Abstract
In March and April 2018, we carried out a survey of myxosporean parasites in coastal fishes collected from Nha Trang Bay in Vietnam’s East Sea. Of the 159 fish specimens, 18 fish species were represented, belonging to 10 families. In 8 host species, 7 myxosporean species were found, representing the genera Kudoa and Unicapsula. Two of these species were new to science: Kudoa igori n. sp. from the gallbladder of Longarm mullet Osteomugil cunnesius (Valenciennes, 1836) (prevalence 10%) and Kudoa borimiri n. sp. from skeletal muscles of Longarm mullet and Longfinned mullet Osteomugil perusii (Valenciennes, 1836) (prevalence 30% and 60%, respectively). Vegetative stages were not found. Spores of K. igori n. sp. were small, orbicular to quadrate in apical view, and with four equal valves. In lateral view, spores were shallowly ovoid with a slightly protruding anterior pole. The 4 polar capsules were slightly unequal sizes and were oriented toward the apex of the spore. Dimensions were as follows: spore length 4.56 ± 0.22 (4.18–4.56), thickness 4.42 ± 0.39 (3.55–5.13), width 5.74 ± 0.46 (4.66–6.50), length of biggest polar capsule 1.38 ± 0.14 (1.1–1.65), middle 1.28 ± 0.12 (1.03–1.53), smallest 1.13 ± 0.11 (0.94–1.30), width of biggest polar capsule 1.03 ± 0.14 (0.83–1.4), middle 0.92 ± 0.12 (0.76–1.08), smallest 0.74 ± 0.12 (0.55–0.94). Spores of K. borimiri n. sp. had four equal valves with slightly rounded ends and were quadrate in apical view. In lateral view, spores were broadly deltoid. Four equal-sized polar capsules opened at the apex of the spore. In O. cunnesius, spore dimensions were as follows: length 3.51 ± 0.15 (3.34–3.92), thickness 3.65 ± 0.38 (2.79–4.21), width 4.97 ± 0.37 (4.13–5.97), length of the polar capsules 1.23 ± 0.18 (0.99–1.57), width 0.88 ± 0.07 (0.70–1.00). Overlap** dimensions for K. borimiri n. sp. spores were also found in O. perusii. Other known myxozoan species we encountered were Kudoa thyrsites and Kudoa whippsi, which had not previously been reported from the East Sea and Vietnam. We also encountered Kudoa monodactyli, which had not previously been reported from Nha Trang Bay. In addition, we report 2 additional species, a Kudoa sp. and a Unicapsula sp., that were not attributable to previously described myxozoans and need further investigation to completely characterize.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
DNA sequence data was deposited in GenBank, and archival tissue as gelatin-glycerine slides submitted to collective use center Collection of Hydrobionts of the World Ocean of A. O. Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of the Southern Seas of RAS (Sevastopol, Russia), alcohol samples of fish organs and tissues with myxosporeans are preserved in the Institute of Ecology and Biological Resources of Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (Ha Noi, Vietnam) and at SUNY-ESF, State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry, Environmental Biology, (Syracuse, USA).
