Search
Search Results
-
The impact of biological soil disinfestation in conjunction with antagonists and organic materials on potato brown rot control
Biological Soil Disinfestation (BSD) is used to control soil-borne phytopathogens like Ralstonia solanacearum by introducing fresh organic matter and...

-
β-1,3-Glucanase production as an anti-fungal enzyme by phylogenetically different strains of the genus Clostridium isolated from anoxic soil that underwent biological disinfestation
Biological (or reductive) soil disinfestation (BSD or RSD) is a bioremediation process to control soil-borne plant pathogens using activities of...

-
Production of β-1,3-glucanase and chitosanase from clostridial strains isolated from the soil subjected to biological disinfestation
Biological soil disinfestation (BSD) or anaerobic (reductive) soil disinfestation (ASD/RSD) is a bioremediation method used to eliminate soil-borne...

-
Organic Management Strategies for Nematode Control in Florida Plasticulture
Most strawberry and vegetable production in Florida occurs in the open field and on plastic-mulch raised beds in combination with drip irrigation....
-
Role of anaerobic bacteria in biological soil disinfestation for elimination of soil-borne plant pathogens in agriculture
Biological soil disinfestation (BSD) or reductive soil disinfestation (RSD) is an environmental biotechnology to eliminate soil-borne plant pathogens...

-
Distinct impacts of reductive soil disinfestation and chemical soil disinfestation on soil fungal communities and memberships
Soil disinfestation is an important agricultural practice to conquer soil-borne diseases and thereby ensure crop productivity. Reductive soil...

-
Potential of algal-based products for the management of potato brown rot disease
BackgroundRalstonia solanacearum causes potato brown rot disease, resulting in lower crop’s production and quality. A sustainable and eco-friendly...

-
Degradation of the fungal cell wall by clostridial strains isolated from soil subjected to biological soil disinfestation and biocontrol of Fusarium wilt disease of spinach
Biological soil disinfestation (BSD) involves elimination of soil-borne plant pathogens in an environmentally friendly manner. Two anaerobic...

-
Eco-friendly Approaches to the Management of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes
Eco-friendly approaches have been increasingly used for the management of plant-parasitic nematodes because of growing worldwide concern regarding...
-
The control of Fusarium oxysporum in soil treated with organic material under anaerobic condition is affected by liming and sulfate content
Five treatments were applied: control (CK), reductive soil disinfestation (RSD) using alfalfa as organic material (RSD 0 ), liming before RSD 0 (RSD 1 ),...
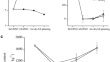
-
The microbial changes during the biological control of cucumber dam**-off disease using biocontrol agents and reductive soil disinfestation
Cucumber dam**-off disease mainly caused by Rhizoctonia solani leads to serious loss in agricultural production. In this study, the effective and...
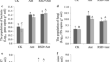
-
Changes in the soil microbial community after reductive soil disinfestation and cucumber seedling cultivation
Reductive soil disinfestation (RSD) has been proven to be an effective and environmentally friendly way to control many soilborne pathogens and...

-
Control of soil-borne pathogen Fusarium oxysporum by biological soil disinfestation with incorporation of various organic matters
Banana Fusarium wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (FOC) is a worldwide soil-borne disease that causes serious economic losses every...

-
Biological soil disinfestation using bioethanol fermentation products: role of residual organic substances
We evaluated the efficacy of biological soil disinfestation (BSD) using bioethanol fermentation products (ethanol fermentation solution and crude...

-
Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation and Soilborne Pest Management
Anaerobic soil disinfestation is a biologically based, preplant soil treatment that provides an alternative to chemical fumigation for soilborne pest...
-
Toxic organic acids produced in biological soil disinfestation mainly caused the suppression of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense
Biological soil disinfestation (BSD) is an effective and environmentally friendly way to suppress soil-borne pathogens. Although it is increasingly...
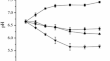
-
Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation (ASD) Combined with Soil Solarization as a Methyl Bromide Alternative: Vegetable Crop Performance and Soil Nutrient Dynamics
Background and AimsSoil treatment by anaerobic soil disinfestation (ASD) combined with soil solarization can effectively control soilborne plant...

-
Changes and recovery of soil bacterial communities influenced by biological soil disinfestation as compared with chloropicrin-treatment
Soil bacterial composition, as influenced by biological soil disinfestation (BSD) associated with biomass incorporation was investigated to observe...

-
Development of biological soil disinfestations in Japan
Biological soil disinfestations (BSDs) were developed separately in Japan and in The Netherlands as an alternative to chemical fumigations. In Japan,...

-
Proliferation of diversified clostridial species during biological soil disinfestation incorporated with plant biomass under various conditions
Biological soil disinfestation (BSD) involves the anaerobic decomposition of plant biomass by microbial communities leading to control of plant...

