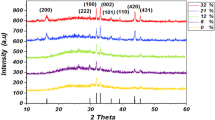
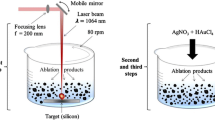
Abstract
Low-dimensional nanomaterials with enhanced size effect properties such as surface plasmon resonance and quantum confinements offer an unprecedented physical phenomenon, reducing devices down to atomic scale. In the last few decades, research interest in nanostructured materials has aroused due to their unusual electronic, optical, magnetic and chemical properties which are different from their bulk counterpart. In recent years, great efforts have been made on the synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles because of their promising application in various fields such as drug delivery, imaging and diagnostics. In this chapter, we discuss the synthesis of metal, semiconductor and ceramic nanoparticles by liquid phase-pulsed laser ablation (LP-PLA) technique. The optical properties of gold and silver nanoparticles grown by LP-PLA method were discussed in detail in this chapter. This chapter also discusses the growth of surfactant-free highly luminescent, transparent, chemically pure and biocompatible zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles by LP-PLA. The dependence of time of ablation, laser fluence, oxygen and nitrogen bubbling during ablation on the properties of the ZnO nanoparticles was investigated. The growth of ZnO nanoparticles by varying the pH of the media gives some inference on the stability of this colloidal solution and the formation of passivation layer on the surface of these particles. The luminescent properties of the europium-doped hydroxyapatite grown by LP-PLA technique were also discussed in this chapter. These luminescent nanoparticles find immense applications in biomedical imaging and cancer detections.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang PH, Sun X, Chiu J-F (2005) Transferrin-mediated gold nanoparticle cellular uptake. Bioconjugate Chem 16(3):494–496
Xueyi Z, Jianrong W, Gareth RW, Shiwei N, Qianqian Q, Li-Min Z (2019) Functionalized MoS2-nanosheets for targeted drug delivery and chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids Surf B 173(1):101–108
Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson M, Chung LWK, Nie S (2004) In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 22(8):969–976
Chen J, Saeki F, Wiley BJ, Chang H, Cobb MJ, Li ZY, Au L, Zhang H, Kimmey MB, Li X, **a Y (2005) Gold nanocages: bioconjugation and their potential use as optical imaging contrast agents. Nano Lett 5(3):473–477
Shengjie X, Dian L, Peiyi W (2015) One-pot, facile, and versatile synthesis of monolayer MoS2/WS2 quantum dots as bioimaging probes and efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv Funct Mater 25(7):1127–1136
Kevin JM, Lihong J, Adam MB, Surangi J, Wen T, Mingyuan G, Robert L, Ana J (2018) Biocompatible semiconductor quantum dots as cancer imaging agents. Adv Mater 30(18):1706356 (1–18)
Brigger I, Dubernet C, Couvreur P (2002) Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54(5):631–651
Chen J, Wiley B, Campbell D, Saeki F, Chang L, Au L, Lee J, Li X, **a Y (2005) Gold nanocages: engineering their structure for biomedical applications. Adv Mater 17(18):2255–2261
Jeong-Eun P, Minho K, Jae-Ho H, Jwa-Min N (2017) Golden opportunities: plasmonic gold nanostructures for biomedical applications based on the second near-infrared window. Small Methods 1(3):1600032 (1–6)
Guanying C, Indrajit R, Chunhui Y, Paras NP (2016) Nanochemistry and nanomedicine for nanoparticle-based diagnostics and therapy. Chem Rev 116(5):2826–2885
Barcikowski S, Hustedt M, Chichkov BN (2008) Nanocomposite manufacturing using ultrashort-pulsed laser ablation in solvents and monomers. Polimery 53(9):657–662
Compagnini G, Scalisi AA, Puglisi O (2002) Ablation of Nobel metals on liquids: a method to obtain nanoparticles in a thin polymeric film. Phys Chem Chem Phys 4(12):2787–2791