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdel-Baki AAS, Abdel-Haleem HM, Al-Quraishy S, Azevedo C, Mansour L (2018) Ultrastructural and molecular charascteristics of Kudoa crenimugilisn. sp. infecting intestinal smooth muscle of fringelip mullet Crenimugil crenilabis in the Red Sea. Dis Aquat Org 129:53–62. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao03225
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Morsy K, Mehlhorn H, Bashtar AR, Shazly MA, Saad AH, Abdel-Gaber R (2012) First report of Kudoa species (Myxozoa: Kudoidae) infecting the spotted coral grouper Plectropomus maculates from the Red Sea. A light and ultrastructural study. Parasitol Res 111:1579–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3011-x
Alama-Bermejo G, Cuadrado M, Raga JA, Holzer AS (2009) Morphological and molecular redescription of the myxozoan Unicapsula pflugfelderi Schubert, Sprague & Reinboth 1975 from two teleost hosts in the Mediterranean. A review of the genus Unicapsula Davis 1924. J Fish Dis 32:335–350. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2008.01000.x
Allen GR (2009) Field guide to marine fishes of tropical Australia and South-East Asia. Western Australian Museum. 287 p
Andrada CG, Tortelly R, Nogueira PP, Andrade CL, Lima FC (2005) Infecção por Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947 (Myxozoa: Multivalvulida) em musculature esquelética de espada Trichiurus lepturus L. (Teleostei: Trichiuridae). Parasitogia Latinoamericana 60:150–153 (In Portuguese). https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-77122005000200008
Arfara S, Bozzetta E, Prearo M, Ghittino C (1995) Casi di Kudoasi in giovani orate d’allevamento. Boll Soc Ital Patologia Ittica 17:12–17
Arthur JR, Te BQ (2006) Checklist of the parasites of fishes of Viet Nam. FAO Fisheries technical paper, 369/2. Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations, Rome. 133 p
Aseeva NL, Chinh NN (2018) Myxosporeans – parasites of mullets from west part of the Pacific Ocean. Proceeding of the VI Congress of the Society of Parasitologists, Russia: International Conference (October 15–19, 2018, Zoological Institute RAS, Saint-Petersburg). (Eds. Galaktionov KV, Frolov AO, Medvedev SG, Ryss AY). Saint Petersburg: Lema Publishing pp. 20 (In Russian)
Atkinson SD, Bartošová-Sojková P, Whipps CM, Bartholomew JL (2015) Approaches for characterizing myxozoan species. In: Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development (pp. 111–123). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14753-6_6
Bunton TE, Poynton SL (1991) Kudoa sp. (Myxosporea, Multivalvulida) infection in juvenile white perch, Morone americana (Gmelin): histopathology and spore morphology. J Fish Dis 14:589–594. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1991.tb00615.x
Burger MAA, Adlard RD (2010) Four new species of Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947 (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from Australia with recommendations for species descriptions in the Kudoidae. Parasitology 137:793–814. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182009991557
Casal G, Soares EC, Rocha S, Silva TJ, Santos EL, Nascimento R, Oliveira E, Azevedo C (2019) Description of a new myxozoan Kudoa eugerres n. sp. and reclassification of two Sphaerospora sensu lato species. Parasitol Res 118:1719–1730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06324-8
Chinh NN, Ngo HD, Duc NH, Linh NT, Doanh PN (2018) Morphological and molecular characteristics of Kudoa scomberomori (Myxosporea: Kudoidae) firstly found from the Indo-Pacific king mackerel Scomberomorus guttatus (Scombridae) in Quang Binh province, Vietnam. J Biol 40:1–6
Chinh NN, Ngo HD, Tuc VV, Naoki I, Tomoyoshi Y, Sho S, Doanh PN (2021) A new myxosporean species, Henneguya lata n. sp. (Myxozoa:Myxobolidae), from the gills of yellowfin seabream Acanthopagrus latus (Perciformes: Sparidae) in the Gulf of Tonkin, Vietnam. Parasitol Res 120:877–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-07031-5
Chinh NN, Ha NV, Doanh PN, Yurakhno V, Yoshinaga T, Shirakashi S, Hallett SL, Whipps CM (2022) Morphological and molecular characterization of Ceratomyxa binhthuanensis n. sp. (Myxosporea: Ceratomyxidae) from the gall bladder of blacktip grouper Epinephelus fasciatus (Perciformes: Serranidae) in the East Sea of Vietnam. Parasitol Res 121:613–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07419-x
