Abstract
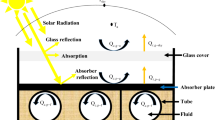
The aim of the present work is to compare thermal efficiency of three flat-plate collectors, which are different in the type of coatings used in the absorber plate. The thermal efficiency of the collector was investigated using three types of absorber plate: the black painted, the black chrome coating, and the carbon coating. The thermal performance of the collectors was considered based on American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers Standard 93 (2010). The volume flow rate varied from 0.5 to 1.5 L min−1. The field emission scanning electron microscope images demonstrated that the carbon coating had high absorption due to trap** the light and avoiding the reflection of the light. The collector with the carbon-coated absorber plate at the flow rate of 1.5 L min−1 has the maximum thermal efficiency of approximately 69.4%. Furthermore, the thermal efficiency of the carbon-coated absorber plate and black chrome-coated absorber plate is averagely 13% and 11.3% higher than the black-painted absorber plate, respectively. Additionally, the removed energy parameter (\(F_{\text{R}} U_{\text{L}}\)) at the flow rate of 1.5 L min−1 decreases approximately 35.4% for the collector with the carbon-coated absorber plate and 28.4% for the collector with the black chrome-coated absorber plate compared to the black-painted absorber plate.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A c :
-
Area of the absorber plate, (m2)
- D :
-
Riser tube diameter, (m)
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient, (W m−2K−1)
- Q u :
-
The useful energy gain, (W)
- T a :
-
Ambient temperature, (K)
- T o :
-
Outlet temperature, (K)
- T in :
-
Inlet temperature, (K)
- T f,o :
-
Outlet fluid temperature, (K)
- T f,i :
-
Inlet fluid temperature, (K)
- T f,o,initial :
-
Outlet initial fluid temperature, (K)
- C p :
-
Specific heat, (J kg−1)
- G :
-
Solar radiation, (W m−2)
- F R :
-
Heat removal factor
- \({\dot{m}}\) :
-
Mass flow rate, (kg s−1)
- U L :
-
Heat loss coefficient, (W m−2 K−1)
- a:
-
Ambient
- f:
-
Fluid
- e:
-
Emissivity
- i:
-
Inlet
- o:
-
Outlet
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Plate absorptance
- \(\eta\) :
-
Thermal efficiency of collector
- \(\tau\) :
-
Glass cover transmittance
- \(\delta R\) :
-
Uncertainty in the result, generic
- \(\delta X_{\text{j}}\) :
-
Uncertainty in the jth variable
- FPC:
-
Flat-plate collector
- Re:
-
Reynolds number, \(\rho UD_{\text{h}} /\mu_{\text{f}}\)
- PH:
-
Power of hydrogen
References
Duffie JA, Beckman, WA, Solar engineering of thermal processes, New York: Wiley; 2013. https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Solar+Engineering+of+Thermal+Processes,+4th+Edition-p-9780470873663. Accessed 17 Apr 2019.
Sakhaei SA, Valipour MS. Performance enhancement analysis of the flat plate collectors: a comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2019;102:186–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2018.11.014.
Asadi J, Amani P, Amani M, Kasaeian A, Bahiraei M. Thermo-economic analysis and multi-objective optimization of absorption cooling system driven by various solar collectors. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;173:715–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.08.013.
Nazari S, Safarzadeh H, Bahiraei M, Experimental and analytical investigations of productivity, energy and exergy efficiency of a single slope solar still enhanced with thermoelectric channel and nanofluid. Renew Energy 2019;729–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.12.059.
Jaisankar S, Radhakrishnan TK, Sheeba KN, Suresh S. Experimental investigation of heat transfer and friction factor characteristics of thermosyphon solar water heater system fitted with spacer at the trailing edge of left-right twisted tapes. Energy Convers Manag. 2009;50:2638–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2009.06.019.
Ananth J, Jaisankar S. Experimental studies on heat transfer and friction factor characteristics of thermosyphon solar water heating system fitted with regularly spaced twisted tape with rod and spacer. Energy Convers Manag. 2013;73:207–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2013.04.022.
García A, Martin RH, Pérez-García J. Experimental study of heat transfer enhancement in a flat-plate solar water collector with wire-coil inserts. Appl Therm Eng. 2013;61:461–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APPLTHERMALENG.2013.07.048.
Ananth J, Jaisankar S. Investigation on heat transfer and friction factor characteristics of thermosiphon solar water heating system with left-right twist regularly spaced with rod and spacer. Energy. 2014;65:357–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2013.12.001.
Jouybari HJ, Saedodin S, Zamzamian A, Nimvari ME, Wongwises S. Effects of porous material and nanoparticles on the thermal performance of a flat plate solar collector: an experimental study. Renew Energy. 2017;114:1407–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2017.07.008.
Javaniyan Jouybari H, Saedodin S, Zamzamian A, Nimvari ME. Experimental investigation of thermal performance and entropy generation of a flat-plate solar collector filled with porous media. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;127:1506–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.08.170.
Chen Z, Gu M, Peng D. Heat transfer performance analysis of a solar flat-plate collector with an integrated metal foam porous structure filled with paraffin. Appl Therm Eng. 2010;30:1967–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APPLTHERMALENG.2010.04.031.
Bazri S, Badruddin IA, Naghavi MS, Bahiraei M. A review of numerical studies on solar collectors integrated with latent heat storage systems employing fins or nanoparticles. Renew Energy. 2018;118:761–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.11.030.
