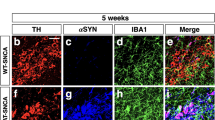
Abstract
Background
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the most common movement disorder. While neuronal deposition of α-synuclein serves as a pathological hallmark of PD and Dementia with Lewy Bodies, α-synuclein-positive protein aggregates are also present in astrocytes. The pathological consequence of astrocytic accumulation of α-synuclein, however, is unclear.
Results
Here we show that PD-related A53T mutant α-synuclein, when selectively expressed in astrocytes, induced rapidly progressed paralysis in mice. Increasing accumulation of α-synuclein aggregates was found in presymptomatic and symptomatic mouse brains and correlated with the expansion of reactive astrogliosis. The normal function of astrocytes was compromised as evidenced by cerebral microhemorrhage and down-regulation of astrocytic glutamate transporters, which also led to increased inflammatory responses and microglial activation. Interestingly, the activation of microglia was mainly detected in the midbrain, brainstem and spinal cord, where a significant loss of dopaminergic and motor neurons was observed. Consistent with the activation of microglia, the expression level of cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1) was significantly up-regulated in the brain of symptomatic mice and in cultured microglia treated with conditioned medium derived from astrocytes over-expressing A53T α-synuclein. Consequently, the suppression of COX-1 activities extended the survival of mutant mice, suggesting that excess inflammatory responses elicited by reactive astrocytes may contribute to the degeneration of neurons.
Conclusions
Our findings demonstrate a critical involvement of astrocytic α-synuclein in initiating the non-cell autonomous killing of neurons, suggesting the viability of reactive astrocytes and microglia as potential therapeutic targets for PD and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
α-synuclein (α-syn) is a major component of Lewy bodies (LB) and Lewy neurites (LN) appearing in the postmortem brain of Parkinson's disease (PD) and other synucleinopathies [1, 2]. Genetic mutations in α-syn, including point mutations (A53T, A30P and E46K) and multiplications have been linked to familial PD and Dementia with LB [3–7]. Although the precise function of α-syn remains elusive, overwhelming evidence indicates that malfunction of α-syn, especially the aggregation of misfolded α-syn, plays an important role in the process of neurodegeneration [5, 8].
Neuronal expression of either human wild-type or PD-related mutant α-syn induces neurodegeneration associated with pathological accumulations of α-syn and reactive astrogliosis [9–Behavioral test Rotarod test: as described previously [53], mice were placed onto a rotating rod with auto acceleration from 0 rpm to 40 rpm in 2 min (San Diego Instruments, San Diego, CA). The length of time the mouse stayed on the rotating rod was recorded. Open-field test: as described previously [53], the ambulatory, fine and rearing activities of mice were measured by the Flex-Field activity system (San Diego Instruments, CA). Flex-Field software was used to trace and quantify mouse movement in the unit as the number of beam breaks per 30 min. Grip strength measurement: as described previously [54], mice were allowed to use their forepaws or hind paws to pull or compress a triangular bar attached to a digital force gauge (Ametek, Largo, FL) set up to record the maximal pulling or compressing force. Five measurements were taken for each animal during each test. As described previously [54], mice were perfused via cardiac infusion with 4% paraformaldehyde in cold PBS. To obtain frozen sections, brain and spinal cord tissues were removed and submerged in 30% sucrose for 24 h and sectioned at 40 μm thickness with cryostat (Leica CM1950). For paraffin sections, sections at 8 μm thickness were obtained according to standard procedure. Antibodies specific to glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (1:1000, Sigma-Aldrich USA, St. Louis, MO), ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule-1 (Iba1, 1:1000, Wako Chemicals USA, Richmond, VA), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH, 1:1000, Pel-Freez Biologicals, Rogers, AR), α-synuclein (C20 &211, 1:1000, Santa Cruz Biotech, Santa Cruz, CA), Aquaporin 4 (1:500, Chemicon International, Inc USA, CA), glucose transporter 1 (1:500, Chemicon), von Willebrand Factor (1:500, Dako USA, Carpinteria, CA), iNOS (1:500, Sgima), SMI32 (Sternberger Monoclonal, Lutherville, MD), NeuN (1:1000, Chemicon) were used as suggested by manufacturers. Alexa 488 or Alex 568-conjugated secondary antibody (1:1000, Invitrogen) was used to visualize the staining, and Topro3 (1:1000, Invitrogen) was used for counterstaining the nuclei. Fluorescence images were captured using a laser scanning confocal microscope (LSM 510; Zeiss, Thornwood, NJ). The Images of 100 × objective (bar = 20 μM) were presented as a single optic layer after acquired in z-series stack scans at 0.8 μM intervals from individual field. The numbers of microglia and microglia cluster in the images taken from 25 × objective (368 μm × 368 μm) were counted. According to stereotaxic coordinates of mouse brains (3rd edition, Keith B.J. Franklin and George Paxinos), a series of coronal sections across the striatum (9 sections by every 10th section, Bregma -2.06-1.54 mm), SNpc (7 sections by every 4th section, Bregma -2.70- -3.82 mm), as well as cervical (approximate T1-T6) and lumbar spinal cord (approximate L1-L5, 10 sections by every 12th section) were stained with NeuN plus TH and NeuN, respectively, and visualized using the Vectastain ABC kit (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). The number of NeuN or TH-positive cells was assessed using Stereo Investigator 8, an unbiased stereological procedure with an optical fractionator (MicroBrightField Inc, Williston, VT). The sampling scheme was designed to have coefficient of error (CE) less than 10% in order to get reliable results. All stereological analyses were performed under the 100 × objective of a Zeiss Axio microscope (Imager A1). Primary cortical neuron cultures were conducted as described previously [55] by using postnatal day 1 pups. For cortical astrocyte and microglia cultures [56], the dispersed cells were collected by centrifugation and plated on 75 cm2 flasks in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). The cells were pre-incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of air/5% CO2 and the medium was changed first 24 h later and on alternate 3-days thereafter. After a pre-culture period of 8-11 days the cellular debris, microglia were lifted from astrocytes layer by shaking the culture flasks at 190 rpm for 3 h at 30°C. The cells attached to the flask were passed and grown in six-well plates for 3 days until harvest for astrocytes culture. The cells floating in the medium were collected by centrifuge and plated on 6-well plates in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS for microglial culture. After 24 h incubation, the medium of microglial cultures was switched to conditioned medium from cultured astrocytes. As previously described (**an et al., in press), brain tissues (cerebral cortex, brainstem) were weighed and homogenized with 10 volumes of sucrose buffer (0.32 M sucrose, 1 mM NaHCO3, 1 mM MgCl2, and 0.5 mM CaCl2, plus protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktails). Lysates were centrifuged at 1, 000 g for 10 min to separate supernatant (S1) and pellet (P1). Protein concentrations in S1 were measured by BCA (Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL). S1 contains total α-synuclein protein, representing the sucrose fraction. An aliquot of S1 was diluted in the same volume of Triton extraction buffer (2% Triton X-100, 20 mM HEPES, plus protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktails), homogenized by sonication, and centrifuged at 20, 000 × g for 30 min to obtain the Triton X-100-soluble (TX-sol) supernatant (S2) and Triton X-100-insoluble (TX-insol) pellet (P2). P2 was washed 4 times by 1% Triton X-100 buffer and centrifuged at 20, 000 × g for 10 min. The pellet fraction was further extracted in 2% SDS buffer (2% SDS, 20 mM HEPES, plus protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktails) by sonication and centrifuged at 20, 800 × g for 5 min. The supernatant (S3) were present as Triton X-100-insoluble (TX-insol) or SDS-soluble fraction. Proteins were size-fractioned by 4-12% NuPage BisTris-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Invitrogen) using MOPS running buffer (Invitrogen), and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) or Nitrocellulose membranes. Antibodies specific to human/mouse α-synuclein (SynC20 recognizing the C terminal of both human and mouse α-synuclein, 1:1000, Santa Cruz; Syn-1 recognizing both human and mouse α-synuclein encoding amino acids 1-100, 1:1000, BD Biosciences, San Diego) [35] and β-actin (1:5000, Sigma) as loading control were used in this study. Horseradish peroxidase conjugated secondary antibodies were from Jackson ImmunoResearch. Signals were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence development (Pierce, Rockford, IL) and quantified by imageJ software (NIH). For COX-1 inhibitor treatment, mutant mice and control littermates at 2 months of age were administrated with SC-560 (30 mg/kg; Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) or vehicle (40% dimethyl sulfoxide in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.4) through intraperitoneal (IP) injection once a day for 7 days [34]. RNA was harvested using Qiagen RNeasy mini kit and converted into first-strand cDNA using RT2 First Strand Kit (SuperArray Bioscience Corporation). Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using an ABI Prism 7900HT Fast Detection System (Applied Biosystems). Statistical analysis was performed using the Graphpad Prism 5 (Graphpad Software Inc. La Jolla, CA). Data are presented as Means ± SEM. Statistical significances were determined by comparing means of different groups using t-test or ANOVA followed by Post Hoc Tukey HSD test, and presented as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.Histology and Immunohistochemical Analyses
Stereology
Primary cell cultures
Tissue fractionation
Western Blot
COX-1 inhibition
Quantitative real-time PCR array
Statistical Analysis
References
Spillantini MG, Goedert M: The alpha-synucleinopathies: Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000, 920: 16-27.
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M: Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature. 1997, 388: 839-840. 10.1038/42166.
Chartier-Harlin MC, Kachergus J, Roumier C, Mouroux V, Douay X, Lincoln S, Levecque C, Larvor L, Andrieux J, Hulihan M, et al: Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2004, 364: 1167-1169. 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17103-1.
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, et al: alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science. 2003, 302: 841-10.1126/science.1090278.
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, et al: Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997, 276: 2045-2047. 10.1126/science.276.5321.2045.
Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kosel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O: Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet. 1998, 18: 106-108. 10.1038/ng0298-106.
Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gomez-Esteban JC, Lezcano E, Ros R, Ampuero I, Vidal L, Hoenicka J, Rodriguez O, Atares B, et al: The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol. 2004, 55: 164-173. 10.1002/ana.10795.
Narhi L, Wood SJ, Steavenson S, Jiang Y, Wu GM, Anafi D, Kaufman SA, Martin F, Sitney K, Denis P, et al: Both familial Parkinson's disease mutations accelerate alpha-synuclein aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1999, 274: 9843-9846. 10.1074/jbc.274.14.9843.
Gallardo G, Schluter OM, Sudhof TC: A molecular pathway of neurodegeneration linking alpha-synuclein to ApoE and Abeta peptides. Nat Neurosci. 2008, 11: 301-308. 10.1038/nn2058.
Lee MK, Stirling W, Xu Y, Xu X, Qui D, Mandir AS, Dawson TM, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL: Human alpha-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson's disease-linked Ala-53 --> Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with alpha-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002, 99: 8968-8973. 10.1073/pnas.132197599.
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Takeda A, Sagara Y, Sisk A, Mucke L: Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science. 2000, 287: 1265-1269. 10.1126/science.287.5456.1265.
Richfield EK, Thiruchelvam MJ, Cory-Slechta DA, Wuertzer C, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG, Di Monte DA, Federoff HJ: Behavioral and neurochemical effects of wild-type and mutated human alpha-synuclein in transgenic mice. Exp Neurol. 2002, 175: 35-48. 10.1006/exnr.2002.7882.
Lin X, Parisiadou L, Gu XL, Wang L, Shim H, Sun L, **e C, Long CX, Yang WJ, Ding J, et al: Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 regulates the progression of neuropathology induced by Parkinson's-disease-related mutant alpha-synuclein. Neuron. 2009, 64: 807-827. 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.11.006.
Beyer K, Ariza A: Protein aggregation mechanisms in synucleinopathies: commonalities and differences. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007, 66: 965-974. 10.1097/nen.0b013e3181587d64.
Shults CW, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Adame A, Mante M, Larrea G, Hashimoto M, Song D, Iwatsubo T, Tsuboi K, Masliah E: Neurological and neurodegenerative alterations in a transgenic mouse model expressing human alpha-synuclein under oligodendrocyte promoter: implications for multiple system atrophy. J Neurosci. 2005, 25: 10689-10699. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3527-05.2005.
