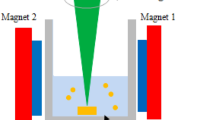
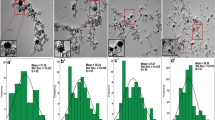
Abstract
With recent advances in nanotechnology, various nanomaterials have been used in various fields. The unique physiochemical properties and biocompatibility of Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONs) allow the exploration of IONs in various applications, including biomedicine, electronics, water/wastewater treatment, and sensors. The charge of IONs, crystallization, zeta potential solution stability, the coating, and synthetic methods are essential parameters that influence their applications in various fields. Each of these factors affects the optical and physical characteristics of the created material as well as determines the field of its application. In this regard, the main challenge of technology is related to the control of its physical properties. Therefore, the synthesis process used determines the properties of the synthesized substance. Pulsed laser ablation in liquid (PLAIL) is regarded as a green and environmentally friendly method for creating metal and metal oxide nanoparticles, and it does not require the use of toxic chemicals. The physical mechanism of laser ablation in a liquid environment, the subsequent growth of nanostructures, the essential laser technological parameters that determine the nanostructures’ properties, and the liquid medium’s influence are discussed. The size, shape, and distribution are crucial factors that influence the pharmacokinetics and bio-distribution of IONPs. Physiochemical properties such as size, shape, and surface and magnetic properties, as well as agglomeration of IONs and methods to enhance their stability, are also discussed. This review focuses on the recent development and various strategies in structure and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles (NPs) as well as the preparation processes of iron oxide NPs via pulsed laser ablation, and their environmental and medical applications.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable
References
Campos EA, Pinto DVBS, Oliveira JISD, Mattos EDC, Dutra RDCL (2015) Synthesis, characterization and applications of iron oxide nanoparticles-a short review. J Aerosp Technol Manag 7:267–276
Salman JAS, Kadhim AA, Haider AJ (2018) Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial effect of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by Lactobacillus Spp. J Global Pharma Technol 10(03):348–355
A**kya N, Yu X, Kaithal P, Luo H, Somani P, Ramakrishna S (2020) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (IONP) synthesis to applications: present and future. Materials 13(20):4644
VeleshKolaei MRH, Gill P, Rafati A, Adiani M (2023) Bioinformatical prediction of G-quadruplex Aptamer for detection of a ligand in practice. J Appl Sci Nanotechnol 3(4)
Attallah AH, Abdulwahid FS, Ali YA, Haider AJ (2024) Enhanced characteristics of iron oxide nanoparticles for efficient pollutant degradation via pulsed laser ablation in liquid. Plasmonics 1–14
Kumar S, Kumar M, Singh A (2021) Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O3, Fe3O4): a brief review. Contemp Phys 62(3):144–164
Haider AJ, Thamir AD, Najim AA, Ali GA (2017) Improving efficiency of TiO 2: Ag/Si solar cell prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Plasmonics 12:105–115
Nikolova MP, Chavali MS (2020) Metal oxide nanoparticles as biomedical materials. Biomimetics 5(2):27
Al-Obaidy R, Haider AJ, Al-Musaw S (2023) Calculation and optimization methods of SPION concentration formation with different laser wavelengths in liquid. AIP Conf Proc 2769:1. AIP Publishing
Amstad E, Textor M, Reimhult E (2011) Stabilization and functionalization of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 3(7):2819–2843
Al-Kinani MA, Haider AJ, Al-Musawi S (2021) Design and synthesis of nanoencapsulation with a new formulation of Fe@ Au-CS-CU-FA NPs by pulsed laser ablation in liquid (PLAL) method in breast cancer therapy: in vitro and in vivo. Plasmonics 16(4):1107–1117
Yousif AA, Habubi NF, Haidar AA (2012) Nanostructure zinc oxide with cobalt dopant by PLD for gas sensor applications. J Nano-and Electron Phys 4(2):02007–02011
Zhu N, Ji H, Yu P, Niu J, Farooq MU, Akram MW, Niu X (2018) Surface modification of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 8(10):810
Ansari SAMK, Ficiarà E, Ruffinatti FA, Stura I, Argenziano M, Abollino O, D’Agata F (2019) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and functionalization for biomedical applications in the central nervous system. Materials 12(3):465
Haider AJ, Thamir AD, Ahmed DS, Mohammad MR (2016) Deposition of silver nanoparticles on multiwalled carbon nanotubes by chemical reduction process and their antimicrobial effects. InAIP Conference Proceedings(1758:1) AIP Publishing