Nazari S, Safarzadeh H, Bahiraei M. Performance improvement of a single slope solar still by employing thermoelectric cooling channel and copper oxide nanofluid: an experimental study. J Clean Prod. 2019;208:1041–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.194.
Olia H, Torabi M, Bahiraei M, Ahmadi MH, Goodarzi M, Safaei MR. Application of nanofluids in thermal performance enhancement of parabolic trough solar collector: state-of-the-art. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:463. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030463.
Kasaeian A, Eshghi AT, Sameti M. A review on the applications of nanofluids in solar energy systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2015;43:584–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.11.020.
Tayebi R, Akbarzadeh S, Valipour MS. Numerical investigation of efficiency enhancement in a direct absorption parabolic trough collector occupied by a porous medium and saturated by a nanofluid. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13010.
Said Z, Sabiha MA, Saidur R, Hepbasli A, Rahim NA, Mekhilef S, Ward TA. Performance enhancement of a flat plate solar collector using titanium dioxide nanofluid and Polyethylene Glycol dispersant. J Clean Prod. 2015;92:343–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2015.01.007.
Noghrehabadi A, Hajidavalloo E, Moravej M. An experimental investigation of a 3-D solar conical collector performance at different flow rates. J Heat Mass Transf Res. 2016;1:57–66.
Bellos E, Tzivanidis C, Tsimpoukis D. Enhancing the performance of parabolic trough collectors using nano fluids and turbulators. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;91:358–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.091.
Frank G, Kauer E, Köstlin H, Schmitte FJ. Transparent heat-reflecting coatings for solar applications based on highly doped tin oxide and indium oxide. Sol Energy Mater. 1983;8:387–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1633(83)90004-7.
Amrutkar SK, Solar Flat Plate Collector Analysis, IOSR J Eng. 2012;2:207–213.
Föste S, Ehrmann N, Giovannetti F, Rockendorf G. Basics for the development of a high efficiency flat-plate collector with a selectively coated double glazing, 30th ISES Bienn. Sol World Congr. 2011;3:2469–74. https://doi.org/10.18086/swc.2011.19.14.
Akbarzadeh S, Valipour MS. Heat transfer enhancement in parabolic trough collectors: A comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;92:198–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2018.04.093.
Bhide VG, Vaishya JS, Nagar VK, Sharma SK. Choice of selective coating for flat plate collectors. Sol Energy. 1982;29:463–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-092X(82)90054-8.
Dias D, Rebouta L, Costa P, Al-Rjoub A, Benelmeki M, Tavares CJ, Barradas NP, Alves E, Santilli P, Pischow K. Optical and structural analysis of solar selective absorbing coatings based on AlSiOx:W cermets. Sol Energy. 2017;150:335–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.04.055.
Ning Y, Wang W, Wang L, Sun Y, Song P, Man H, Zhang Y, Dai B, Zhang J, Wang C, Zhang Y, Zhao S, Tomasella E, Bousquet A, Cellier J. Optical simulation and preparation of novel Mo/ZrSiN/ZrSiON/SiO2 solar selective absorbing coating. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2017;167:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2017.04.017.
Yin Y, Pan Y, Hang LX, McKenzie DR, Bilek MMM. Direct current reactive sputtering Cr–Cr2O3 cermet solar selective surfaces for solar hot water applications, Thin Solid Films. 2009:517:1601–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TSF.2008.09.082.
Voinea M, Bogatu C, Chitanu GC, Duta A. Copper cermets used as selective coatings for flat plate solar collectors. Rev Chim. 2008;59:1–6.
Konttinen P, Lund PD. Microstructural optimization and extended durability studies of low-cost rough graphite–aluminium solar absorber surfaces. Renew Energy. 2004;29:823–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2003.11.008.
Moncada MLT, Muñoz BC, Yoshida MM, Rodríguez RD. Comparative experimental study of new absorbent surface coatings for flat plate solar collectors, Energy Procedia. 2014;57:2131–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.10.179.
Shamshirgaran SR, Khalaji Assadi M, Badescu V, Al-Kayiem HH. Upper limits for the work extraction by nanofluid-filled selective flat-plate solar collectors. Energy. 2018;160:875–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2018.06.154.
Alami AH, Aokal K. Enhancement of spectral absorption of solar thermal collectors by bulk graphene addition via high-pressure graphite blasting. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;156:757–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2017.11.040.
Kasaeian A, Daviran S, Azarian RD. Optical and thermal investigation of selective coatings for solar absorber tube. Int J Renew Energy Res. 2016;6:15–20.
Kasaeian A, Daviran S, Azarian RD, Rashidi A. Performance evaluation and nanofluid using capability study of a solar parabolic trough collector. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;89:368–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.09.056.
Standards A, November C, Board A, Janu D. Methods of testing to determine the thermal performance of solar collectors, 1991;1986.
Moffat RJ. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 1988;1:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/0894-1777(88)90043-X.
Müller S, Giovannetti F, Reineke-Koch R, Kastner O, Hafner B. Simulation study on the efficiency of thermochromic absorber coatings for solar thermal flat-plate collectors. Solar Energy. 2019;188:865–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakhaei, S.A., Valipour, M.S. Investigation on the effect of different coated absorber plates on the thermal efficiency of the flat-plate solar collector. J Therm Anal Calorim 140, 1597–1610 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09148-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09148-x