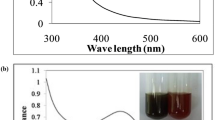
Abstract
Aqueous extract of Neolamarchia cadamba leaves were used in the synthesis of silver/silver chloride nanoparticles (Ag/AgCl NPs). Further they were separated based on their using step-wise centrifugation approach at 09,000, 12,000, and 15,000 rpm. Thus obtained NPs were characterized for their physicochemical features. NPs showed maximum absorbance at 455 nm, 415 nm, and 402 nm. All the NPs were found to be crystalline in nature with average crystallite size (nm) of 58.31, 23.43, and 09.56. Particle size distribution (nm) of NPs was observed to 435.43, 276.75, and 105.49, Surface charge (-mV) of NPs was observed to be 14.59, 23.90, and 32.17. Ag/AgCl NPs-rpm@15,000 showed antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, coagulase-negative Staphylococci, and Staphylococcus aureus with zone of inhibition (mm) of 16.65, 13.69, and 14.02 at 50 µg per well, respectively. Ag/AgCl NPs-rpm@15,000 showed excellent catalytic activity in degradation of methyl red, methylene blue, rhodamine-B, and methyl orange dyes in the presence of sodium borohydride under 4, 6, 5, and 4 min with pseudo-first order rate constant (min−1) of 0.981 (96.4%), 0.666 (97.1%), 0.905 (98.1%), and 1.032 (96.6%), respectively. Furthermore, Ag/AgCl NPs-rpm@15,000 showed good catalytic efficiency even under different dye combinations. Total combination was degraded under 18 min.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Apart from the data presented, if required additional data can be submitted upon journal's requirement.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abd Alamer IS, Tomah AA, Ahmed T, et al (2021) Biosynthesis of Silver Chloride Nanoparticles by Rhizospheric Bacteria and Their Antibacterial Activity against Phytopathogenic Bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum. Molecules 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27010224
Alula MT, Madingwane ML, Yan H et al (2022) Biosynthesis of bifunctional silver nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of organic pollutants and optical monitoring of mercury (II) ions using their oxidase-mimic activity. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21619-7
Asong JA, Frimpong EK, Seepe HA et al (2023) Green Synthesis of Characterized Silver Nanoparticle Using Cullen tomentosum and Assessment of Its Antibacterial Activity. Antibiotics 12:203. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020203
Attia YA, Abdel-Hafez SH (2020) Reusable photoresponsive Ag/AgCl nanocube-catalyzed one-pot synthesis of seleno[2,3-b]pyridine derivatives. Res Chem Intermed 46:3165–3177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-020-04143-6
Banu R, Ramakrishna D, Reddy GB et al (2020) Facile one-pot microwave-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Bael gum: Potential application as catalyst in the reduction of organic dyes. Mater Today Proc 43:2265–2273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.861
Chikkanayakanahalli Paramesh C, Halligudra G, Gangaraju V et al (2021) Silver nanoparticles synthesized using saponin extract of Simarouba glauca oil seed meal as effective, recoverable and reusable catalyst for reduction of organic dyes. Results Surf Interfaces 3:100005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsurfi.2021.100005
da Fernandes DGS, Andrade VB, Lucena LN et al (2022) Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Properties of Photosynthesized Silver Chloride Nanoparticles Using Plant Extract from Stryphnodendron adstringens (Martius) Coville. J Clust Sci 33:687–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02011-w
Ebrahimi A, Samari F, Eftekhar E, Yousefinejad S (2022) Rapid and efficient colorimetric sensing of clindamycin and Fe3+ using controllable phyto-synthesized silver/silver chloride nanoparticles by Syzygium cumini fruit extract. J Anal Sci Technol 13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-022-00318-5
Fazary AE, Al-Shihri AS, Alfaifi MY et al (2016) Microbial production of four biodegradable siderophores under submerged fermentation. Int J Biol Macromol 88:527–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.011
Gudkov SV, Burmistrov DE, Serov DA et al (2021) A Mini Review of Antibacterial Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles. Front Phys 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2021.641481
Hadi AA, Ng JY, Shamsuddin M et al (2022) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Diplazium esculentum extract: catalytic reduction of methylene blue and antibacterial activities. Chem Pap 76:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01835-0
Hashemi Z, Mizwari ZM, Mohammadi-Aghdam S et al (2022) Sustainable green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Sambucus ebulus phenolic extract (AgNPs@SEE): Optimization and assessment of photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange and their in vitro antibacterial and anticancer activity: Sustainable green. Arab J Chem 15:103525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103525
Hassan KT, Ibraheem IJ, Hassan OM et al (2021) Facile green synthesis of Ag/AgCl nanoparticles derived from Chara algae extract and evaluating their antibacterial activity and synergistic effect with antibiotics. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105359
Huo Y, Han YX, Singh P et al (2021) Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer potentials of AgCl nanoparticles biosynthesized by Flavobacterium panacis. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 127:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04386-z
Ismail M, Khan MI, Khan SB et al (2018) Catalytic reduction of picric acid, nitrophenols and organic azo dyes via green synthesized plant supported Ag nanoparticles. J Mol Liq 268:87–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.07.030