Negrescu AM, Killian MS, Raghu SN, Schmuki P, Mazare A, Cimpean A (2022) Metal oxide nanoparticles: review of synthesis, characterization and biological effects. J Func Biomater 13(4):274
Li Y, Zheng Z, Yan J, Lu B, Li X (2022) A review on pulsed laser preparation of nanocomposites in liquids and their applications in photocatalysis. Catalysts 12(12):1532
Attallah AH, Abdulwahid FS, Ali YA, Haider AJ (2023) Effect of liquid and laser parameters on fabrication of nanoparticles via pulsed laser ablation in liquid with their applications: a review. Plasmonics1–17
Kim M, Osone S, Kim T, Higashi H, Seto T (2017) Synthesis of nanoparticles by laser ablation: A review. Kona Powder Part J 34:80–90
Amendola V, Amans D, Ishikawa Y, Koshizaki N, Scirè S, Compagnini G, Barcikowski S (2020) Room‐temperature laser synthesis in liquid of oxide, metal‐oxide core‐shells, and doped oxide nanoparticles. Chem A Euro J 26(42):9206–9242
Zhang D, Gokce B, Barcikowski S (2017) Laser synthesis and processing of colloids: fundamentals and applications. Chem Rev 117(5):3990–4103
Khalaf AA, Attallah AH, Dheyab AB, Alwan AM (2021) Influence of magnetic field on the characteristics of n-type PSi prepared by photo-electro-chemical etching process. J Phys Conf Ser 1963(1):012015. IOP Publishing
Amendola V, Riello P, Meneghetti M (2011) Magnetic nanoparticles of iron carbide, iron oxide, iron@ iron oxide, and metal iron synthesized by laser ablation in organic solvents. J Phys Chem C 115(12):5140–5146
Svetlichnyi VA, Shabalina AV, Lapin IN, Goncharova DA, Velikanov DA, Sokolov AE (2017) Characterization and magnetic properties study for magnetite nanoparticles obtained by pulsed laser ablation in water. Appl Phys A 123:1–8
Svetlichnyi VA, Shabalina AV, Lapin IN, Goncharova DA, Kharlamova TS, Stadnichenko AI (2019) Comparative study of magnetite nanoparticles obtained by pulsed laser ablation in water and air. Appl Surf Sci 467:402–410
Rivera-Chaverra MJ, Restrepo-Parra E, Acosta-Medina CD, Mello A, Ospina R (2020) Synthesis of oxide iron nanoparticles using laser ablation for possible hyperthermia applications. Nanomaterials 10(11):2099
Kebede A, Singh AK, Rai PK, Giri NK, Rai AK, Watal G, Gholap AV (2013) Controlled synthesis, characterization, and application of iron oxide nanoparticles for oral delivery of insulin. Lasers Med Sci 28:579–587
Fazio E, Santoro M, Lentini G, Franco D, Guglielmino SPP, Neri F (2016) Iron oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation: synthesis, structural properties and antimicrobial activity. Colloids Surf, A 490:98–103
Queraltó A, del Pino AP, Logofatu C, Datcu A, Amade R, Bertran-Serra E, György E (2018) Reduced graphene oxide/iron oxide nanohybrid flexible electrodes grown by laser-based technique for energy storage applications. Ceram Int 44(16):20409–20416
Duque JS, Madrigal BM, Riascos H, Avila YP (2019) Colloidal metal oxide nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation technique and their antibacterial test. Colloid Interface 3(1):25
Kupracz P, Coy E, Grochowska K, Karczewski J, Rysz J, Siuzdak K (2020) The pulsed laser ablation synthesis of colloidal iron oxide nanoparticles for the enhancement of TiO2 nanotubes photo-activity. Appl Surf Sci 530
Ahmed MK, Menazea AA, Mansour SF, Al-Wafi R (2020) Differentiation between cellulose acetate and polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous scaffolds containing magnetite nanoparticles/graphene oxide via pulsed laser ablation technique for tissue engineering applications. J Market Res 9(5):11629–11640
Lopez JD, Keley M, Dante A, Werneck MM (2021) Optical fibre sensor coated with copper and iron oxide nanoparticles for hydrogen sulfide sensing. Opt Fiber Technol 67
Al-Salih M, Samsudin S, Arshad SS (2021) Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide carbon nanotubes nanocomposite by laser ablation for anti-microbial applications. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 19(1):76
Wang BY, Huang SY, Hsiao YS, Wei PC, Chou CM, Hsiao VK (2022) Pulsed-laser-induced photolysis of synthesizing magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for visible-light photocatalysis. Catalysts 12(11):1459
Menazea AA, Ibrahium HA, Awwad NS, Moustapha ME, Farea MO, Bajaber MA (2022) Facile synthesis and high-performance dielectric properties of polyethene oxide-chitosan-iron oxide nano-composite for electrical applications. J Market Res 18:2273–2281
Al-Obaidy R, Haider AJ, Al-Musawi S, Arsad N (2023) Targeted delivery of paclitaxel drug using polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticles for fibrosarcoma therapy: in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci Rep 13(1):3180
