Abstract
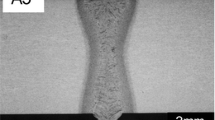
In this study, laser welding was employed to butt-weld warm-rolled 6.86% medium Mn transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steel (MMS). The investigation focused on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the base metal (BM) as well as the welded joint (WJ). The BM exhibited a mixed microstructure consisting of austenite and δ-ferrite, while the fusion zone (FZ) contained martensite and δ-ferrite. In terms of hardness, the cross section of the FZ in the WJ displayed higher values compared to the BM. The heat-affected zone (HAZ) did not exhibit significant hardness reduction. Tensile testing revealed that the WJ of the MMS exhibited ductile fracture behavior, with the elongation initially increasing and then decreasing with the rise in laser power. Notably, experimental data demonstrated that a laser power of 1500 W outperformed all other power settings in terms of macro morphology and performance.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data in this study are available from the corresponding author by request.
References
B. Hu and H. Luo, A Strong and Ductile 7Mn Steel Manufactured by Warm Rolling and Exhibiting Both Transformation and Twinning Induced Plasticity, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 725, p 684–693.
F. Yang, J. Zhou, Y. Han, P. Liu, H.W. Luo, and H. Dong, A Novel Cold-Rolled Medium Mn Steel with an Ultra-High Product of Tensile Strength and Elongation, Mater. Lett., 2020, 258, 126804.
D.K. Matlock, J.G. Speer, E.D. Moor, and P.J. Gibbs, Recent Developments in Advanced High Strength Sheet Steels for Automotive Applications: An Overview, Int. J. Eng. Sci., 2012, 15(1), p 1–12.
F. Yang, H. Luo, C. Hu, E. Pu, and H. Dong, Effects of Intercritical Annealing Process on Microstructures and Tensile Properties of Cold-Rolled 7Mn Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 685, p 115–122.
H.J. Pan, J. Peng, Y. Zhang, W.P. Wu, Z.Z. Wang, Q. Wang, and H.Y. Li, Microstructure Evolution and Enhanced Mechanical Properties of a Nb–Mo Microalloyed Medium Mn Alloy Fabricated by a Novel Cyclic Quenching Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 797, 140076.
H.J. Pan, W.W. Yu, C.F. Wei, J.S. Zhang, J. Li, G. Wei, X.Y. Li, B. Qiao, and L. Liu, Enhanced Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance of Medium Mn Steel by Tailoring Retained Austenite Morphology, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07118-3
R. Zhang, W.Q. Cao, Z.J. Peng, J. Shi, H. Dong, and C.X. Huang, Intercritical Rolling Induced Ultrafine Microstructure and Excellent Mechanical Properties of the Medium-Mn Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 583, p 84–88.
D.W. Suh and S.J. Kim, Medium Mn Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steels: Recent Progress and Challenges, Scr. Mater., 2017, 126, p 63–67.
R. Chen, H.J. Kong, J.H. Luan, A.D. Wang, P. Jiang, and C.T. Liu, Effect of External Applied Magnetic Field on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Laser Welding Joint of Medium-Mn Nanostructured Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 792, p 139787–1397973.
Y. Cao, L. Zhao, and Y. Peng, Effect of Heat Input on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Welded Medium Mn Steel Joints, Chin. J. Lasers, 2018, 45, 110200.
N. Lun, D.C. Saha, A. Macwan, H. Pan, L. Wang, F. Goodwin, and Y. Zhou, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fiber Laser Welded Medium Manganese TRIP Steel, Mater. Des., 2017, 131, p 450–459.
M.H. Razmpoosh, E. Biro, F. Goodwin, and Y. Zhou, Dynamic Tensile Behavior of Fiber Laser Welds of Medium Manganese Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys Metall. Mater. Sci., 2019, 50, p 3578–3588.
S. Kaar, D. Krizan, J. Schwabe, H. Hofmann, T. Hebesberger, C. Commenda, and L. Samek, Influence of the Al and Mn Content on the Structure-Property Relationship in Density Reduced TRIP-Assisted Sheet Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 735, p 475–486.