Ismail M, Khan MI, Khan MA et al (2019) Plant-supported silver nanoparticles: Efficient, economically viable and easily recoverable catalyst for the reduction of organic pollutants. Appl Organomet Chem 33:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4971
Kabir SR, Islam F, Asaduzzaman AKM (2022) Biogenic silver/silver chloride nanoparticles inhibit human cancer cells proliferation in vitro and Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells growth in vivo. Sci Rep 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-12974-z
Kandiah M, Chandrasekaran KN (2021) Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Catharanthus roseus Flower Extracts and the Determination of Their Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Photocatalytic Activity. J Nanotechnol 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5512786
Karimi S, Samimi T (2019) Green and simple synthesis route of Ag@AgCl nanomaterial using green marine crude extract and its application for sensitive and selective determination of mercury. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 222:117216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.117216
Khan W, Khan N, Jamila N et al (2022) Antioxidant, antibacterial, and catalytic performance of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles of Rhus javanica, Rumex hastatus, and Callistemon viminalis. Saudi J Biol Sci 29:894–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.10.016
Khatoon UT, Nageswara Rao GVS, Mohan KM et al (2017) Antibacterial and antifungal activity of silver nanospheres synthesized by tri-sodium citrate assisted chemical approach. Vacuum 146:259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.10.003
Khatoon UT, Rao GVSN, Mohan MK et al (2018) Comparative study of antifungal activity of silver and gold nanoparticles synthesized by facile chemical approach. J Environ Chem Eng 6:5837–5844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.08.009
Khatoon UT, Velidandi A, Nageswara Rao GVS (2022) Sodium borohydride mediated synthesis of nano-sized silver particles: Their characterization, anti-microbial and cytotoxicity studies. Mater Chem Phys 294:126997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126997
Khatoon UT, Velidandi A, Nageswara Rao GVS (2023) Copper oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis via chemical reduction, characterization, antibacterial activity, and possible mechanism involved. Inorg Chem Commun 149:110372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.110372
Kim B, Song WC, Park SY, Park G (2021) Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles via sargassum serratifolium extract for catalytic reduction of organic dyes. Catalysts 11:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030347
Nguyen DT, Duong NL, Nguyen VM et al (2020) Chromolaena odorata extract as a green agent for the synthesis of Ag@AgCl nanoparticles inactivating bacterial pathogens. Chem Pap 74:1849–1857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-01033-z
Nguyen TTB, Nguyen TH, Nguyen XT (2022) Preparation and Antibacterial Evaluation of Polyethylene Glycol Ointment Containing In Situ Silver Chloride Nanoparticles. Bionanoscience 12:203–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-021-00935-1
Okaiyeto K, Ojemaye MO, Hoppe H et al (2019) Phytofabrication of Silver/ Silver Chloride Oedera genistifolia : Characterization and Antibacterial Potential. Molecules 24:4382
Patil MP, Piad LLA, Bayaraa E et al (2019) Doxycycline hyclate mediated silver–silver chloride nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. J Nanostructure Chem 9:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-019-0297-6
Priyadarshini S, Sonsudin F, Mainal A et al (2021) Phytosynthesis of biohybrid nano-silver anchors enhanced size dependent photocatalytic, antibacterial, anticancer properties and cytocompatibility. Process Biochem 101:59–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2020.11.008
Rajasekar R, Samuel M, Edison TNJI, Raman N (2021) Sustainable synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Alstonia scholaris for enhanced catalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Mol Struct 1246:131208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131208
Ramzan M, Karobari MI, Heboyan A, et al (2022) Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Extracts of Wild Ginger (Zingiber zerumbet) with Antibacterial Activity against Selective Multidrug Resistant Oral Bacteria. Molecules 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27062007
Saha P, Mahiuddin M, Islam ABMN, Ochiai B (2021) Biogenic Synthesis and Catalytic Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles Based on Peel Extracts of Citrus macroptera Fruit. ACS Omega 6:18260–18268. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c02149
Şahin M, Arslan Y, Tomul F et al (2022) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lathyrus brachypterus extract for efficient catalytic reduction of methylene blue, methyl orange, methyl red and investigation of a kinetic model. React Kinet Mech Catal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02299-3
Sarkar M, Denrah S, Das M, Das M (2021a) Statistical optimization of bio-mediated silver nanoparticles synthesis for use in catalytic degradation of some azo dyes. Chem Phys Impact 3:100053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chphi.2021.100053
Sarkar M, Denrah S, Patra M, Basu T (2021b) Studies on the Antibacterial and Catalytic Activities of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Cyperus rotundus L. J Clust Sci 32:265–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01785-9