Nochehdehi AR, Thomas S, Sadri M, Afghahi SSS, Hadavi SM (2017) Iron oxide biomagnetic nanoparticles (IO-BMNPs); synthesis, characterization and biomedical application–a review. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 8(1):1–9
de Souza TC, Costa AFDS, Vinhas GM, Sarubbo LA (2023) Synthesis of iron oxides and influence on final sizes and distribution in bacterial cellulose applications. Polymers 15(15):3284
Ali A, Zafar H, Zia M, ul Haq I, Phull AR, Ali JS, Hussain A (2016) Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 49–67
Islam MS, Kurawaki J, Kusumoto Y, Abdulla-Al-Mamun M, Mukhlish MZ (2012) Hydrothermal novel synthesis of neck-structured hyperthermia-suitable magnetic (Fe 3 O 4, γ-Fe 2 O 3 and α-Fe 2 O 3) Nanoparticles. J Sci Res 4(1)
Luo T, Yang C, Tian X, Luo W, Nie Y, Wang Y (2020) Application of iron oxide nanomaterials for the removal of heavy metals. Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications 1–25
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26(18):3995–4021
Teja AS, Koh PY (2009) Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater 55(1–2):22–45
Al-Kinani MA, Haider AJ, Al-Musawi S (2020) High uniformity distribution of Fe@ Au preparation by a micro-emulsion method. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 987(1):012013. IOP Publishing
Guo H, Barnard AS (2013) Naturally occurring iron oxide nanoparticles: morphology, surface chemistry and environmental stability. J Mater Chem A 1(1):27–42
Ghazanfari MR, Kashefi M, Shams SF, Jaafari MR (2016) Perspective of Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles role in biomedical applications. Biochem Res Int 2016
Samrot AV, Sahithya CS, Selvarani J, Purayil SK, Ponnaiah P (2021) A review on synthesis, characterization and potential biological applications of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Curr Res Green Sustain Chem 4:100042
Hasany F, S., H Abdurahman, N., R Sunarti, A., & Jose, R. (2013) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: chemical synthesis and applications review. Curr Nanosci 9(5):561–575
Yusefi M, Shameli K, Jumaat AF (2020) Preparation and properties of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications: a brief review. J AdvRes Mater Sci 75(1):10–18
Baki A, Wiekhorst F, Bleul R (2021) Advances in magnetic nanoparticles engineering for biomedical applications—A Review. Bioeng 8(10):134
Wu W, He Q, Jiang C (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res Lett 3:397–415
Liang SXT, Wong LS, Dhanapal ACTA, Djearamane S (2020) Toxicity of metals and metallic nanoparticles on nutritional properties of microalgae. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:1–14
Abu-Huwaij R, Al-Assaf SF, Mousli F, Kutkut MS, Al-Bashtawi A (2020) Perceptive review on properties of iron oxide nanoparticles and their antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Sys Rev Pharm 11(8):418–431
Roca AG, Gutiérrez L, Gavilán H, Brollo MEF, Veintemillas-Verdaguer S, del Puerto Morales M (2019) Design strategies for shape-controlled magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 138:68–104
Singh N, Jenkins GJ, Asadi R, Doak SH (2010) Potential toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION). Nano Rev 1(1):5358
Hussain SM, Hess KL, Gearhart JM, Geiss KT, Schlager JJ (2005) In vitro toxicity of nanoparticles in BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicol In Vitro 19(7):975–983
Jeng HA, Swanson J (2006) Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in mammalian cells. J Environ Sci Health Part A 41(12):2699–2711
DeDiego ML, Portilla Y, Daviu N, López-García D, Villamayor L, Mulens-Arias V, Barber DF (2022) Iron oxide and iron oxyhydroxide nanoparticles impair SARS-CoV-2 infection of cultured cells. JNanobiotechnology 20(1):352
Feng Q, Liu Y, Huang J, Chen K, Huang J, **ao K (2018) Uptake, distribution, clearance, and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles with different sizes and coatings. Sci Rep 8(1):1–13
Sengul AB, Asmatulu E (2020) Toxicity of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles: a review. Environ Chem Lett 18(5):1659–1683
Nedyalkova M, Donkova B, Romanova J, Tzvetkov G, Madurga S, Simeonov V (2017) Iron oxide nanoparticles–in vivo/in vitro biomedical applications and in silico studies. Adv Coll Interface Sci 249:192–212
Abdulwahid FS, Haider AJ, Al-Musawi S (2022) Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs): synthesis, surface functionalization, and targeting drug delivery strategies: mini-review. NANO 17(11):2230007
Dhakshinamoorthy V, Manickam V, Perumal E (2017) Neurobehavioural toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles in mice. Neurotox Res 32:187–203
Arami H, Khandhar A, Liggitt D, Krishnan KM (2015) In vivo delivery, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 44(23):8576–8607
