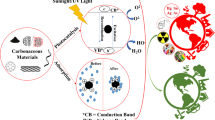
Abstract
Air pollution, owing to gaseous pollutants, especially NOx, VOCs (toluene), acidic gas (H2S), and elemental mercury (Hg0), and the resulting climate issues have become major concerns. Carbon-based catalysts play a key role in removing toxic gases through selective catalytic reduction (SCR), oxidation, and adsorption processes. Catalyst selection has a crucial effect on the final toxic gas removal performance of catalyst. Herein, strategies for modifying carbon-based catalysts through physical or chemical treatment/activation, metal oxide do**, and heteroatom do** are systematically reviewed. In addition, the effects of the carbonization temperature, pore structure, heteroatom dopants, and oxidizing agents on the surface area, pore structure, and catalytic effects of carbon-based catalysts are analyzed and discussed. Finally, the further direction and need for develo** carbon-based catalysts for environmental remediation is prospected.
Highlights
-
Carbon-based catalysts for environmental remediation are discussed.
-
Modification strategies for carbon-based catalysts are provided in detail.
-
Various air pollutant-removal performances of the modified catalyst are briefed.
-
Challenges and future prospects of carbon catalysts are presented.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors have included all the relevant data and the source of freely available data in the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Activated catalyst
- C/SAC-2:
-
Chemically activated catalyst
- Co/SAC-2:
-
Co-activated catalyst
- NOAC:
-
N- and O-doped AC
- NHPC:
-
N-doped hierarchical porous carbon
- NPC:
-
N-doped porous carbon
- NSDG-10:
-
N- and S-doped nanoporous carbon
- PBC900 :
-
P-doped biochar
- PAN:
-
Polyacrylonitrile
- P/SAC:
-
Physically activated catalyst
- SAC:
-
Sargassum-Based carbon
- SCR:
-
Selective catalytic reduction
- SMC-900:
-
S-doped mesoporous carbon
- SSA:
-
Specific surface area
- WS:
-
Wheat straw
- NG:
-
Nitrogen doped graphene
- ORR:
-
Oxygen reductive reaction
References
Ahmadi R, Alivand MS, Haj Mohammad Hossein Tehrani N, Ardjmand M, Rashidi A, Rafizadeh M, Seif A, Mollakazemi F, Noorpoor Z, Rudd J (2021) Preparation of fiber-like nanoporous carbon from jute thread waste for superior CO2 and H2S removal from natural gas: experimental and DFT study. Chem Eng J 415:129076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129076
Anthonysamy SBI, Afandi SB, Khavarian M, Mohamed ARB (2018) A review of carbon-based and non-carbon-based catalyst supports for the selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:740–761. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.68
Bai X, Han J, Niu X, Guan J (2023a) The d-orbital regulation of isolated manganese sites for enhanced oxygen evolution. Nano Res 16:10796–10802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5859-8
Bai X, Wang Y, Han J, Niu X, Guan J (2023b) Engineering the electronic structure of isolated manganese sites to improve the oxygen reduction, Zn-air battery and fuel cell performances. Appl Catal B Environ 337:122966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.122966
Balsamo M, Cimino S, de Falco G, Erto A, Lisi L (2016) ZnO-CuO supported on activated carbon for H2S removal at room temperature. Chem Eng J 304:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.085
Bazan-Wozniak A, Nowicki P, Pietrzak R (2017) The influence of activation procedure on the physicochemical and sorption properties of activated carbons prepared from pistachio nutshells for removal of NO2 /H2S gases and dyes. J Clean Prod 152:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.114
Chen W, Zhang G, Li D, Ma S, Wang B, Jiang X (2020) Preparation of nitrogen-doped porous carbon from waste polyurethane foam by hydrothermal carbonization for H2S adsorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:7447–7456. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c00498
Chen L, Yuan J, Li T, Jiang X, Ma S, Cen W, Jiang W (2021) A regenerable N-rich hierarchical porous carbon synthesized from waste biomass for H2S removal at room temperature. Sci Total Environ 768:144452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144452
Chen L, Jiang X, Chen W, Dai Z, Wu J, Ma S, Jiang W (2022) H2O2-assisted self-template synthesis of N-doped biochar with interconnected mesopore for efficient H2S removal. Sep Purif Technol 297:121410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121410
Cheng T, Bian Y, Li J, Ma X, Yang L, Zhou L, Wu H (2023) Nitrogen-doped porous biochar for selective adsorption of toluene under humid conditions. Fuel 334:126452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126452
Chiang Y-C, Chiang P-C, Huang C-P (2001) Effects of pore structure and temperature on VOC adsorption on activated carbon. Carbon 39:523–534
Cho S-H, Lee S, Kim Y, Song H, Lee J, Tsang YF, Chen W-H, Park Y-K, Lee D-J, Jung S, Kwon EE (2023) Applications of agricultural residue biochars to removal of toxic gases emitted from chemical plants: A review. Sci Total Environ 868:161655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161655
