Search
Search Results
-
Effect of Drought and Heavy Precipitation on CH4 Emissions and δ13C–CH4 in a Northern Temperate Peatland
Shifting precipitation patterns due to climate change may impact peatland methane (CH 4 ) emissions, as precipitation affects water table level which...

-
Establishment and characterization of a novel cell line (SCCOHT-CH-1) and PDX models derived from Chinese patients of small cell ovarian carcinoma of the hypercalcemic type
Small cell carcinoma of the ovary hypercalcemic type (SCCOHT) is a rare and aggressive malignancy that poses a significant clinical challenge due to...

-
CH4 transport in wetland plants under controlled environmental conditions – separating the impacts of phenology from environmental variables
Background and AimsMethane (CH 4 ) fluxes at peatland plant surfaces are net results of transport of soil-produced CH 4 and within-plant CH 4 production...

-
Fertilization Methods Effect Spring Wheat Yield and Soil CH4 Fluxes in the Loess Plateau of China
Dryland agricultural soils are recognized as significant sites of methane (CH 4 ) absorption, making them integral to the global CH 4 budget. Nitrogen...

-
Emissions of CO2 and CH4 from Agricultural Soil with Kitchen Compost at Different Temperatures
Emissions of CO 2 from the soil are mainly derived from soil microbial respiration, whereas CH 4 emissions originate from anaerobic degradation of...

-
Dissolved greenhouse gas (CO2, CH4, and N2O) emissions from highland lakes of the Andes cordillera in Northern Ecuador
We report, in 15 Ecuadorian mountainous lakes, dissolved concentrations of CO 2 , CH 4 , and N 2 O and a suite of ancillary biogeochemical variables...

-
Co-existence of Congenital Hypothyroidism (CH) and TBG-Excess in a Boy Causing Simultaneous Elevation in Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) and Thyroxine (T4) Levels: First Report from India and Review of the Literature
A certain population of patients exhibits discordant thyroid function tests (TFT) consistently along with unclear symptoms may lead to equivocal...

-
Application of phosphorus in red paddy soils enhances growth and yield of rice and alters CO2 and CH4 emission from soils in a time- and dose-dependent manner
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from rice paddies have gained widespread attention, and fertilization management can mitigate GHG emissions. Red paddy...

-
Tree Species Effects on Soil CO2 and CH4 Fluxes in a Mixed Temperate Forest
Temperate forest soils are net sources of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and net sinks for methane (CH 4 ), the two greenhouse gases most responsible for...

-
Membrane-associated RING-CH 7 inhibits stem-like capacities of bladder cancer cells by interacting with nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1
BackgroundCancer stem-like capacities are major factors contributing to unfavorable prognosis. However, the associated molecular mechanisms...
-
Sources and intensity of CH4 production in paddy soils depend on iron oxides and microbial biomass
A paddy soil, with microbial biomass considerably reduced by chloroform fumigation, was treated with low-crystalline ferrihydrite and...

-
White Clover does not Increase Soil N2O Emissions Compared to Ryegrass in Non-Frozen Winter, but Increases CH4 Uptake
As one of the most important forage species in Europe, white clover ( Trifolium repens ) is a legume that is well recognized for its potential to...

-
Linear relationship between CH4 fluxes and atmospheric CO2 concentration levels controlled by rice biomass and soil methanogenic communities
The contribution of CH 4 emissions from paddy soils to greenhouse gas emissions is key in the evaluation of future climate change scenarios. Most...

-
Soil-tree-atmosphere CH4 flux dynamics of boreal birch and spruce trees during spring leaf-out
AimsStudies on tree CH 4 exchange in boreal forests regarding seasonality and role of tree canopies are rare. We aimed to quantify the contribution...

-
Biotic and Abiotic Control Over Diurnal CH4 Fluxes in a Temperate Transitional Poor Fen Ecosystem
To understand the variability of methane (CH 4 ) fluxes between a temperate mid-altitude Sphagnum- dominated peatland and the atmosphere, we monitored...

-
Linking transcriptional dynamics of CH4-cycling grassland soil microbiomes to seasonal gas fluxes
Soil CH 4 fluxes are driven by CH 4 -producing and -consuming microorganisms that determine whether soils are sources or sinks of this potent greenhouse...

-
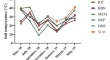
Amendment of organic manure to natural saline soil reduced N2O but enhanced CO2 and CH4 emissions
Association of agriculture with climate change is widely established. Soil constituents and soil salinity along with the amendments for soil...
-
Does replacing chemical fertilizer with ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) mitigate CH4 and N2O emissions and reduce global warming potential from paddy soil?
PurposeThe incorporation of ryegrass ( Lolium multiflorum Lam.; RG), a winter manure, could partly replace chemical N and reduce N loss during the...

-
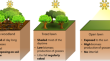
Soil CO2, CH4 and N2O fluxes in open lawns, treed lawns and urban woodlands in Angers, France
Urban green spaces (UGSs) are mostly represented by lawns and wooded areas. These UGSs can store carbon in soil and above-ground biomass, potentially...
-
Simulated Yak and Tibetan Sheep Urine Deposition Fleetingly Promoted N2O, CO2 and CH4 Emissions in an Alpine Steppe of Northern **zang Plateau
The urine of yaks ( Bos grunniens ) and Tibetan sheep ( Pantholops hodgsoni ) represents a vital source of nutrients in the alpine grasslands on the...