Malhotra N, Lee JS, Liman RAD, Ruallo JMS, Villaflores OB, Ger TR, Hsiao CD (2020) Potential toxicity of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles: a review. Molecules 25(14):3159
Mahmoudi M, Simchi A, Milani AS, Stroeve P (2009) Cell toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 336(2):510–518
Yang G (ed) (2012) Laser ablation in liquids: principles and applications in the preparation of nanomaterials. CRC Press
Jwad ZA, Mohammed AZ, Attallah AH, Mahdi, BR (2020) Study of the effect of building TEA laser nitrogen system with multi-stage printed circuits on the value of laser energy and the duration of the outgoing pulse. AIP Conf Proc 2213(1). AIP Publishing
Kanitz A, Kalus MR, Gurevich EL, Ostendorf A, Barcikowski S, Amans D (2019) Review on experimental and theoretical investigations of the early stage, femtoseconds to microseconds processes during laser ablation in liquid-phase for the synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 28(10)
Abdulwahid FS, Haider AJ, Al-Musawi S (2023) Effect of laser parameter on Fe3O4 NPs formation by pulsed laser ablation in liquid. AIP Conf Proc 2769(1). AIP Publishing
**ao J, Liu P, Wang CX, Yang GW (2017) External field-assisted laser ablation in liquid: an efficient strategy for nanocrystal synthesis and nanostructure assembly. Prog Mater Sci 87:140–220
Al-Obaidy R, Hadier AJ, Al-Musawi S, Arsad N (2023) Study of the effects of solution types on concentration of iron oxide by pulsed laser ablation in liquid. J Appl Sci Nanotechnol 3(1):137–150
Liang SX, Zhang LC, Reichenberger S, Barcikowski S (2021) Design and perspective of amorphous metal nanoparticles from laser synthesis and processing. Phys Chem Chem Phys 23(19):11121–11154
Fazio E, Gökce B, De Giacomo A, Meneghetti M, Compagnini G, Tommasini M, Neri F (2020) Nanoparticles engineering by pulsed laser ablation in liquids: Concepts and applications. Nanomaterials 10(11):2317
Baladi A, Mamoory RS (2010) Investigation of different liquid media and ablation times on pulsed laser ablation synthesis of aluminum nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 256(24):7559–7564
Kanitz A, Hoppius JS, Gurevich EL, Ostendorf A (2016) Influence of the liquid on femtosecond laser ablation of iron. Phys Procedia 83:114–122
Rawat R, Tiwari A, Arun N, Rao SN, Pathak AP, Shadangi, Y, Tripathi A (2021) Nanosecond pulsed laser ablation of Al–Cu–Fe quasicrystalline material: effects of solvent and fluence. J Alloys Compd 859:157871
Naser H, Alghoul MA, Hossain MK, Asim N, Abdullah MF, Ali MS, Amin N (2019) The role of laser ablation technique parameters in synthesis of nanoparticles from different target types. J Nanoparticle Res 21:1–28
Mehta K, Soumyashree S, Pandya J, Singh P, Kushawaha RK, Kumar P, Baruah PK (2023) Impact of viscosity of liquid on nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in liquid: an experimental and theoretical investigation. Appl Phys A 129(5):388
Forsythe RC, Cox CP, Wilsey MK, Muller AM (2021) Pulsed laser in liquids made nanomaterials for catalysis. Chem Rev 121(13):7568–7637
Mat Isa SZ, Zainon R, Tamal M (2022) State of the art in gold nanoparticle synthesisation via pulsed laser ablation in liquid and its characterisation for molecular imaging: a review. Materials 15(3):875
Nyabadza A, Vazquez M, Brabazon D (2023) A review of bimetallic and monometallic nanoparticle synthesis via laser ablation in liquid. Curr Comput-Aided Drug Des 13(2):253
Yogesh GK, Shukla S, Sastikumar D, Koinkar P (2021) Progress in pulsed laser ablation in liquid (PLAL) technique for the synthesis of carbon nanomaterials: A review. Appl Phys A 127:1–40
Svetlichnyi VA, Shabalina AV, Lapin IN, Goncharova DA (2016) Metal oxide nanoparticle preparation by pulsed laser ablation of metallic targets in liquid. Applications of Laser Ablation–Thin Film Deposition, Nanomaterial Synthesis and Surface Modification; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia 245–263
Subhan A, Mourad AHI, Al-Douri Y (2022) Influence of laser process parameters, liquid medium, and external field on the synthesis of colloidal metal nanoparticles using pulsed laser ablation in liquid: a review. Nanomaterials 12(13):2144
Menendez-Manjon A, Chichkov BN, Barcikowski S (2010) Influence of water temperature on the hydrodynamic diameter of gold nanoparticles from laser ablation. J Phys Chem C 114(6):2499–2504
Amendola V, Meneghetti M (2009) Laser ablation synthesis in solution and size manipulation of noble metal nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11(20):3805–3821
Liu G, Gao J, Ai H, Chen X (2013) Applications and potential toxicity of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Small 9(9–10):1533–1545