Chinh NN, Duc NV, Ha NV, Ngo HD, Nghiem DX (2015) A Protozoa species, Kudoa monodactyli Gunter, 2006 (Multivalvulida: Kudoidae), in the muscle of some coastal marine fishes in Quang Binh province. Proceeding of the 42th Vietnam National Conference of Parasitology. Publishing house for science and technology. pp. 273–280 (In Vietnamese)
Chinh NN, Ngo HD, Yurakhno V, Doanh PN (2019) First report of Auerbachia chakravartyi (Myxosporea: Bilvavulida) from the gall bladder of Torpedo scad (Megalaspis cordyla) in Vietnam. School for Theoretical and Marine Parasitology.VII All-Russian Conference, with international participation, 9–14 September, Sevastopol: abstract book / Ed. К. V. Galaktionov. – Sevastopol: FRC IBSS Publ. pp. 49
Clopton RE (2004) Standard nomenclature and metrics of plane shapes for use in gregarine taxonomy. Comp Parasitol 71:130–140. https://doi.org/10.1654/4151
Diamant A, Whipps CM, Kent ML (2004) A new species of Sphaeromyxa (Myxosporea: Sphaeromyxina: Sphaeromyxidae) in devil firefish, Pterois miles (Scorpaenidae), from the northern Red Sea: Morphology, ultrastructure, and phylogeny. J Parasitol 90:1434–1442. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-336R
Diamant A, Ucko M, Paperna I, Colorni A, Lipshitz A (2005) Kudoa iwatai (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) in wild and cultured fish in the Red Sea: redescription and molecular phylogeny. J Parasitol 91:1175–1189. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-491R.1
Donets ZS, Schulman SS (1973) About methods of research Myxosporidia (Protozoa, Cnidosporidia). Parasitologiya 7:191–193
Dyková I, Lom J, Overstreet RM (1994) Myxosporean parasites of the genus Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947 from some gulf of Mexico fishes: description of two new species and notes on their ultrastructure. Europ J Protistol 30:316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0932-4739(11)80078-7
Egusa S, Shiomitsu T (1983) Studies on the Myxosporidian parasites of the genus Kudoa found in marine fish cultured in Japan. Fish Pathol 18:163–171
Eiras JC, Saraiva A, Cruz C (2014) Synopsis of the species of Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Multivalvulida). Syst Parasitol 87:153–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-013-9461-4
Fiala I (2006) The phylogeny of Myxosporea (Myxozoa) based on small subunit ribosomal RNA gene analysis. Int J Parasitol 36:1521–1534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.06.016
Fujita T (1930) On a new Myxosporidia in the muscle of the grey-mullet Chloromyxum bora nov. sp. Zool Magaz 42:45–48
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syq010
Gunter N, Cribb T, Whipps Ch, Adlard RD (2006) Characterization of Kudoa monodactyli n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from the Muscle of Monodactylus argenteus (Teleostei: Monodactylidae) from Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. J Eukaryot Microbiol 53:374–378. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2006.00115.x
Ha K, Bui QT (2007) Parasites on fresh water fish in Vietnam. In: Huong T, Su V (eds) Science and Technics Publishing House, Hanoi, p 360
Hallett SL, Lester RJG (1997) Infections by Kudoa ciliatae (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) in indo-pacific whiting Sillago spp. Dis Aquat Org 30:11–16
Heiniger H, Cribb TH, Adlard RD (2013) Intra-specific variation of Kudoa spp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from apogonid fishes (Perciformes), including the description of two new species, K. cheilodipteri n. sp. and K. cookii n. sp., from Australian waters. Syst Parasitol 84:193–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-012-9400-9
Kasai A, Li YC, Setsuda A, Mafie E, Sato H (2015) Genetic characterization of Kudoa iwatai and Kudoa trachuri in commercial marine fish (Platycephalus sp. and Trachurus japonicus) for human consumption. Jpn J Vet Parasitol 14:22–30
Kasai A, Setsuda A, Sato H (2017) Morphological and genetic characterization of Kudoa whippsi (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from Cheilodactylus zonatus in the western Pacific Ocean off Japan, and two new Kudoa spp. (K. akihitoi n. sp. and K. empressmichikoae n. sp.) from Acanthogobius hasta in the Sea of Ariake, Japan. Parasitol Res 116:647–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-5329-2