D.W. Suh, S.J. Park, T.H. Lee, C.S. Oh, and S.J. Kim, Influence of Al on the Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Behavior of Low-Carbon Manganese TRIP-Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, 41, p 397–408.
H. Yi, Review on Delta-Transformation-Induced Plasticity (TRIP) Steels with Low Density: The Concept and Current Progress, JOM, 2014, 66, p 1759–1769.
J. Maki, J. Mahieu, B. Cooman, and S. Claessens, Galvanisability of Silicon Free C-Mn-Al TRIP Steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2003, 19, p 125–131.
S.S. Nayak, V. Hernandez, Y. Okita, and Y.N. Zhou, Microstructure–Hardness Relationship in the Fusion Zone of TRIP Steel Welds, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 551, p 73–81.
Y. Najafi, F.M. Ghaini, Y. Palizdar, and M. Pakniat, Microstructural Characteristics of Fusion Zone in Continuous Wave Fiber Laser Welded Nb-Modified δ-TRIP Steel, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, 15, p 3635–3646.
M. **a, Z. Tian, L. Zhao, and Y. Zhou, Fusion Zone Microstructure Evolution of Al-Alloyed TRIP Steel in Diode Laser Welding, Mater Trans, 2008, 49, p 746–753.
S.S. Nayak, V.H. Baltazar Hernandez, Y. Okita, and Y.N. Zhou, Microstructure–Hardness Relationship in the Fusion Zone of TRIP Steel Welds, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2012, 551, p 73–81.
U. Reisgen, M. Schleser, O. Mokrov, and E. Ahmed, Uni- and Bi-axial Deformation Behavior of Laser Welded Advanced High Strength Steel sHeets, J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2010, 210, p 2188–2196.
T. Wang, M. Zhang, R.D. Liu, L. Zhang, L. Lu, and W.H. Wu, Effect of Welding Speed on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser-Welded Transformation Induced plasticity (TRIP) Steels, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2020, 27, p 1087–1098.
M.S. **a, Z.L. Tian, L. Zhao, and Y.N. Zhou, Metallurgical and Mechanical Properties of Fusion Zones of TRIP Steels in Laser Welding, ISIJ Int, 2018, 48, p 483–488.
G.Q. Li, Y.F. Shen, N. Jia, X.W. Feng, and W.Y. Xue, Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Micro-Alloyed Low-Density δ-TRIP Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2022, 848, 143430.
S.H. Zhang, L. Deng, and L.Z. Che, An Integrated Model of Rolling Force for Extra-Thick Plate by Combining Theoretical Model and Neural Network Model, J. Manuf. Process., 2022, 75, p 100–109.
S.H. Zhang, L. Deng, W.H. Tian, L.Z. Che, and L. Yan, Deduction of a Quadratic Velocity Field and its Application to Rolling Force of Extra-Thick Plate, Comput. Math. with Appl., 2022, 109, p 58–73.
M. Du, W.Q. Wang, X.G. Zhang, J.F. Niu, and L. Liu, Influence of Laser Power on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Welded TWIP Steel Butted Joint, Opt. Laser. Technol, 2022, 149, 107911.
ASTM E8M-16, Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, ASTM, West Conshohocken, PA, USA (2016).
X.N. Wang, Q. Sun, Z. Zheng, and H.S. Di, Microstructure and Fracture Behavior of Laser Welded Joints of DP Steels with Different Heat Inputs, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 699, p 18–25.
V. Bharadwaj, A.K. Rai, B.N. Upadhyaya, R. Singh, S.K. Rai, and K.S. Bindra, A Study on Effect of Heat Input on Mode of Welding, Microstructure and Mechanical Strength in Pulsed Laser Welding of Zr-25 wt.% Nb Alloy, J. Nucl. Mater., 2022, 564, p 153685.
D. Westerbaan, D. Parkes, S.S. Nayak, D.L. Chen, E. Biro, F. Goodwin, and Y.N. Zhou, Effects of Concavity on Tensile and Fatigue Properties in Fibre Laser Welding of Automotive Steels, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2014, 19, p 60–68.