Thomas R, Park IK, Jeong YY (2013) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and therapy of cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14(8):15910–15930
Blasiak B, van Veggel FC, Tomanek B (2013) Applications of nanoparticles for MRI cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Nanomater 2013:12–12
Oberdick SD, Jordanova KV, Lundstrom JT, Parigi G, Poorman ME, Zabow G, Keenan KE (2023) Iron oxide nanoparticles as positive T1 contrast agents for low-field magnetic resonance imaging at 64 mT. Sci Rep 13(1):11520
Zhao X, Zhao H, Chen Z, Lan M (2014) Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14(1):210–220
Kievit FM, Zhang M (2011) Surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Acc Chem Res 44(10):853–862
Stephen ZR, Kievit FM, Zhang M (2011) Magnetite nanoparticles for medical MR imaging. Mater Today 14(7–8):330–338
Yang H, Wang H, Wen C, Bai S, Wei P, Xu B, Zhang L (2022) Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles as T 2-MRI contrast agents on reproductive system in male mice. J Nanobiotechnology 20(1):98
Wang YXJ (2011) Superparamagnetic iron oxide based MRI contrast agents: current status of clinical application. Quant Imaging Med Surg 1(1):35
Avasthi A, Caro C, Pozo-Torres E, Leal MP, García-Martín ML (2020) Magnetic nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents. Surface-modified Nanobiomater Electrochem Biomed App 49–91
Salehipour M, Rezaei S, Mosafer J, Pakdin-Parizi Z, Motaharian A, Mogharabi-Manzari M (2021) Recent advances in polymer-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J Nanopart Res 23:1–35
Zhao Z, Li M, Zeng J, Huo L, Liu K, Wei R, Gao J (2022) Recent advances in engineering iron oxide nanoparticles for effective magnetic resonance imaging. Bioact Mater 12:214–245
Shah RR, Davis TP, Glover AL, Nikles DE, Brazel CS (2015) Impact of magnetic field parameters and iron oxide nanoparticle properties on heat generation for use in magnetic hyperthermia. J Magn Magn Mater 387:96–106
Montazersaheb P, Pishgahzadeh E, Jahani VB, Farahzadi R, Montazersaheb S (2023) Magnetic nanoparticle-based hyperthermia: a prospect in cancer stem cell tracking and therapy. Life Sci 121714
Sivakumar B, Aswathy RG, Romero-Aburto R, Mitcham T, Mitchel KA, Nagaoka Y, Sakthikumar DN (2017) Highly versatile SPION encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles as photothermal ablators of cancer cells and as multimodal imaging agents. Biomater Sci 5(3):432–443
Vangijzegem T, Lecomte V, Ternad I, Van Leuven L, Muller RN, Stanicki D, Laurent S (2023) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION): from fundamentals to state-of-the-art innovative applications for cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 15(1):236
Ebrahimisadr S, Aslibeiki B, Asadi R (2018) Magnetic hyperthermia properties of iron oxide nanoparticles: The effect of concentration. Phys C (Amsterdam, Neth) 549:119–121
Shi D, Sadat ME, Dunn AW, Mast DB (2015) Photo-fluorescent and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 7(18):8209–8232
Abenojar EC, Wickramasinghe S, Bas-Concepcion J, Samia ACS (2016) Structural effects on the magnetic hyperthermia properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 26(5):440–448
Strączek T, Fiejdasz S, Rybicki D, Goc K, Przewoźnik J, Mazur W, Kapusta C (2019) Dynamics of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with various polymeric coatings. Materials 12(11):1793
Saeed M, Ren W, Wu A (2018) Therapeutic applications of iron oxide based nanoparticles in cancer: basic concepts and recent advances. Biomater Sci 6(4):708–725
Tong S, Quinto CA, Zhang L, Mohindra P, Bao G (2017) Size-dependent heating of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 11(7):6808–6816
**e W, Guo Z, Gao F, Gao Q, Wang D, Liaw BS, Zhao L (2018) Shape-, size-and structure-controlled synthesis and biocompatibility of iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic theranostics. Theranostics 8(12):3284
Wu X, Tan Y, Mao H, Zhang M (2010) Toxic effects of iron oxide nanoparticles on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int J Nanomed 385–399
Polychronopoulos ND, Gkountas AA, Sarris IE, Spyrou LA (2021) A computational study on magnetic nanoparticles hyperthermia of ellipsoidal tumors. Appl Sci 11(20):9526
Sharma KIRTI, Chauhan C (2021) Role of magnetic nanoparticle (MNPs) in cancer treatment: a review. Mater Today Proc
Palanisamy S, Wang YM (2019) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticulate system: synthesis, targeting, drug delivery and therapy in cancer. Dalton Trans 48(26):9490–9515
Price PM, Mahmoud WE, Al-Ghamdi AA, Bronstein LM (2018) Magnetic drug delivery: where the field is going. Front Chem 6:619