Kovaleva AA, Shulman SS, Yakovlev VN (1979) Myxosporidia of the genus Kudoa (Myxosporidia, Multivalvulida) from the basin of the Atlantic Ocean. Systematics and ecology of sporozoans and cnidosporidians. Tr Zool Inst Akad Nauk SSSR 87:42–64
Krasin VK (1976) Myxosporidian and microsporidian infections of the musculature of fish in the northeastern part of the Pacific Ocean. Kratkie Tezisy Dokladov II Vsesoyuuznogo Simpoziuma po Parazitam I Boleznyam Morskikh Zhivotnykh. Ministerstvo Rybn. Khoz. SSSR, AtlantNIRO, Kaliningrad, USSR, pp. 35–36
Laird M, Bullock WL (1969) Marine fish haematozoa from New Brunswick and New England. J Fish Res Board Can 26:1075–1102. https://doi.org/10.1139/f69-100
Li YC, Inoue K, Tanaka S, Zhang JY, Sato H (2020a) Identification of four new Kudoa spp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea:Multivalvulida) in commercial fishes collected from South China Sea, Atlantic Ocean, and Bering Sea by integrated taxonomic approach. Parasitol Res 119:2113–2128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06707-2
Li YC, Inoue K, Zhang JY, Sato H (2020b) Phylogenetic relationships of three Kudoa spp. with morphologically similar myxospores (K. iwatai, K. lutjanus, and K. bora), with the redescription of K. uncinata and K. petala and description of a new species (K. fujitai n. sp.) in fishes in the South China Sea. Parasitol Res 119:1221–1236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-020-06636-0
Li YC, Tamemasa S, Zhang JY, Sato H (2020c) Phylogenetic characterisation of seven Unicapsula spp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from commercial fish in southern China and Japan. Parasitology 147:448–464. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182019001793
Lom J, Arthur JR (1989) A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. J Fish Dis 12:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1989.tb00287.x
Lom J, Dyková I, Rohde K (1992) Studies on protozoan parasites of Australian fishes, 1: new species of the genera Coccomyxa, Ortholinea and Kudoa (Myxozoa, Myxosporea). Folia Parasitol 39:289–306
Maeno YK, Nagasawa K, Sorimachi M (1993) Kudoa intestinalis n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from the intestinal musculature of the striped mullet, Mugil cephalus, from Japan. J Parasitol 79:190–192
Matsukane Y, Sato H, Tanaka S, Kamata Y, Sugita-Konishi Y (2011) Kudoa iwatai and two novel Kudoa spp., K. trachuri n. sp. and K. thunni n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida), from daily consumed marine fish in western Japan. Parasitol Res 108:913–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2133-2
Monteiro EP, da Silva DT, Hamoy I, Sanches O, Matos E (2019) Morphological and molecular characteristics of Kudoa viseuensis n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida), found in the muscle of Batrachoides surinamensis (Teleostei: Batrachoididae) in the Brazilian Amazon region. Acta Protozool 58:7–16. https://doi.org/10.4467/16890027AP.19.002.10833
Moran JDW, Whitaker DJ, Kent ML (1999) A review of the myxosporean genus Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947, and its impact on the international aquaculture industry and commercial fisheries. Aquaculture 172:163–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(98)00437-2
Özer A, Okkay S, Gürkanlı CT, Çiftçi Y, Yurakhno V (2018) Two novel myxosporean parasites in Black Sea fishes: Kudoa niluferi sp. nov. and Kudoa anatolica sp. nov. (Cnidaria: Myxosporea). Dis Aquat Org 128:225–233. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao03227
Paperna I (1982) Kudoa infection in the glomeruli, mesentery and peritoneum of cultured Sparus aurata L. J Fish Dis 5:539–543. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1982.tb00514.x
Paperna I, Overstreet RM (1981) Parasites and Diseases of Mullets (Muligidae). In: Oren OH (ed) Aquaculture of Grey Mullets. International Biological Programme 26. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 411–493
Paperna I, Zwerner DE (1974) Kudoa cerebralis n. sp. (Myxosporidea, Chloromyxidae) from the striped bass, Morone saxatilis (Walbaum). J Protozool 21:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03610.x
Quaglio F, Delgado ML, Caffara M, Florio D, Marcer F, Fioravanti ML, Restani R (2002) Histopathological observations in marine farmed fish infected by Myxosporidia. II Osservazioni istopatologiche in pescimarini d’allevamento affetti da mixosporidiosi. II Boll Soc Ital Patol Ittica 14:44–67
