Abstract
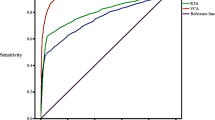
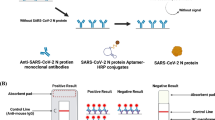
The correlation between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) risk has been extensively researched. The continual monitoring of EBV-IgAs provides a promising approach of NPC screening in its early stage. In this study, we successfully synthesized a single-atom nanozyme (SANzyme) through the application of iron-porphyrin based metal organic framework (MOF-FeP). The MOF-FeP possesses precisely-defined electronic and geometric structures that accurately mimic highly-evolved catalytic site of natural peroxidase. The peroxidase-like activity of MOF-FeP enables it to catalyze the chemiluminescence of luminol substrate. By integrating MOF-FeP into a traditional strip, we created a rapid and highly-sensitive evaluation tool for detecting EBV-IgAs. Importantly, the MOF-FeP strip enables the simultaneous detection of three EBV-IgAs, greatly improving the accuracy of EBV-associated NPC screening. The sensitivities of the MOF-FeP strip (75.56%–93.30%) surpass those of current enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) methods (64.44%–82.22%). This test takes only 16 min to perform as opposed to the customary 1–2 h required for standard ELISA. Additionally, the MOF-FeP strip is suitable for whole blood samples, thereby significantly simplifying the sample preparation and detection process. In conclusion, the MOF-FeP strip combines the simplicity of traditional strip with the high catalytic activity of SANzyme. Our innovative MOF-FeP strip offers a new point-of-care strategy for EBV-IgAs detection, which is expected to markedly facilitate early screening for EBV-associated diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, H. M.; Okuda, K. S.; González, F. E.; Patel, V. Current perspectives on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. In Human Cell Transformation. Rhim, J. S.; Dritschilo, A.; Kremer, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, 2019; pp 11–34.
Wei, K. R.; Zheng, R. S.; Zhang, S. W.; Liang, Z. H.; Li, Z. M.; Chen, W. Q. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China, 2013. Chin. J. Cancer 2017, 36, 90.
Zheng, S. H.; Wang, Y. T.; Liu, S. R.; Huang, Z. L.; Wang, G. N.; Lin, J. T.; Ding, S. R.; Chen, C.; **a, Y. F. Addition of chemoradiotherapy to palliative chemotherapy in de novo metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A real-world study. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 36.
Mahdavifar, N.; Ghoncheh, M.; Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A.; Khosravi, B.; Salehiniya, H. Epidemiology and inequality in the incidence and mortality of nasopharynx cancer in Asia. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2016, 7, 360–372.
Lu, T. Z.; Guo, Q. J.; Lin, K. Y.; Chen, H. L.; Chen, Y. X.; Xu, Y. J.; Lin, C.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M. Y. et al. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs BART7-3p and BART13-3p as novel biomarkers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1711–1723.
Soldan, S. S.; Lieberman, P. M. Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 51–64.
Feng, G. F.; Xu, Y. F.; Ma, N.; Midorikawa, K.; Oikawa, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Nakamura, S.; Ishinaga, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, G. W. et al. Influence of Epstein-Barr virus and human papillomavirus infection on macrophage migration inhibitory factor and macrophage polarization in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 929.
Li, Y. Q.; Khin, N. S.; Chua, M. L. K. The evolution of Epstein-Barr virus detection in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2018, 15, 1–5.
Ji, M. F.; Wang, D. K.; Yu, Y. L.; Guo, Y. Q.; Liang, J. S.; Cheng, W. M.; Zong, Y. S.; Chan, K. H.; Ng, S. P.; Wei, W. I. et al. Sustained elevation of Epstein-Barr virus antibody levels preceding clinical onset of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 623–630.
Cao, S. M.; Liu, Z. W.; Jia, W. H.; Huang, Q. H.; Liu, Q.; Guo, X.; Huang, T. B.; Ye, W. M.; Hong, M. H. Fluctuations of Epstein-Barr virus serological antibodies and risk for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A prospective screening study with a 20-year follow-up. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19100.
Chien, Y. C.; Chen, J. Y.; Liu, M. Y.; Yang, H. I.; Hsu, M. M.; Chen, C. J.; Yang, C. S. Serologic markers of Epstein-Barr virus infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwanese men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1877–1882.
Li, T. D.; Guo, X. Y.; Ji, M. F.; Li, F. G.; Wang, H.; Cheng, W. M.; Chen, H. L.; Ng, M.; Ge, S. X.; Yuan, Y. et al. Establishment and validation of a two-step screening scheme for improved performance of serological screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 1458–1467.