Wang L, Chen M, Ran X, Tang H, Cao D (2023) Sorafenib-based drug delivery systems: applications and perspectives. Polymers 15(12):2638
Khalkhali M, Sadighian S, Rostamizadeh K, Khoeini F, Naghibi M, Bayat N, Hamidi M (2015) Synthesis and characterization of dextran coated magnetite nanoparticles for diagnostics and therapy. Bioimpacts 5(3):141
Yao Y, Zhou Y, Liu L, Xu Y, Chen Q, Wang Y, Shao A (2020) Nanoparticle-based drug delivery in cancer therapy and its role in overcoming drug resistance. Front Mol Biosci 7:193
Elahi N, Rizwan M (2021) Progress and prospects of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Artif Organs 45(11):1272–1299
Sun T, Zhang YS, Pang B, Hyun DC, Yang M, **a Y (2021) Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Nanomater Neoplasms 31–142
Dilnawaz F, Singh A, Mohanty C, Sahoo SK (2010) Dual drug loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Biomater 31(13):3694–3706
Wei Y, Han B, Hu X, Lin Y, Wang X, Deng X (2012) Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their magnetic properties. Procedia Eng 27:632–637
Ling Y, Wei K, Luo Y, Gao X, Zhong S (2011) Dual docetaxel/superparamagnetic iron oxide loaded nanoparticles for both targeting magnetic resonance imaging and cancer therapy. Biomater 32(29):7139–7150
He Y, Zhang L, Zhu D, Song C (2014) Design of multifunctional magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles/mitoxantrone-loaded liposomes for both magnetic resonance imaging and targeted cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine 4055–4066
Saikia C, Das MK, Ramteke A, Maji TK (2016) Effect of crosslinker on drug delivery properties of curcumin loaded starch coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 93:1121–1132
Huang Y, Mao K, Zhang B, Zhao Y (2017) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with folic acid for dual target-specific drug delivery and MRI in cancer theranostics. Mater Sci Eng, C 70:763–771
Prabha G, Raj V (2018) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan–polyvinylpyrrolidone–bovine serum albumin-coated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as potential carrier for delivery of tamoxifen. J Iran Chem Soc 15:871–884
Panda J, Satapathy BS, Majumder S, Sarkar R, Mukherjee B, Tudu B (2019) Engineered polymeric iron oxide nanoparticles as potential drug carrier for targeted delivery of docetaxel to breast cancer cells. J Magn Magn Mater 485:165–173
Jeon M, Lin G, Stephen ZR, Kato FL, Zhang M (2019) Paclitaxel-loaded iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted breast cancer therapy. Adv Therap 2(12):1900081
Khaledian M, Nourbakhsh MS, Saber R, Hashemzadeh H, Darvishi MH (2020) Preparation and evaluation of doxorubicin-loaded pla–peg–fa copolymer containing superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Spions) for cancer treatment: Combination therapy with hyperthermia and chemotherapy. Int J Nanomed 6167–6182
Mahdi SA, Kadhim AA, Albukhaty S, Nikzad S, Haider AJ, Ibraheem S, Al-Musawi S (2021) Gene expression and apoptosis response in hepatocellular carcinoma cells induced by biocompatible polymer/magnetic nanoparticles containing 5-fluorouracil. Electron J Biotechnol 52:21–29
Haider AJ, Al-Musawi S, Haider MJ, Al-Shibaany ZYA (2022) Formulation of curcumin in folate functionalized polymeric coated Fe3O4@ Au core-shell nanosystem for targeting breast cancer therapy. Researchsquare
Senapati S, Mahanta AK, Kumar S, Maiti P (2018) Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Signal Transduct Target Ther 3(1):7
Hossen S, Hossain MK, Basher MK, Mia MNH, Rahman MT, Uddin MJ (2019) Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy and toxicity studies: A review. J Adv Res 15:1–18
Edan MS, Sultan FI, Attallah AH, Haider AJ, Haider MJ, Tawfeeq AT, Khalif OH (2023) Effect of silver nanoparticles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in liquid on the hematological, hepatic, and renal functions of albino rats. Iraqi J Sci
Goya GF, Grazu V, Ibarra MR (2008) Magnetic nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Curr Nanosci 4(1):1–16
Zhang J, Zhang T, Gao J (2022) Biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer gene therapy: A review. Nanomaterials 12(19):3323
Vangijzegem T, Stanicki D, Laurent S (2019) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery: applications and characteristics. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 16(1):69–78
Rosen JE, Chan L, Shieh DB, Gu FX (2012) Iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer imaging and diagnostics. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 8(3):275–290
Fard JK, Jafari S, Eghbal MA (2015) A review of molecular mechanisms involved in toxicity of nanoparticles. Adv Pharm Bull 5(4):447