Sathiyaraj S, Suriyakala G, Dhanesh Gandhi A et al (2021) Biosynthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of gold nanoparticles. J Infect Public Health 14:1842–1847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2021.10.007
Sattari R, Khayati GR, Hoshyar R (2021) Biosynthesis of Silver-Silver Chloride Nanoparticles Using Fruit Extract of Levisticum Officinale: Characterization and Anticancer Activity Against MDA-MB-468 Cell Lines. J Clust Sci 32:593–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01818-3
Shaikh JA (2022) Green synthesis of surfactant-capped silver nanoparticles using ginger extract and investigation of its catalytic activity in the reductive degradation of methyl orange dye and 4-nitrophenol. J Iran Chem Soc 19:4149–4158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-022-02593-w
Singh C, Anand SK, Upadhyay R et al (2023) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by root extract of Premna integrifolia L. and evaluation of its cytotoxic and antibacterial activity. Mater Chem Phys 297:127413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127413
Song WC, Kim B, Park SY et al (2022) Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Sargassum horneri extract as catalyst for industrial dye degradation. Arab J Chem 15:104056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104056
Tran MT, Nguyen LP, Nguyen DT et al (2021) A novel approach using plant embryos for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles as antibacterial and catalytic agent. Res Chem Intermed 47:4613–4633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-021-04548-x
Vankdoth S, Velidandi A, Sarvepalli M, Vangalapati M (2022a) Poly-Extract Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Catalysed Rhodamine-B and Methyl Orange Dye Degradation: Influence of Physicochemical Parameters and their Recyclability. Nano World J 8:42–54. https://doi.org/10.17756/nwj.2022-099
Vankdoth S, Velidandi A, Sarvepalli M, Vangalapati M (2022b) Role of plant (tulasi, neem and turmeric) extracts in defining the morphological, toxicity and catalytic properties of silver nanoparticles. Inorg Chem Commun 140:109476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109476
Velidandi A, Dahariya S, Pabbathi NPP et al (2020a) A Review on Synthesis, Applications, Toxicity, Risk Assessment and Limitations of Plant Extracts Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles. Nano World J 6:35–60. https://doi.org/10.17756/nwj.2020-079
Velidandi A, Pabbathi NPP, Dahariya S, Baadhe RR (2020b) Catalytic and eco-toxicity investigations of bio-fabricated monometallic nanoparticles along with their anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-oxidative and anti-cancer potentials. Colloids Interface Sci Commun 38:100302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2020.100302
Velidandi A, Pabbathi NPP, Baadhe RR (2021a) Study of parameters affecting the degradation of rhodamine-B and methyl orange dyes by Annona muricata leaf extract synthesized nanoparticles as well as their recyclability. J Mol Struct 1236:130287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130287
Velidandi A, Pabbathi NPP, Dahariya S, Baadhe RR (2021c) Green synthesis of novel Ag – Cu and Ag – Zn bimetallic nanoparticles and their in vitro biological, eco-toxicity and catalytic studies. Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects 26:100687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2021.100687
Velidandi A, Sarvepalli M, Pabbathi NPP, Baadhe RR (2021d) Biogenic synthesis of novel platinum-palladium bimetallic nanoparticles from aqueous Annona muricata leaf extract for catalytic activity. 3 Biotech 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02935-0
Velidandi A, Pabbathi NPP, Dahariya S, et al (2021b) Bio‑fabrication of silver‑silver chloride nanoparticles using Annona muricata leaf extract: characterization, biological, dye degradation and eco‑toxicity studies. Int J Environ Sci Technol 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03461-5
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Dr. Syam Prasad P (Associate Professor), Department of Physics (National Institute of Technology, Warangal) for providing the FTIR broker alpha II and Particle Analyzer facilities for analysis. Authors thank the Director, National Institute of Technology, Warangal (Telangana, India) for providing the research facilities required for the work. Also thank the M.H.R.D. for providing the fellowship.
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aditya Velidandi: Conceptualization, Methodology, Experimentation, Data curation, Writing-Original draft preparation, Reviewing and Editing. Mounika Sarvepalli: Experimentation. Prasad Aramanda: Experimentation. Maha Lakshmi Amudala: Experimentation. Dr. Rama Raju Baadhe: Supervision. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1. Ag/AgCl NPs solution was centrifuged at rpm (09000, 12000, and 15000) to get varying sizes of NPs.
2. Ag/AgCl NPs were characterized using UV-Vis spec., FTIR, DLS, ZP, and XRD.
3. Ag/AgCl NPs-rpm@15000 showed good antibacterial activity against test bacteria.
4. Ag/AgCl NPs-rpm@15000 showed excellent catalytic activity in dye degradation in presence of SBH.
5. Ag/AgCl NPs-rpm@15000 activity was studied for different dye combinations in presence of SBH.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Velidandi, A., Sarvepalli, M., Aramanda, P. et al. Effect of size on physicochemical, antibacterial, and catalytic properties of Neolamarckia cadamba (burflower-tree) synthesized silver/silver chloride nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 63231–63249 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26427-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26427-1