Rybaltovskii AO, Buznik VM, Zavorotny YuS, Minaev NV, Timashev PS, Churbanov SN, Bagratashvili BN (2018) Synthesis of film nanocomposites under laser ablation and drift embedding of nanoparticles into polymer in supercritical carbon dioxide. Russ J Phys Chem B 12(7):1160–1165
Chacko L, Poyyakkara A, Kumar VBS, Aneesh PM (2018) MoS2-ZnO nanocomposites as highly functional agents for anti-angiogenic and anti-cancer theranostics. J Mater Chem B. 6(19):3048–3057
Dijkkamp D, Venkatesan T, Wu XD, Shaheen SA, Jisrawi N, Minlee YH, Mclean WL, Croft M (1987) Preparation of Y-Ba-Cu oxide superconductor thin films using pulsed laser evaporation from high TC bulk material. Appl Phys Lett 51(8):619–621
Silvia H, Kota H, Hikaru S, Hidenori H, Hideo H (2016) In-situ growth of superconducting SmO1−xFxFeAs thin films by pulsed laser deposition. Sci Rep 6(35797):1–6
Pappas DL, Saenger KL, Bruley J, Krakow W, Cuomo JJ, Gu T, Collins RW (1992) Pulsed laser deposition of diamond-like carbon films. Appl Phys 71(11):5675
Cheng Y, Lu YM, Guo YL, Huang GJ, Wang SY, Tian FT (2017) Multilayers diamond-like carbon film with germanium buffer layers by pulsed laser deposition. Surf Rev Lett 24(02):1750014 (1–6)
Radhakrishnan G, Adams PM (1999) Pulsed-laser deposition of particulate-free TiC coatings for tribological applications. Appl Phys A 69(Suppl 1):S33–S38
Balakrishnan G, Elangovan T, Shin-Sung Y, Kim D-E, Kuppusami P, Venkatesh BR, Sastikumar D, Jungil S (2017) Microstructural and tribological studies of Al2O3/ZrO2 nanomultilayer thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Adv Mater Lett 8(4):410–417
Dureuil V, Ricolleau C, Gandais M, Grigis C, Lacharme JP, Naudon A (2001) Growth and morphology of cobalt nanoparticles on alumina. J Cryst Growth 233(4):737–748
Ayman MD, Wael HE, Ali AS, Mohamed HT (2015) Synthesis of nano-cadmium sulfide by pulsed laser ablation in liquid environment. Spectrosc Lett 48(9):638–645
Patil PP, Phase DM, Kulkarni SA, Ghaisas SV, Kulkarni SK, Kanetkar SM, Ogale SB, Bhide VG (1987) Pulsed-laser-induced reactive quenching at liquid–solid interface: aqueous oxidation of iron. Phys Rev Lett 58(3):238–241
Scherer GW (1985) Glasses and ceramics from colloids. J Non-Cryst Solids 73(1):661–667
Dahl JA, Maddux BL, Hutchison JE (2007) Towards greener nanosynthesis. Chem Rev 107(6):2228–2269
Hartmann S, Brandhuber D, Husing N (2007) Glycol-modified silanes: novel possibilities for the synthesis of hierarchically organized (hybrid) porous materials. Acc Chem Res 40(9):885–894
Mende S, Stenger F, Peukert W, Schwedes J (2004) Production of sub-micron particles by wet comminution in stirred media mills. J Mater Sci 39(16):5223–5226
Besner S, Kabashin AV, Winnik FM, Meunier M (2008) Ultrafast laser based “green” synthesis of non-toxic nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Appl Phys A 93(4):955–959
Wang JB, Zhang CY, Zhong XL, Yang GW (2002) Cubic and hexagonal structures of diamond nanocrystals formed upon pulsed laser induced liquid–solid interfacial reaction. Chem Phys Lett 361(1–2):86–90
Suha IA, Adel KM, Zaineb FM (2015) Study the effect of different liquid media on the synthesis of alumina (Al2O3) nanoparticle by pulsed laser ablation technique. Manuf Sci Technol 3(4):77–81
Fabbro R, Fournier J, Ballard P, Devaux D, Virmont J (1990) Physical study of laser-produced plasma in confined geometry. J Appl Phys 68(2):775–784
Yang GW (2007) Laser ablation in liquids: applications in the synthesis of nanocrystals. Prog Mater Sci 52(4):648–698
Liu P, Cui H, Wang C, Yang GW (2010) From nanocrystal synthesis to functional nanostructure fabrication: laser ablation in liquid. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12(16):3942–3952
Berthe L, Fabbro R, Peyre P, Tollier L, Bartnicki E (1997) Shock waves from a water-confined laser-generated plasma. J Appl Phys 82(6):2826–2832
Zhu S, Lu YF, Hong MH (2001) Laser ablation of solid substrates in a water-confined environment. Appl Phys Lett 79(9):1396–1398
Zhu S, Lu YF, Hong MH, Chen XY (2001) Laser ablation of solid substrates in water and ambient air. J Appl Phys 89(4):2400–2403