Arias LS, Pessan JP, Vieira APM, Lima TMTD, Delbem ACB, Monteiro DR (2018) Iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications: a perspective on synthesis, drugs, antimicrobial activity, and toxicity. Antibiotics 7(2):46
Al-Obaidy R, Haider AJ, Al-Musawi S, Arsad N (2022) In vitro and in vivo studies of folate-functionalized pegylated chitosan/superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle for the fibrosarcoma-targeted delivery of paclitaxel. Researchsquare
Abdulwahid FS, Haider AJ, Al-Musawi S (2023) Folate decorated dextran-coated magnetic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of ellipticine in cervical cancer cells. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 14(1):015001
Hajipour MJ, Fromm KM, Ashkarran AA, de Aberasturi DJ, de Larramendi IR, Rojo T, Mahmoudi M (2012) Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol 30(10):499–511
Mani U, kumar Ponnala A, Jayabharathi T, Shanmugavel M, Sujatha D, Ezhilarasan D (2023) Antibacterial properties of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles—an overview: Special Column on Microbial Nanotechnology. Appl Microbiol Theor Technol 33–49
Lara HH, Ayala-Núñez NV, Ixtepan Turrent LDC, Rodríguez Padilla C (2010) Bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:615–621
Rashed HH, Fadhil FA, Hadi IH (2017) Preparation and characterization of lead oxide nanoparticles by laser ablation as antibacterial agent. Baghdad Sci J 14(4):0801–0801
Gudkov SV, Burmistrov DE, Serov DA, Rebezov MB, Semenova AA, Lisitsyn AB (2021) Do iron oxide nanoparticles have significant antibacterial properties? Antibiotics 10(7):884
Gupta A, Mumtaz S, Li CH, Hussain I, Rotello VM (2019) Combatting antibiotic-resistant bacteria using nanomaterials. Chem Soc Rev 48(2):415–427
Abdulsada FM, Hussein NN, Sulaiman GM, Al Ali A, Alhujaily M (2022) Evaluation of the antibacterial properties of iron oxide, polyethylene glycol, and gentamicin conjugated nanoparticles against some multidrug-resistant bacteria. J Funct Biomater 13(3):138
Dizaj SM, Lotfipour F, Barzegar-Jalali M, Zarrintan MH, Adibkia K (2014) Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng, C 44:278–284
Ismail RA, Sulaiman GM, Abdulrahman SA, Marzoog TR (2015) Antibacterial activity of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in liquid. Mater Sci Eng, C 53:286–297
Bahjat HH, Ismail RA, Sulaiman GM, Mohammed HA, Al-Omar M, Mohammed SA, Khan RA (2022) Preparation of iron oxide and titania-based composite, core-shell populated, nanoparticulates material by two-step LASER ablation in aqueous media as antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2022
Nagajyothi PC, Prabhakar Vattikuti SV, Devarayapalli KC, Yoo K, Shim J, Sreekanth TVM (2020) Green synthesis: photocatalytic degradation of textile dyes using metal and metal oxide nanoparticles-latest trends and advancements. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 50(24):2617–2723
Chekir N, Benhabiles O, Tassalit D, Laoufi NA, Bentahar F (2016) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in aqueous suspensions using TiO2 and ZnO. Desalin Water Treat 57(13):6141–6147
Muraro PCL, Mortari SR, Vizzotto BS, Chuy G, Dos Santos C, Brum LFW, da Silva WL (2020) Iron oxide nanocatalyst with titanium and silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity on the degradation of Rhodamine B dye. Sci Rep 10(1):3055
Saleh AA, Haider AJ, Nazar A (2021) Preparation and properties of mattel oxide nanoparticles by pulse laser ablation in liquid as photo-catalysis. Key Eng Mater 900:197–204
Shenoy MR, Ayyasamy S, Reddy MVV, Kadarkarai G, Suryakanth J, Tamilarasan S, Jeyaramane AC (2020) The effect of morphology-dependent surface charges of iron oxide on the visible light photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31:17703–17717
Pang YL, Lim S, Ong HC, Chong WT (2016) Research progress on iron oxide-based magnetic materials: synthesis techniques and photocatalytic applications. Ceram Int 42(1):9–34
Qumar U, Hassan JZ, Bhatti RA, Raza A, Nazir G, Nabgan W, Ikram M (2022) Photocatalysis vs adsorption by metal oxide nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Technol 131:122–166
Mehtab A, Ahmed J, Alshehri SM, Mao Y, Ahmad T (2022) Rare earth doped metal oxide nanoparticles for photocatalysis: a perspective. Nanotechnology 33(14)
Wu W, Jiang C, Roy VA (2015) Recent progress in magnetic iron oxide–semiconductor composite nanomaterials as promising photocatalysts. Nanoscale 7(1):38–58
Singh P, Sharma K, Hasija V, Sharma V, Sharma S, Raizada P, Thakur VK (2019) Systematic review on applicability of magnetic iron oxides–integrated photocatalysts for degradation of organic pollutants in water. Mater Today Chem 14:100186
Qader MQ, Shekha YA (2023) Role of microalgae in environmental biotechnology to remove heavy metals. J Appl Sci Nanotechnol 3(1)
