surg 24(9):1121–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002680010182
Hamada S, Shimosegawa T (2011) Biomarkers of pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology 11(suppl 2):14–19. https://doi.org/10.1159/000323479
Simeone DM, Ji B, Banerjee M, Arumugam T, Li D, Anderson MA, Bamberger AM, Greenson J, Brand RE, Ramachandran V, Logsdon CD (2007) CEACAM1, a novel serum biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 34(4):436–443. https://doi.org/10.1097/mpa.0b013e3180333ae3
Kunovsky L, Tesarikova P, Kala Z, Kroupa R, Kysela P, Dolina J, Trna J (2018) The use of biomarkers in early diagnostics of pancreatic cancer. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5389820
Tempero MA, Malafa MP, Al-Hawary M et al (2017) Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2017, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 15(8):1028–1061. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2017.0131
Bunduc S, Gede N, Váncsa S, Lillik V, Kiss S, Dembrovszky F, Eróss B, Szakács Z, Gheorghe C, Mikó A, Hegyi P (2022) Prognostic role of cell-free DNA biomarkers in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and meta–analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 169:103548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103548
Brancaccio M, Natale F, Falco G, Angrisano T (2019) Cell-free DNA methylation: the new frontiers of pancreatic cancer biomarkers’. Discov Genes 11(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010014
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75(5):843–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-y
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403(6772):901–906. https://doi.org/10.1038/35002607
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Müller P, Spring J, Srinivasan A, Fishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408(6808):86–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/35040556
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294(5543):853–858. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1064921
Trang P, Weidhaas JB, Slack FJ (2008) MicroRNAs as potential cancer therapeutics. Oncogene 27(Suppl 2):S52-57. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.353
Slater PE, Strauch K, Rospleszcz S, Ramaswamy A, Esposito I, Klöppel G, Matthäi E, Heeger K, Fendrich V, Langer P, Bartsch DK (2014) MicroRNA-196a and -196b as potential biomarkers for the early detection of familial pancreatic cancer. Translational Oncology 7(4):464–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2014.05.007
Ishige F, Hoshino I, Iwatate Y et al (2020) MIR1246 in body fluids as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep 10(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65695-6
Yu Y, Tong Y, Zhong A, Wang Y, Lu R, Guo L (2020) Identification of Serum microRNA-25 as a novel biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Medicine 99(52):e23863. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000023863
Zhang J, Zhao CY, Zhang SH, Yu DH, Chen Y, Liu QH, Shi M, Ni CR, Zhu MH (2014) Upregulation of miR194 contributes to tumor growth and progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep 31(3):1157–1164. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2013.2960
Zhao C, Zhang J, Zhang S, Yu D, Chen Y, Liu Q, Shi M, Ni C, Zhu M (2013) Diagnostic and biological significance of microRNA-192 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep 30(1):276–284. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2013.2420
Panarelli NC, Chen YT, Zhou XK, Kitabayashi N, Yantiss RK (2012) MicroRNA expression aids the preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 41(5):685–690. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e318243a905
Li F, Xu JW, Wang L, Liu H, Yan Y, Hu SY (2017) MicroRNA-221-3p is up-regulated and serves as a potential biomarker in pancreatic cancer. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46(3):482–487. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1315429
Morimura R, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Takeshita H, Tsujiura M, Nagata H, Konishi H, Shiozaki A, Ikoma H, Okamoto K, Ochiai T, Taniguchi H, Otsuji E (2011) Novel diagnostic value of circulating miR18a in plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 105(11):1733–1740. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.453
Li A, Yu J, Kim H, Wolfgang CL, Canto MI, Hruban RH, Goggins M (2013) MicroRNA array analysis finds elevated serum miR 1290 accurately distinguishes patients with low-stage pancreatic cancer from healthy and disease controls. Clin Cancer Res 19(13):3600–3610. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3092
Hussein NA, Kholy ZA, Anwar MM, Ahmad MA, Ahmad, (2017) Plasma miR-22-3p, miR-642b-3p and miR-885-5p as diagnostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143(1):83–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2248-7
Li A, Omura N, Hong SM, Vincent A, Walter K, Griffith M, Borges M, Goggins M (2010) Pancreatic cancers epigenetically silence SIP1 and hypomethylate and overexpress miR200a/200b in association with elevated circulating miR200a and miR200b levels. Cancer Res 70(13):5226–5237. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4227
Khan IA, Rashid S, Singh N, Rashid S, Singh V, Gunjan D, Das P, Dash NR, Pandey RM, Chauhan SS, Gupta S, Saraya A (2021) Panel of serum miRNAs as potential non-invasive biomarkers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep 11(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-82266-5
Cote GA, Gore AJ, McElyea SD, Heathers LE, Xu H, Sherman S, Korc M (2014) A pilot study to develop a diagnostic test for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on differential expression of select miRNA in plasma and bile. Am J Gastroenterol 109(12):1942–1952. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2014.331