Shaw SJ, Schiffers WP, Gentry TP, Emmony DC (1999) A study of the interaction of a laser-generated cavity with a nearby solid boundary. J Phys D 32(14):1612–1617
Takada N, Sasaki T, Sasaki K (2008) Synthesis of crystalline TiN and Si particles by laser ablation in liquid nitrogen. Appl Phys A 93(4):833–836
Rawat R, Tiwari A, Vendamani VS, Pathak AP, VenugopalRao S, Tripathi A (2018) Synthesis of Si/SiO2 nanoparticles using nanosecond laser ablation of silicate-rich garnet in water. Opt Mater 75:350–356
Simakin AV, Voronov VV, Kirichenko NA, Shafeev GA (2004) Nanoparticles produced by laser ablation of solids in liquid environment. Appl Phys A 79(4):1127–1132
Anton AP, Gleb T, Noé D, Charlotte B, Khaled M, Nicola J, Al-Kattan A, Benoit L, Diane B, Serge M, Da Silva A, Marie-Anne E, Andrei VK (2019) Laser-synthesized TiN nanoparticles as promising plasmonic alternative for biomedical applications. Sci Rep 9(1):1194 (1–11)
Singh SC, Gopal R (2007) Zinc nanoparticles in solution by laser ablation technique. Bull Mater Sci 30(3):291–293
Neli M, Aljulaih AA, Wilfried W, Sergei AK, Satoru I (2018) Laser-ablated ZnO nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity toward organic pollutants. Materials 11(7):1127 (1–11)
Tsuji T, Hamagami T, Kawamura T, Yamaki J, Tsuji M (2005) Laser ablation of cobalt and cobalt oxides in liquids: influence of solvent on composition of prepared nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 243(1–4):214–219
Borghei SM, Bakhtiyari F (2017) Study of the physical properties of cobalt/cobalt oxide particles synthesized by pulsed laser ablation in different liquid media. Acta Phys Pol A 131(3):332–335
Sreeja R, Reshmi R, Aneesh PM, Jayaraj MK (2012) Liquid phase pulsed laser ablation of metal nanoparticles for nonlinear optical applications. Sci Adv Mater 4(3–4):439–448
Dongshi Z, Wonsuk C, Jurij J, Mark-Robert K, Stephan B, Sung-Hak C, Koji S (2018) Spontaneous shape alteration and size separation of surfactant-free silver particles synthesized by laser ablation in acetone during long-period storage. Nanomaterials 8(7):529 (1–17)
Yeh MS, Yang YS, Lee YP, Lee HF, Yeh YH, Yeh CS (1999) Formation and characteristics of Cu colloids from CuO powder by laser irradiation in 2-propanol. J Phys Chem B 103(33):6851–6857
Marzun G, Bönnemann H, Lehmann C, Spliethoff B, Weidenthaler C, Barcikowski S (2017) Role of dissolved and molecular oxygen on Cu and PtCu alloy particle structure during laser ablation synthesis in liquids. Chemphyschem 18(9):1175–1184
Sylvestre JP, Poulin S, Kabashin AV, Sacher E, Meunier M, Luong JHT (2004) Surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles produced by laser ablation in aqueous media. J Phys Chem B 108(43):16864
**aoxia X, Lei G, Guotao D (2018) The fabrication of Au@C core/shell nanoparticles by laser ablation in solutions and their enhancements to a gas sensor. Micromachines 9(6):278 (1–13)
Dolgaev SI, Simakin AV, Voronov VV, Shafeev GA, Bozon-Verduraz F (2002) Nanoparticles produced by laser ablation of solids in liquid environment. Appl Surf Sci 186(1–4):546–551
De Bonis A, Santagata A, Galasso A, Laurita A, Teghil R (2017) Formation of titanium carbide (TiC) and TiC@C core–shell nanostructures by ultra-short laser ablation of titanium carbide and metallic titanium in liquid. J Colloid Interface Sci 489:76–84
Sugiyama M, Okazaki H, Koda S (2002) Size and shape transformation of TiO2 nanoparticles by irradiation of 308-nm laser beam. Jpn J Appl Phys 41(7A):4666–4674
Wisam JA, Saja QA, Jassim NZ (2018) Production TiO2 nanoparticles using laser ablation in ethanol. Silicon 10(5):2101–2107
Ankin KV, Melnik NN, Simakin AV, Shafeev GA, Voronov VV, Vitukhonovsky AG (2002) Formation of ZnSe and CdS quantum dots via laser ablation in liquids. Chem Phys Lett 366(3–4):357–360
Ismail RA, Hamoudi WK, Abbas HF (2018) New route for cadmium sulfide nanowires synthesis via pulsed laser ablation of cadmium in thiourea solution. Mater Res Express 5(2):025017 (1–26)