Suhaimi NAA, Kong CPY, Shahri NNM, Nur M, Hobley J, Usman A (2022) Dynamics of diffusion-and immobilization-limited photocatalytic degradation of dyes by metal oxide nanoparticles in binary or ternary solutions. Catalysts 12(10):1254
Abid MA, Kadhim DA (2020) Novel comparison of iron oxide nanoparticle preparation by mixing iron chloride with henna leaf extract with and without applied pulsed laser ablation for methylene blue degradation. J Environ Chem Eng 8(5)
Chatterjee SG, Chatterjee S, Ray AK, Chakraborty AK (2015) Graphene–metal oxide nanohybrids for toxic gas sensor: a review. Sens Actuators, B Chem 221:1170–1181
Li T, Yin W, Gao S, Sun Y, Xu P, Wu S, Wei G (2022) The combination of two-dimensional nanomaterials with metal oxide nanoparticles for gas sensors: a review. Nanomaterials 12(6):982
Mahmoud ZH, Abdalstar OD, Sabah N (2020) Semiconductor metal oxide nanoparticles: a review for the potential of H2S gas sensor application. Earthline J Chem Sci 4(2):199–208
Aljbar NA, Mahdi BR, Khalid AH, Attallah, AH, Abdulwahid FS, Haider AJ (2024) Enhanced surface plasmon resonance (SPR) fiber optic sensor for environmental monitoring: a coreless fiber–based design. Plasmonics 1–10
Wang C, Yin L, Zhang L, **ang D, Gao R (2010) Metal oxide gas sensors: sensitivity and influencing factors. sensors 10(3):2088–2106
Chavali MS, Nikolova MP (2019) Metal oxide nanoparticles and their applications in nanotechnology. SN applied sciences 1(6):607
Mortezaali A, Moradi R (2014) The correlation between the substrate temperature and morphological ZnO nanostructures for H2S gas sensors. Sens Actuators, A 206:30–34
Franke ME, Koplin TJ, Simon U (2006) Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in chemiresistors: does the nanoscale matter? Small 2(1):36–50
Sucharitakul W (2022) Detection of acetone using si doped wo3 nanorods based gas sensors prepared by magnetron sputtering for diabetes diagnosis(Doctoral dissertation, School of Biomedical Innovation Engineering Institute of Engineering Suranaree University of Technology)
Korotcenkov G (2007) Metal oxides for solid-state gas sensors: What determines our choice? Mater Sci Eng, B 139(1):1–23
Chen Y, Chen X, Zhang Y (2021) A comprehensive review on metal-oxide nanocomposites for high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes. Energy Fuels 35(8):6420–6442
AL-Saedi SI, Haider AJ, Naje AN, Bassil N (2020) Improvement of Li-ion batteries energy storage by graphene additive. Energy Rep 6:64–71
Koo B, **ong H, Slater MD, Prakapenka VB, Balasubramanian M, Podsiadlo P, Shevchenko EV (2012) Hollow iron oxide nanoparticles for application in lithium ion batteries. Nano Lett 12(5):2429–2435
Zhang L, Wu HB, Lou XW (2014) Iron-oxide-based advanced anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv Energy Mater 4(4):1300958
Mendes PC, Song Y, Ma W, Gani TZ, Lim KH, Kawi S, Kozlov SM (2023) Opportunities in the design of metal@ oxide core-shell nanoparticles. Adv Phys: X 8(1):2175623
Wang R, Li X, Nie Z, Zhao Y, Wang H (2021) Metal/metal oxide nanoparticles-composited porous carbon for high-performance supercapacitors. J Energy Storage 38:102479
Fadeev M, Kozlovskiy A, Korolkov I, Egizbek K, Nazarova A, Chudoba D, Zdorovets M (2020) Iron oxide@ gold nanoparticles: synthesis, properties and potential use as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries.Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp 603:125178
Bruck AM, Cama CA, Gannett CN, Marschilok AC, Takeuchi ES, Takeuchi KJ (2016) Nanocrystalline iron oxide based electroactive materials in lithium ion batteries: the critical role of crystallite size, morphology, and electrode heterostructure on battery relevant electrochemistry. Inorg Chem Front 3(1):26–40
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial and technical support provided by the Applied Sciences Department, university of technology, Baghdad-Iraq.
Funding
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author Contributions: Conceptualization and methodology, A.J. and A.H.; formal analysis, A.J.H and F.SH.; writing A.H. and Y.A. and H.J.A., review and editing, A.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This manuscript has not been previously released and is not now under consideration by any journal for publication
Informed Consent
Not applicable
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Attallah, A.H., Abdulwahid, F.S., Abdulrahman, H.J. et al. Investigate Toxicity and Control Size and Morphological of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesis by PLAIL Method for Industrial, Environmental, and Medical Applications: A Review. Plasmonics (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02383-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-024-02383-5