Sakai H, Kato E, Sakaguchi S, Setsuda A, Sato H (2018) Morphological and molecular genetic characterization of Kudoa konishiae n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) in the muscle of Japanese Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius). Parasitol Res 117:893–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-5770-5
Sarkar NK, Chaudhury SR (1996) Kudoa cascasian. sp. (Myxosporea : Kudoidae) parasitic in the mesentery of Sicamugil cascasia (Ham.) from Hooghly estuary of west Bengal, India. Acta Protozool 35:335–338
Sitjà-Bobadilla A, Alvarez-Pellitero P (1992) Light and electron microscopic description of Sphaerospora dicentrarchi n. sp. (Myxosporea: Sphaerosporidae) from wild and cultured sea bass, Dicentrarchus Labrax L. J Protozool 39:273–281. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1992.tb01314.x
Stöver BC, Müller KF (2010) Tree Graph 2, combining and visualizing evidence from different phylogenetic analyses. BMC Bioinform 11:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-7
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 24:4876–4882. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Tomochi H, Li YC, Tran BT, Yanagida T, Sato H (2014) Three Unicapsula species (Myxosporea: Trilosporidae) of Asian marine fishes, including the description of Unicapsula setoensis n. sp. in the yellowfin goby (Acanthogobius flavimanus) from the Inland Sea of Japan. Parasitol Res 113:3807–3816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4048-9
Velasco M, Videira M, Viana da Silva JM, Sanches O, Matos PS, de São C, Clemente S, Matos E (2015) Esophageal infection due to Kudoa sp. (Myxozoa) in mapara catfish, Hypophthalmus Marginatus. Aquac Rep 2:22–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2015.05.001
Vo TD, Bristow GA, Dung NH, Dung VT, Nhon NNT (2012) The parasites of grouper and sea bass in Vietnam. Science and Technics Publishing House, Ho Chi Minh
Wang PC, Huang JP, Tsai MA, Cheng SY, Tsai SS, Chen SD, Chen SP, Chiu SH, Liaw LL, Chang LT, Chen SC (2005) Systemic infection of Kudoa lutjanus n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) in red snapper Lutjanus erythropterus from Taiwan. Dis Aquat Org 67:115–124. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao067115
Whipps CM, Font WF (2013) Interaction of two myxozoan parasites from naked goby Gobiosoma bosc, in Lake Pontchartrain, Louisiana. J Parasitol 99:441–447. https://doi.org/10.1645/12-49.1
Whipps CM, Kent ML (2006) Phylogeography of the cosmopolitan marine parasite Kudoa thyrsites (Myxozoa: Myxosporea). J Eukaryot Microbiol 53:364–373. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2006.00114.x
Whipps CM, Adlard RD, Bryant MS, Lester RJG, Findlay V, Kent ML (2003a) First report of three Kudoa species from Eastern Australia: Kudoa thyrsites from Mahi mahi (Coryphaena hippurus), Kudoa amamiensis and Kudoa minithyrsites n. sp. from Sweeper (Pempheris ypsilychnus). J Eukaryot Microbiol 50:215–219. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2003.tb00120.x
Whipps CM, Adlard RD, Bryant MS, Kent ML (2003b) Two unusual myxozoans, Kudoa quadricornis n. sp. (Multivalvulida) from the muscle of goldspotted trevally (Carangoides fulvoguttatus) and Kudoa permulticapsula n. sp. (Multivalvulida) from the muscle of Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus commerson) from the Great Barrier Reef. Australia J Parasitol 89:168–173. https://doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2003)089[0168:TUMKQN]2.0.CO;2
Whipps CM, Grossel G, Adlard RD, Yokoyama H, Bryant MS, Munday BL, Kent ML (2004) Phylogeny of the Multivalvulidae (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) based upon comparative rDNA sequence analysis. J Parasitol 90:618–622. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-153R
Whipps CM, McAllister CT, Lindsay KA (2021) Genetic diversity of Cystodiscus species in amphibians in the Southern United States. J Parasitol 107:912–922. https://doi.org/10.1645/21-73
Whitaker DJ, Kabata Z, Margolis L (1994) Myxosporean parasites and their potential impact on the aquaculture industry, with emphasis on Kudoa species. In: Conley DC (ed) Kudoa workshop proceedings; Nanaimo, BC). Aquaculture Industry Development Report 94–01, British Columbia Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries & Food, Victoria, pp 2–7