**ao Y, Deng G, Feng G, Ning S, Wang S, Chen X, Yang H, Zhou S (2019) Femtosecond laser induced nano-meter size surface structures on ZnSe film. AIP Adv 9:015106 (1–6)
Compagnini G, Scalisi AA, Puglisi O (2003) Production of gold nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid alkanes. J Appl Phys 94(12):7874–7877
Wang JB, Yang GW, Zhang CY, Zhong XL, Ren ZHA (2003) Cubic-BN nanocrystals synthesis by pulsed laser induced liquid–solid interfacial reaction. Chem Phys Lett 367(1–2):10–14
Yang L, May PW, Yin L, Smith JA, Rosser KN (2007) Growth of diamond nanocrystals by pulsed laser ablation of graphite in liquid. Diamond Relat Mater 16(4–7):725–729
Sasaki T, Liang C, Nichols WT, Shimizu Y, Koshizaki N (2004) Fabrication of oxide base nanostructures using pulsed laser ablation in aqueous solutions. Appl Phys A 79(4):1489–1492
Liang CH, Shimizu Y, Sasaki T, Koshizaki N (2003) Synthesis of ultrafine SnO2−x nanocrystals by laser-induced reactive quenching in liquid medium. J Phys Chem B 107(35):9220–9225
Liang CH, Shimizu Y, Sasaki T, Koshizaki N (2005) Preparation of ultrafine TiO2 nanocrystals via pulsed-laser ablation of titanium metal in surfactant solution. Appl Phys A 80(4):819–822
Zeng HB, Cai WP, Hu JL, Duan GT, Liu PS, Li Y (2006) Violet photoluminescence from shell layer of Zn/ZnO core–shell nanoparticles induced by laser ablation. Appl Phys Lett 88(17):171910 (1–3)
Ajimsha RS, Anoop G, Aravind A, Jayaraj MK (2008) Luminescence from surfactant-free Zno quantum dots prepared by laser ablation in liquid. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 11(2):K14–K17
Aneesh PM, Shijeesh MR, Aravind A, Jayaraj MK (2014) Highly luminescent undoped and Mn-doped Zns nanoparticles by liquid phase pulsed laser ablation. Appl Phys A: Mater Sci Process 116(3):1085–1089
Papavassiliou GC (1979) Optical properties of small inorganic and organic metal particle. Prog Solid State Chem 12(3–4):185–271
Festag G, Steinbruck A, Wolff A, Csaki A, Moller R, Fritzsche W (2005) Optimization of gold nanoparticle-based DNA detection for microarrays. J Fluoresc 15(2):161–170
Mishra YK, Mohapatra S, Avasthi DK, Kabiraj D, Lalla NP, Pivin JC, Sharma H, Kar R, Singh N (2007) Gold-silica nanocomposites for the detection of human ovarian cancer cells: a preliminary study. Nanotechnology 18(34):345606 (1–5)
Mulvaney P (1996) Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nanosized metal particles. Langmuir 12(3):788–800
Favier F, Walter EM, Zach MP, Benter T, Penner RM (2001) Hydrogen sensors and switches from electrodeposited palladium mesowire arrays. Science 293(5538):2227–2231
Hu J, Odom TW, Lieber CM (1999) Chemistry and physics in one dimension: synthesis and properties of nanowires and nanotubes. Acc Chem Res 32(5):435–445
Kabashin AV, Meunier M (2003) Synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles during femtosecond laser ablation of gold in water. J Appl Phys 94(12):7941–7943
Mafune F, Kohno JY, Takeda Y, Kondow T, Sawabe H (2000) Formation and size control of silver nanoparticles by laser ablation in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B 104(39):9111–9117
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J (1951) A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. J Discuss Faraday Soc 11:55–75
Gamaly EG, Rode AV, Davies BL (2002) Ablation of solids by femtosecond lasers: ablation mechanism and ablation thresholds for metals and dielectrics. Phys Plasmas 9(9):949–957
Link S, El Sayed MA (2003) Optical properties and ultrafast dynamics of metallic nanocrystals. Annu Rev Phys Chem 54:331–366
Karthikeyan B, Thomas J, Philip R (2005) Optical nonlinearity in glass-embedded silver nanoclusters under ultrafast laser excitation. Chem Phys Lett 414(4):346–350
Tilaki RM, Irajizad A, Mahdavi SM (2006) Stability, size and optical properties of silver nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation in different carrier media. Appl Phys A 84(1):215–219