Yazawa I, Giasson BI, Sasaki R, Zhang B, Joyce S, Uryu K, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM: Mouse model of multiple system atrophy alpha-synuclein expression in oligodendrocytes causes glial and neuronal degeneration. Neuron. 2005, 45: 847-859. 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.01.032.
Braak H, Sastre M, Del Tredici K: Development of alpha-synuclein immunoreactive astrocytes in the forebrain parallels stages of intraneuronal pathology in sporadic Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114: 231-241. 10.1007/s00401-007-0244-3.
Terada S, Ishizu H, Yokota O, Tsuchiya K, Nakashima H, Ishihara T, Fujita D, Ueda K, Ikeda K, Kuroda S: Glial involvement in diffuse Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 105: 163-169.
Wakabayashi K, Hayashi S, Yoshimoto M, Kudo H, Takahashi H: NACP/alpha-synuclein-positive filamentous inclusions in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes of Parkinson's disease brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2000, 99: 14-20. 10.1007/PL00007400.
Stefanova N, Klimaschewski L, Poewe W, Wenning GK, Reindl M: Glial cell death induced by overexpression of alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci Res. 2001, 65: 432-438. 10.1002/jnr.1171.
McGeer PL, McGeer EG: Glial reactions in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2008, 23: 474-483. 10.1002/mds.21751.
Iwai A, Masliah E, Yoshimoto M, Ge N, Flanagan L, de Silva HA, Kittel A, Saitoh T: The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer's disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron. 1995, 14: 467-475. 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90302-X.
Pascual O, Casper KB, Kubera C, Zhang J, Revilla-Sanchez R, Sul JY, Takano H, Moss SJ, McCarthy K, Haydon PG: Astrocytic purinergic signaling coordinates synaptic networks. Science. 2005, 310: 113-116. 10.1126/science.1116916.
Vaccarino FM, Fagel DM, Ganat Y, Maragnoli ME, Ment LR, Ohkubo Y, Schwartz ML, Silbereis J, Smith KM: Astroglial cells in development, regeneration, and repair. Neuroscientist. 2007, 13: 173-185. 10.1177/1073858406298336.
Smith KM, Ohkubo Y, Maragnoli ME, Rasin MR, Schwartz ML, Sestan N, Vaccarino FM: Midline radial glia translocation and corpus callosum formation require FGF signaling. Nat Neurosci. 2006, 9: 787-797. 10.1038/nn1705.
Wang DD, Bordey A: The astrocyte odyssey. Prog Neurobiol. 2008, 86: 342-367.
Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E: Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006, 7: 41-53. 10.1038/nrn1824.
Zlokovic BV: The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron. 2008, 57: 178-201. 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.003.
Warth A, Kroger S, Wolburg H: Redistribution of aquaporin-4 in human glioblastoma correlates with loss of agrin immunoreactivity from brain capillary basal laminae. Acta Neuropathol. 2004, 107: 311-318. 10.1007/s00401-003-0812-0.
Lauriat TL, McInnes LA: EAAT2 regulation and splicing: relevance to psychiatric and neurological disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2007, 12: 1065-1078. 10.1038/sj.mp.4002065.
Farina C, Aloisi F, Meinl E: Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends in Immunology. 2007, 28: 138-145. 10.1016/j.it.2007.01.005.
Tansey MG, Goldberg MS: Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease: Its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiol Dis. 2009, 37 (3): 510-8. 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.11.004.
Choi SH, Aid S, Bosetti F: The distinct roles of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 in neuroinflammation: implications for translational research. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009, 30: 174-181. 10.1016/j.tips.2009.01.002.
Choi SH, Langenbach R, Bosetti F: Genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition of cyclooxygenase-1 attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response and brain injury. Faseb J. 2008, 22: 1491-1501. 10.1096/fj.07-9411com.
Li W, West N, Colla E, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Marsh L, Dawson TM, Jakala P, Hartmann T, Price DL, Lee MK: Aggregation promoting C-terminal truncation of alpha-synuclein is a normal cellular process and is enhanced by the familial Parkinson's disease-linked mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005, 102: 2162-2167. 10.1073/pnas.0406976102.