H.J. Pan, X.Y. Li, B. Qiao, Y. Zhang, N.M. Miao, L. Liu, H. Ding, and M.H. Cai, New Insights to Understand the Influence of Nb/Mo on Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance of Warm-Rolled Medium-Mn Steels, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022, 31, p 3228–3233.
D.C. Saha, S.S. Nayak, E. Biro, A.P. Gerlich, and Y.N. Zhou, Mechanism of Secondary Hardening in Rapid Tempering of Dual-Phase Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45, p 6153–6162.
D.C. Saha, E. Biro, A.P. Gerlich, and Y.N. Zhou, Influences of Blocky Retained Austenite on the Heat-Affected Zone Softening of Dual-Phase Steels, Mater. Lett., 2020, 264, 127368.
W.D. Callister and D.G. Rethwisch, Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering: An Integrated Approach, 2nd ed. Wiley, New York, 2005, p 212–214
H.J. Pan, C.F. Wei, W.W. Yu, X.Y. Li, and B. Qiao, Achieving Excellent Strength-Ductility Combination by Cyclic Quenching Treatment in 22MnB5 Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform, 2022 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06737-0
H.J. Pan, H. Ding, M.H. Cai, D. Kibaroglu, Y. Ma, and W.W. Song, Precipitation Behavior and Austenite Stability of Nb or Nb–Mo Micro-Alloyed Warm-Rolled Medium-Mn Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 766, p 138371.
Z.H. Cai, H. Ding, R.D.K. Misra, H. Kong, and H.Y. Wu, Unique Impact of Ferrite in Influencing Austenite Stability and Deformation Behavior in a Hot-Rolled Fe-Mn-Al-C Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 595, p 86–91.
I. Gilath, J.M. Signamarcheix, and P. Bensussan, A Comparison of Methods for Estimating the Weld-Metal Cooling Rate in Laser Welds, J. Mater. Sci., 1994, 29, p 3358–3362.
H.S. Wang, X.N. Wang, and M. Zhang, Effect of Heat Input on Microstructure and Properties of Microalloyed C-Mn Steel Full Penetration Welded Joint Using Laser Welding, Chin. J. Lasers, 2016, 43, p 0103003.
Y. Palizdar, D. San Martin, A.P. Brown, M. Ward, R.C. Cochrane, R. Brydson, and A.J. Scott, Demonstration of Elemental Partitioning During Austenite Formation in Low-Carbon Aluminium Alloyed Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 2011, 46, p 2384–2387.
D.Q. Zhang, Z.L. Tian, Z.Y. Du, and S.H. Yun, Effect of Heat Input on Microstructure and Properties of Weld Metal in X65 stEel, Trans. China Weld. Institut., 2001, 22, p 31–33.
S.I. Wright, M.M. Nowell, and D.P. Field, A Review of Strain Analysis Using Electron Backscatter Diffraction, Microsc. Microanal., 2011, 17, p 316–329.
D.N. Crowther and B. Mintz, Influence of Grain Size and Precipitation on Hot Ductility of Microalloyed Steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1986, 2, p 1099–1105.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank you for the project support from Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 52204382 and 52274381), Jiangsu Province (No. BK20200985 and No. BK20220629), Postdoctoral Administration Office in China (No.2021M701717) and Changzhou (No. CQ20210102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HP provide conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing–review & editing, formal analysis, funding acquisition, and supervision. WY gave resources, data curation, and writing–original draft. BZ did visualization, writing–review & editing, and supervision. BH done visualization, writing–review & editing, and supervision. XL contributed visualization, writing–review & editing, and supervision. YZ performed visualization, writing–review & editing, and supervision. JL provides writing–review & editing and supervision. MJ did writing–review & editing and supervision. ZS done writing–review & editing and supervision. ZZ contributed writing–review & editing and supervision. LL performed writing–review & editing and supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, W., Pan, H., Zhang, B. et al. Influence of Laser Power on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Welded Medium Manganese Transformation-Induced Plasticity Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08508-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08508-x