Nichols WT, Sasaki T, Koshizaki N (2006) Laser ablation of a platinum target in water: III. Laser induced reactions. J Appl Phys 100(11):114913 (1–7)
Kooli F, Chsem IC, Vucelic W, Jones W (1996) Synthesis and properties of terephthalate and benzoate in intercalates of Mg-Al layered double hydroxides possessing varying layer charge. Chem Mater 8(8):1969–1977
Aneesh PM, Aravind A, Reshmi R, Ajimsha RS, Jayaraj MK (2009) Dependence of size of liquid phase pulsed laser ablated ZnO nanoparticles on pH of the medium. Trans Mater Res Soc Jpn 34(4):759–763
Zeng HB, Cai WP, Li Y, Hu JL, Liu PS (2005) Composition/structural evolution and optical properties of ZnO/Zn nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid media. J Phys Chem B 109(39):18260–18266
Lin BX, Fu ZX, Jia YB (2001) Green luminescent center in undoped zinc oxide films deposited on silicon substrates. Appl Phys Lett 79(7):943–945
Djurisic AB, Leung YH (2006) Optical properties of ZnO nanostructures. Small 2(8–9):944–961
Zhou H, Alves H, Hofmann DM, Kriegseis W, Meyer BK, Kaczmarczyk G, Hoffmann A (2002) Behind the weak excitonic emission of ZnO quantum dots: ZnO/Zn(OH)2 core–shell structure. Appl Phys Lett 80(2):210–212
Joshy NV, Saji KJ, Jayaraj MK (2008) Spatial and temporal studies of laser ablated ZnO plasma. J Appl Phys 104(5):053307 (1–6)
Nakagawa M, Mitsudo H (1986) Anomalous temperature dependence of the electrical conductivity of zinc oxide thin films. Surf Sci 175(1):157–176
He C, Saski T, Usui H, Shimizu Y, Koshizaki N (2007) Fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation in aqueous media and pH-dependent particle size: an approach to study the mechanism of enhanced green photoluminescence. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 191(1):66–73
Weissleder R (2001) A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat Biotechnol 19(4):316–317
Mahmoudi M, Hosseinkhani H, Hosseinkhani M, Boutry S, Simchi A, Journeay WS, Subramani K, Laurent S (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging tracking of stem cells in vivo using iron oxide nanoparticles as a tool for the advancement of clinical regenerative medicine. Chem Rev 111(2):253–280
Paulus MJ, Gleason SS, Easterly ME, Foltz CJ (2001) A review of high-resolution X-ray computed tomography and other imaging modalities for small animal research. Lab Anim 30(3):36–45
Zondervan R, Kulzer F, Kol’chenko MA, Orrit M (2004) Photobleaching of Rhodamine 6G in poly(vinyl alochol) at the ensemble and single-molecule levels. J Phys Chem A 108(10):1657–1665
Dosev D, Nichkova M, Kennedy IM (2008) Inorganic lanthanide nanophosphors in biotechnology. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8(3):1052–1067
Yang C, Yang P, Wang W, Gai S, Wang J, Zhang M, Lin J (2009) Synthesis and characterization of Eu-doped hydroxyapatite through a microwave assisted microemulsion process. Solid State Sci 11(11):1923–1928
Chane-Ching JY, Lebugle A, Rousselot I, Pourpoint A, Pelle F (2007) Colloidal synthesis and characterization of monocrystalline apatite nanophosphors. J Mater Chem 17(28):2904–2913
Jagannathan R, Kottaisamy M (1995) Eu3+ luminescence: a spectral probe in M5(PO4)3X apatites (M = Ca or Sr; X = F−, Cl−, Br− or OH−). J Phys: Condens Mater 7(44):8453–8466
Yan Z, Chrisey DB (2012) Pulsed laser ablation in liquid for micro-/nanostructure generation. J Photochem Photobiol C 13(3):204–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Aneesh, P.M., Jayaraj, M.K. (2020). Optical Properties of Metal, Semiconductor and Ceramic Nanostructures Grown by Liquid Phase-Pulsed Laser Ablation. In: Jayaraj, M. (eds) Nanostructured Metal Oxides and Devices. Materials Horizons: From Nature to Nanomaterials. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3314-3_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3314-3_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-3313-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-3314-3
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)