Gao, L. Z.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J. B.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T. H.; Feng, J.; Yang, D. L.; Perrett, S. et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577–583.
Lin, L. H.; Li, H.; Gu, H. F.; Sun, Z. Y.; Huang, J.; Qian, Z. N.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Z.; **, H. Y.; Wu, P. F. et al. Asymmetrically coordinated single-atom iron nanozymes with Fe-N1C2 structure: A peroxidase mimetic for melatonin detection. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 4751–4757.
Chen, M.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X. K.; Yuan, T. W.; Wang, W. Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y. F.; Zhou, F. Y.; Wang, X.; Xue, Z. G. et al. Single iron site nanozyme for ultrasensitive glucose detection. Small 2020, 16, 2002343.
Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Gu, N. Iron-based nanozymes in disease diagnosis and treatment. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 2722–2732.
Duan, D. M.; Fan, K. L.; Zhang, D. X.; Tan, S. G.; Liang, M. F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. L.; Zhang, P. H.; Liu, W.; Qiu, X. G. et al. Nanozyme-strip for rapid local diagnosis of Ebola. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 134–141.
Liu, D.; Ju, C. H.; Han, C.; Shi, R.; Chen, X. H.; Duan, D. M.; Yan, J. H.; Yan, X. Y. Nanozyme chemiluminescence paper test for rapid and sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 173, 112817.
Jiang, B.; Duan, D. M.; Gao, L. Z.; Zhou, M. J.; Fan, K. L.; Tang, Y.; **, J. Q.; Bi, Y. H.; Tong, Z.; Gao, G. F. et al. Standardized assays for determining the catalytic activity and kinetics of peroxidase-like nanozymes. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1506–1520.
Gong, W.; Zhang, W. Q.; Son, F. A.; Yang, K. W.; Chen, Z. J.; Chen, X. F.; Jiang, J. W.; Liu, Y.; Farha, O. K.; Cui, Y. Topological strain-induced regioselective linker elimination in a chiral Zr(IV)-based metal-organic framework. Chem 2021, 7, 190–201.
Dai, S.; Nouar, F.; Zhang, S. J.; Tissot, A.; Serre, C. One-step room-temperature synthesis of metal(IV) carboxylate metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 4328–4334.
Wei, D. L.; Zhang, X. Y.; Chen, B.; Zeng, K. Using bimetallic Au@Pt nanozymes as a visual tag and as an enzyme mimic in enhanced sensitive lateral-flow immunoassays: Application for the detection of streptomycin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1126, 106–113.
Xu, B. L.; Wang, H.; Wang, W. W.; Gao, L. Z.; Li, S. S.; Pan, X. T.; Wang, H. Y.; Yang, H. L.; Meng, X. Q.; Wu, Q. W. et al. A single-atom nanozyme for wound disinfection applications. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4911–4916.
Huang, L.; Chen, J. X.; Gan, L. F.; Wang, J.; Dong, S. J. Single-atom nanozymes. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav5490.
Jiao, L.; Xu, W. Q.; Yan, H. Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C. R.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. H.; Zhu, C. Z. Fe-N-C single-atom nanozymes for the intracellular hydrogen peroxide detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11994–11999.
Leung, S. F.; Tam, J. S.; Chan, A. T. C.; Zee, B.; Chan, L. Y. S.; Huang, D. P.; Van Hasselt, A.; Johnson, P. J.; Lo, Y. M. D. Improved accuracy of detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by combined application of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA and anti-Epstein-Barr viral capsid antigen IgA antibody. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 339–345.
Connolly, Y.; Littler, E.; Sun, N.; Chen, X. Y.; Huang, P. C.; Stacey, S. N.; Arrand, J. R. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus thymidine kinase: A characteristic marker for the serological detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 692–697.
Ebrahim, A.; DeVore, K.; Fischer, T. Limitations of accelerated stability model based on the Arrhenius equation for shelf life estimation of in vitro diagnostic products. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 684–688.
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Zhe Zhang from First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University for his guidance on this study. This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFA0709204), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32200744), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Nos. 2021A1515110028 and 2022A1515220147), the Science and Technology Program for Basic Research in Shenzhen (Nos. JCYJ20210324103015039, JCYJ20190809095811254, and JCYJ20200109140412476), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81930050 and 22121003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2023_5915_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Rapid and sensitive detection of Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by chemiluminescence strips based on iron-porphyrin single atom nanozyme
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Wang, J., Liu, D. et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of Epstein-Barr virus antibodies in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by chemiluminescence strips based on iron-porphyrin single atom nanozyme. Nano Res. 17, 1827–1836 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5915-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5915-4