Mori F, Tanji K, Yoshimoto M, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K: Demonstration of alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in neuronal and glial cytoplasm in normal human brain tissue using proteinase K and formic acid pretreatment. Exp Neurol. 2002, 176: 98-104. 10.1006/exnr.2002.7929.
Putten van der H, Wiederhold KH, Probst A, Barbieri S, Mistl C, Danner S, Kauffmann S, Hofele K, Spooren WP, Ruegg MA, et al: Neuropathology in mice expressing human alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci. 2000, 20: 6021-6029.
Kahle PJ, Neumann M, Ozmen L, Muller V, Odoy S, Okamoto N, Jacobsen H, Iwatsubo T, Trojanowski JQ, Takahashi H, et al: Selective insolubility of alpha-synuclein in human Lewy body diseases is recapitulated in a transgenic mouse model. Am J Pathol. 2001, 159: 2215-2225.
Wootz H, Weber E, Korhonen L, Lindholm D: Altered distribution and levels of cathepsinD and cystatins in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis transgenic mice: possible roles in motor neuron survival. Neuroscience. 2006, 143: 419-430. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.07.048.
Qiao L, Hamamichi S, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA, Yacoubian TA, Wilson S, **e ZL, Speake LD, Parks R, Crabtree D, et al: Lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D protects against alpha-synuclein aggregation and toxicity. Mol Brain. 2008, 1: 17-10.1186/1756-6606-1-17.
Cullen V, Lindfors M, Ng J, Paetau A, Swinton E, Kolodziej P, Boston H, Saftig P, Woulfe J, Feany MB, et al: Cathepsin D expression level affects alpha-synuclein processing, aggregation, and toxicity in vivo. Mol Brain. 2009, 2: 5-10.1186/1756-6606-2-5.
Nafia I, Re DB, Masmejean F, Melon C, Kachidian P, Kerkerian-Le Goff L, Nieoullon A, Had-Aissouni L: Preferential vulnerability of mesencephalic dopamine neurons to glutamate transporter dysfunction. J Neurochem. 2008, 105: 484-496. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05146.x.
Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ: Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005, 5: 629-640. 10.1038/nri1664.
Hanisch UK, Kettenmann H: Microglia: active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci. 2007, 10: 1387-1394. 10.1038/nn1997.
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS: Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007, 8: 57-69. 10.1038/nrn2038.
Lawson LJ, Perry VH, Dri P, Gordon S: Heterogeneity in the distribution and morphology of microglia in the normal adult mouse brain. Neuroscience. 1990, 39: 151-170. 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90229-W.
Kim WG, Mohney RP, Wilson B, Jeohn GH, Liu B, Hong JS: Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci. 2000, 20: 6309-6316.
Qin L, Wu X, Block ML, Liu Y, Breese GR, Hong JS, Knapp DJ, Crews FT: Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia. 2007, 55: 453-462. 10.1002/glia.20467.
Saijo K, Winner B, Carson CT, Collier JG, Boyer L, Rosenfeld MG, Gage FH, Glass CK: A Nurr1/CoREST pathway in microglia and astrocytes protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-induced death. Cell. 2009, 137: 47-59. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.038.
Ilieva H, Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW: Non-cell autonomous toxicity in neurodegenerative disorders: ALS and beyond. J Cell Biol. 2009, 187: 761-772. 10.1083/jcb.200908164.
Yamanaka K, Chun SJ, Boillee S, Fujimori-Tonou N, Yamashita H, Gutmann DH, Takahashi R, Misawa H, Cleveland DW: Astrocytes as determinants of disease progression in inherited amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Neurosci. 2008, 11: 251-253. 10.1038/nn2047.
Bradford J, Shin JY, Roberts M, Wang CE, Li XJ, Li S: Expression of mutant huntingtin in mouse brain astrocytes causes age-dependent neurological symptoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009, 106: 22480-22485. 10.1073/pnas.0911503106.