Shao H, Zhang Y, Yan J, Ban X, Fan X, Chang X, Lu Z, Wu Y, Zong L, Mo S, Yu S, Chen J (2021) Upregulated microRNA-483-3p is an early event in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and as a powerful liquid biopsy biomarker in PDAC. Onco Targets Ther 14:2163–2175. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S288936
Xu J, Cao Z, Liu W, You L, Zhou L, Wang C, Lou W, Sun B, Miao Y, Liu X, Zhang T, Zhao Y (2016) Plasma miRNAs effectively distinguish patients with pancreatic cancer from controls. Ann Surg 263(6):1173–1179. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000001345
Debernardi S, Massat NJ, Radon TP, Sangaralingam A, Banissi A, Ennis DP, Dowe T, Chelala C, Pereira SP, Kocher HM, Young BD, Bond-Smith G, Hutchins R, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T (2015) Noninvasive urinary miRNA biomarkers for early detection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Am J Cancer Res 5(11):3455–3466 (PMID: 26807325)
**a N, Zhang L (2014) Nanomaterials-based sensing strategies for electrochemical detection of microRNAs. Materials (Basel) 7(7):5366–5384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7075366
Yammouri G, Mohammadi H, Amine A (2019) A highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor based on carbon black and gold nanoparticles modified pencil graphite electrode for microRNA-21 detection. Chem Afr 2:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-019-00058-x
Chen SC, Chen KT, Fang-Ju Jou A (2021) Polydopamine-gold composite based electrochemical biosensor using dual-amplification strategy for detecting pancreatic cancer-associated microRNA. Biosens Bioelectron 173:112815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112815
Guo J, Yuan C, Yan Q, Duan Q, Li X, Yi G (2018) An electrochemical biosensor for microRNA-196a detection based on cyclic enzymatic signal amplification and template-free DNA extension reaction with the adsorption of methylene blue. Biosens Bioelectron 105:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.01.036
Zeng D, Wang Z, Meng Z, Wang P, San L, Wang W, Aldalbahi A, Li L, Shen J, Mi X (2017) DNA tetrahedral nanostructure-based electrochemical miRNA biosensor for simultaneous detection of multiple miRNAs in pancreatic carcinoma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(28):24118–24125. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b05981
Mao L, Liu S, Hu L (2018) miR30 family: a promising regulator in development and disease. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9623412
Liu Mm, Li Z, Han Xd et al (2017) MiR30e inhibits tumor growth and chemoresistance via targeting IRS1 in Breast Cancer. Sci Rep 7(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16175-x
Wang Z, Zhang J, Zhang S, Yan S, Wang Z, Wang C, Zhang X (2019) MiR30e and miR92a are related to atherosclerosis by targeting ABCA1. Mol Med Rep 19(4):3298–3304. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.9983
Hu W, Yao W, Li H, Chen L (2020) MiR30e-5p inhibits the migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via regulating the expression of MTA1. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20194309
Bhattacharya S, Steele R, Shrivastava S (2015) Serum miR30e and miR223 as novel noninvasive biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol 186(2):242–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.10.003
Dieter C, Assmann TS, Costa AR, Canani LH, de Souza BM, Bauer AC, Crispim D (2019) MiR30e-5p and MiR15a-5p expressions in plasma and urine of type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic kidney disease. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00563
Leva-Bueno J, Peyman SA, Millner PA (2020) A review on impedimetric immunosensors for pathogen and biomarker detection. Med Microbiol Immunol 209(3):343–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-020-00668-0
Ramos MDM, Correia MGH (2011) Electric field induced charge transfer through single- and double-stranded DNA polymer molecules. Soft Matter 7:10091–10099. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1SM05641G
Asadzadeh-Firouzabadi A, Zare HR (2017) Application of cysteamine-capped gold nanoparticles for early detection of lung cancer-specific miRNA (miR25) in human blood plasma. Anal Methods 9(25):3852–3861. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AY01098B
Zhuravel R, Huang H, Polycarpou G, Polydorides S, Motamarri P, Katrivas L, Rotem D, Sperling J, Zotti LA, Kotlyar AB, Cuevas JC, Gavini V, Skourtis SS, Porath D (2020) Backbone charge transport in double-stranded DNA. Nat Nanotechnol 15:836–840. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-0741-2
Chandra S, Adeloju S (2020) A new sensor for detecting microrna 133b (Parkinson’s disease biomarker). Sens Int 1:100005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sintl.2020.100005
Zouari M, Campuzano S, **arronN RN (2018) Amperometric biosensing of miRNA21 in serum and cancer cells at nanostructured platforms using Anti-DNA−RNA hybrid antibodies. ACS Omega 3:8923–8931. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00986
Daneshpour M, Omidfar K, Ghanbarian H (2016) A novel electrochemical nanobiosensor for the ultrasensitive and specific detection of femtomolar-level gastric cancer biomarker miRNA106a. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 7:2023–2036. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.7.193
Acknowledgements
Namita is thankful to Jaypee Institute of Information Technology Noida, India for providing research fellowship and other research facilities for completion of this project. The authors are also thankful to advanced instrumentation and research facility (AIRF), Jawaharlal Nehru University for extending the facility for transmission electron microscopy analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, N., Srivastava, S. Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer Using miRNA30e Biosensor. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 14, 804–813 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-022-00531-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-022-00531-1