Whitaker DJ, Kent ML (1991) Myxosporean Kudoa thyrsites: a cause of soft flesh in farm-reared Atlantic salmon. J Aquat Anim Health 3:291–294. https://doi.org/10.1577/1548-8667(1991)003%3c0291:MKTACO%3e2.3.CO;2
Yurakhno VM (2007) Premilinary data on Myxosporea and Microsporidia of fish from the Charleston Harbour (Atlantic Ocean). Parassitologia. 49(Suppl. 2):171 (Abstr. 7th International Symposium on Fish Parasites, 24-28 September 2007, Viterbo, Italy)
Yurakhno VM, Maltsev VN (2002) New data on myxosporeans of mullets in the Atlantic Ocean basin. Ekologija Morya 61:39–42
Yurakhno VM, Ovcharenko MO (2014) Study of Myxosporea (Myxozoa), infecting worldwide mullets with description of a new species. Parasitol Res 113:3661–3674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4031-5
Yurakhno VM, Vo TH (2019) First data on Bivalvulida myxosporeans of Nha Trang Bay mullets Vietnam. Mar Biol J 4:82–88. https://doi.org/10.21072/mbj.2019.04.4.07
Yurakhno VM, Vo TH (2019a) First data on fish myxosporeans of Nha Trang Gulf Mugilidae (Vietnam, Eastern Sea). School for Theoretical and Marine Parasitology.VII All-Russian Conference, with international participation, 9–14 September, Sevastopol: abstract book / Ed. К. V. Galaktionov. – Sevastopol: FRC IBSS Publ. P. 59.
Zhou Y, Zhao YJ (2008) Descriptions of three news species of Kudoa (Myxosporea, Multivalvulida, Kudoidae) parasitic in marine fishes from the East China Sea. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 32:51–56
Acknowledgements
Part of this work was supported by budget funding of RAS (project 121030100028-0 “Regularities of formation and anthropogenic transformation of biodiversity and biological resources of the Azov-Black Sea basin and other areas of the World Ocean,” No. 121051100109-1 (Systematics, diversity, biology and ecology of aquatic and near-water invertebrates, structure of populations and communities in continental waters), the Vietnam-Russia Joint Tropical Science and Technology Research Center (ECOLAN E-3.1) “Conservation, restoration and sustainable use of marine coastal ecosystems based on the study of their structural and functional organization” (subsection 8 “Composition of species and community structure of parasites of mullet fish of Nha Trang Bay”) (Russia, Vietnam). The study was also partly funded by the JSPS RONPAKU program (R12206) (Japan). We are grateful to Dr. Jean-Dominique Durand, Université de Montpellier, for checking the correctness of the mullet species identification.
Funding
The main part of V. M. Yurakhno (Russia) and Ha Vo (Vietnam) was carried out at the expense of funding the Joint Russian-Vietnamese Tropical Research and Technology Center. One of the Vietnamese authors, Nguyen Ngoc Chinh, received financial support from the JSPS RONPAKU program (R12206) (Japan). Work carried out by CMW at ESF was supported in part by the SUNY Center for Applied Microbiology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
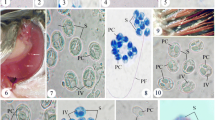
V.T.H. provided support for the fieldwork portion of the study, including transport, supplies, and purchase of fish. V.M.Y., N.N.C. carried out dissections and parasitological examinations with some assistance from V.T.H. When parasites were encountered, they were photographed by V.M.Y. and N.N.C. Figure 1 was created by V.M.Y. Line drawings in Fig. 2 were drawn by N.N.C. For molecular work, E.E.S. and C.M.W. generated DNA sequence data from infected tissues. C.M.W conducted all the phylogenetic analyses and prepared Figs. 3 and 4. V.M.Y. and C.M.W. created and revised all the manuscript tables. V.M.Y. wrote the first draft of the manuscript. C.M.W. wrote and oversaw all subsequent revisions of the manuscript and wrote the final version for journal review. All authors reviewed the manuscript and provided edits on the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Animal handling and use
All fish used in this study were purchased from fish markets. No live animals were used.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Una Ryan
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yurakhno, V.M., Slynko, E.E., Chinh, N.N. et al. Multivalvulidan myxosporeans from marine fishes in Nha Trang Bay, Vietnam, with descriptions of Kudoa igori n. sp. and Kudoa borimiri n. sp. from mullets. Parasitol Res 121, 2927–2943 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-022-07620-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-022-07620-6