Chandran JS, Lin X, Zapata A, Hoke A, Shimoji M, Moore SO, Galloway MP, Laird FM, Wong PC, Price DL, et al: Progressive behavioral deficits in DJ-1-deficient mice are associated with normal nigrostriatal function. Neurobiol Dis. 2008, 29: 505-514. 10.1016/j.nbd.2007.11.011.
Lai C, Lin X, Chandran J, Shim H, Yang WJ, Cai H: The G59S mutation in p150(glued) causes dysfunction of dynactin in mice. J Neurosci. 2007, 27: 13982-13990. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4226-07.2007.
Cai H, Lin X, **e C, Laird FM, Lai C, Wen H, Chiang HC, Shim H, Farah MH, Hoke A, et al: Loss of ALS2 function is insufficient to trigger motor neuron degeneration in knock-out mice but predisposes neurons to oxidative stress. J Neurosci. 2005, 25: 7567-7574. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1645-05.2005.
Mann SA, Versmold B, Marx R, Stahlhofen S, Dietzel ID, Heumann R, Berger R: Corticosteroids reverse cytokine-induced block of survival and differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells from rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2008, 5: 39-10.1186/1742-2094-5-39.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the intramural research programs of National Institute on Aging at the National Institutes of Health (H.C., Z01-AG000959-05). We thank Dr. **ao-Jiang Li for helpful suggestions. We thank the NIH Fellows Editorial Board for manuscript editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
XLG and HC designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. XLG, CXL, CSX and LS performed the experiments. XL provided some materials. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
13041_2010_72_MOESM1_ESM.TIFF
Additional file 1: PD-related human A53T α-synuclein was selectively expressed in the astrocytes of A53T transgenic mice. (A) Western blot analysis reveals the expression level of exogenous α-syn in asymptomatic A53T mice. Protein extracts (5 μg) from the hippocampus were diluted by 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 64-fold and equal volume of diluted samples was subjected to Western blot with a human/mouse specific α-syn antibody, α-syn (C20). (B-E) To determine the expression pattern of tTA under the GFAP promoter, GFAP-tTA mice were crossbred with tetO-HIST1H2BJ/GFP to yield GFAP-tTA/tetO-GFP mice. HIST1H2BJ/GFP is located in the nucleus. Brain sections of GFAP-tTA/tetO-GFP mice were stained with NeuN (neuronal marker, B), Iba1 (microglia marker, C), OSP (oligodentrocyte specific protein, D), and GFAP (marker for astrocytes, E). Scale bars: 20 μm. (TIFF 8 MB)
13041_2010_72_MOESM2_ESM.TIFF
Additional file 2: Progressive reduction of body weight and spontaneous locomotor activities in A53T mice. (A) Representative photos of A53T mice and age-matched littermate controls under anesthetized condition. (B) Bar graph shows the body weight of A53T mice and control littermates at 1 and 2 months of age. ***p < 0.001. (C-D) Bar graphs depict the fine movement (C) and rearing activities (D) of A53T mice and control littermates at 1 and 2 months of age. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. (E) Bar graph displays results from Rotarod test of A53T mice and littermate controls. Latency to fall was recorded at 1 and 2 months of age. (F) Body weight curves of A53T mice and littermates from 1 to 3 months of age. The body weight of A53T mice and littermates was measured twice a week. Concurrent with the abnormal motor behavior symptoms, the body weight of A53T mice was dropped continuously. Once the mice were unable to feed themselves (usually, body weight was dropped by 30%), they were sacrificed for histology and biochemistry study. (TIFF 5 MB)
13041_2010_72_MOESM6_ESM.TIFF
Additional file 6: Behavior analysis of A53T mice treated with doxycycline (DOX) from embryonic stages to postnatal day 21 (P21). (A) Diagram outlines the treatment of A53T mice with DOX. DOX-containing mouse feed (200 mg/kg, Bioserv, Frenchtown, NJ) was provided to breeding pairs and young pups till the pups were weaned at postnatal day 21. The new weanlings were then switched to regular feed. (B) Dot plot shows the change of body weight of A53T mice and littermate controls after the stop of DOX treatment at P21. (C-E) Dot plots show the results of Open-field test of A53T and control mice after the stop of DOX treatment at P21. The spontaneous ambulatory (C), fine movement (D), and rearing activities (E) were quantified. (F) Dot plot depicts the performance of A53T and control mice on Rotarod test after the stop of DOX-treatment at P21. (G) Line graph shows the onset of paralysis of A53T mice after the stop of DOX-treatment at P21. (TIFF 8 MB)
13041_2010_72_MOESM7_ESM.TIFF
Additional file 7: Increase of GFAP and Iba1 expression in A53T mice. (A-B) Bar graph shows quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Gfap and Iba1 transcripts expressed in the brainstem and cortex of A53T mice and age-matched GFAP-tTA mice (n = 3 per genotype). BS, brainstem; Ctx, cortex; 1 M, 1 month of age; 2.5 M, 2.5 months of age; A53T*, symptomatic A53T mice. *p < 0.05, and ***p < 0.001. (C) Western blots analysis of GFAP and Iba1 protein expression in the brainstem of A53T mice and littermate controls. (D-E) Bar graphs show the quantification GFAP (D) and Iba1 (E) expression in the brainstem, spinal cord, and cerebral cortex (n = 3 per genotype) of A53T and control mice. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. (TIFF 2 MB)
13041_2010_72_MOESM8_ESM.TIFF
Additional file 8: Activated microglia surrounded dopaminergic and spinal motor neurons. (A-F) Representative images show double immunofluorescent labeling of Iba1 (green) with TH (red) and SMI32 (red) in the SNpc (A-C) and spinal cord (SC) (D-F) of symptomatic A53T mice. Scale bar: 20 μm. (TIFF 2 MB)
13041_2010_72_MOESM9_ESM.TIFF
Additional file 9: Quantification of cortical and striatal neurons remained in symptomatic A53T mice. (A), Bar graph depicts the numbers of TH-positive dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and ventral tegmentum area (VTA) in nTg and A53T mice at 1 month of age. N = 3 per genotype.(B), Bar graph depicts the numbers of NeuN-positive neurons in the cerebral cortex and striatum of symptomatic A53T mice and age-matched nTg littermates estimated by unbiased stereological methods. N = 3 per genotype. (TIFF 4 MB)
13041_2010_72_MOESM10_ESM.TIFF
Additional file 10: Reactive astrocytes in the brainstem and substantia nigra pars compacta of A53T lower expresser mice ( A53T-A8 ). (A, C, E) Representative images of GFAP (red) and Iba1 (green) staining show mild astrocytosis in the brainstem and SNpc but not in the cerebral cortex of 12-month old A53T-A8 mice compared to littermate nTg mice. (B, D, F) High magnification views of (A, C, E) reveal the morphology of astrocyte and microglia in control nTg and A53T mice at 12 month of age. Scale bars: 50 μm(A, C, E); 20 μm (B, D, F). (TIFF 10 MB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Additional file 3: The TreadScan Gait Analysis System (Clever Sys, Reston, VA) was used to record the gait information of A53T mice. Each mouse was placed on the belt of treadmill unit. The movement of each paw was recorded with the treadmill running at 17 cm/s, 5 cm/s and 2 cm/s, respectively [54]. A representative control nTg mouse was running on the treadmill with the speed set at 17 cm/s. The later part of movie was replayed four times slower than the first part to better visualize the placement of each paw on the belt. (MOV 2 MB)
Additional file 4: Symptomatic A53T mice were only able to run at the speed of 5 cm/s. The first mouse showed paralysis in both forelimbs. The second mouse displayed paralysis in the left forelimb and in both hindlimbs. (MOV 2 MB)
Additional file 5: A53T mice developed rapid progression of paralysis in four limbs. This mouse was able to run at the speed of 5 cm/s on postnatal day 65 (P65), but 2 cm/s on P70. The right forelimb started to show paralysis on P71 and then the left forelimb was affected on P73. (MOV 3 MB)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, XL., Long, CX., Sun, L. et al. Astrocytic expression of Parkinson's disease-related A53T α-synuclein causes neurodegeneration in mice. Mol Brain 3, 12 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-3-12
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-3-12