Cui S, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Pan J (2022) Preparation of copper-based biochar adsorbent with outstanding H2S adsorption capacity and study on H2S removal. J Energy Inst 105:481–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2022.11.004
Damma D, Ettireddy P, Reddy B, Smirniotis P (2019) A review of low temperature NH3-SCR for removal of NOx. Catalysts 9:349. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9040349
de Falco G, Montagnaro F, Balsamo M, Erto A, Deorsola FA, Lisi L, Cimino S (2018) Synergic effect of Zn and Cu oxides dispersed on activated carbon during reactive adsorption of H2S at room temperature. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 257:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.08.025
Dou Z, Wang Y, Liu Y, Zhao Y, Huang R (2023) Enhanced adsorption of gaseous mercury on activated carbon by a novel clean modification method. Sep Purif Technol 308:122885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122885
Du Y, Chen H, Xu X, Wang C, Zhou F, Zeng Z, Zhang W, Li L (2020) Surface modification of biomass derived toluene adsorbent: hierarchically porous characterization and heteroatom doped effect. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 293:109831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109831
Fang H, Zhao J, Fang Y, Huang J, Wang Y (2013) Selective oxidation of hydrogen sulfide to sulfur over activated carbon-supported metal oxides. Fuel 108:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.05.030
Fidalgo B, Menéndez JÁ (2011) Carbon materials as catalysts for decomposition and CO2 reforming of methane: a review. Chin J Catal 32:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(10)60166-0
Gao L, Li C, Zhang J, Du X, Li S, Zeng J, Yi Y, Zeng G (2018) Simultaneous removal of NO and Hg0 from simulated flue gas over CoOx -CeO2 loaded biomass activated carbon derived from maize straw at low temperatures. Chem Eng J 342:339–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.100
Gao L, Li C, Li S, Zhang W, Du X, Huang L, Zhu Y, Zhai Y, Zeng G (2019) Superior performance and resistance to SO2 and H2O over CoOx-modified MnOx/biomass activated carbons for simultaneous Hg0 and NO removal. Chem Eng J 371:781–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.104
Gao L, Yi L, **e D, Wang H, Li C, Li L, Liu Y, **e J, Zhou Y, Liu Y (2023) Insight into the design and construction of Cr substituted Co-based columnar activated coke catalysts for effective and reliable removal of methylbenzene and Hg0 concurrently. Fuel 334:126732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126732
Guo J, Luo Y, Lua AC, Chi R, Chen Y, Bao X, **ang S (2007) Adsorption of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) by activated carbons derived from oil-palm shell. Carbon 45:330–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2006.09.016
Guo F, Huang X, Chen Z, Sun H, Shi W (2020) Investigation of visible-light-driven photocatalytic tetracycline degradation via carbon dots modified porous ZnSnO3 cubes: Mechanism and degradation pathway. Sep Purif Technol 253:117518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117518
Gupta VK, Saleh TA (2013) Sorption of pollutants by porous carbon, carbon nanotubes and fullerene- an overview. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2828–2843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1524-1
Huang B, Huang R, ** D, Ye D (2007) Low temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over carbon nanotubes supported vanadium oxides. Catal Today 126:279–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2007.06.002
Huang X, Tang M, Li H, Wang L, Lu S (2023) Adsorption of multicomponent VOCs on various biomass-derived hierarchical porous carbon: a study on adsorption mechanism and competitive effect. Chemosphere 313:137513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137513
Jia X et al (2022) Lotus leaves-derived MnOx/biochar as an efficient catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR removal of NOx: effects of modification methods of biochar. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 97:3100–3110
Jiang L, Liu Q, Ran G, Kong M, Ren S, Yang J, Li J (2019) V2O5-modified Mn-Ce/AC catalyst with high SO2 tolerance for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO. Chem Eng J 370:810–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.225
** B, Li J, Wang Y, Yang Z, Yao X, Sun W, Lu Y, Zhu X, Zhang T (2022a) Nitrogen do** and porous tuning carbon derived from waste biomass boosting for toluene capture: experimental study and density functional theory simulation. Chem Eng J Adv 10:100276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2022.100276
** Y, Ding S, Li P, Wang X (2022b) Coordination of thin-film nanofibrous composite dialysis membrane and reduced graphene oxide aerogel adsorbents for elimination of indoxyl sulfate. Chin J Chem Eng 49:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2022.01.024
Kan X, Chen X, Chen W, Mi J, Zhang J-Y, Liu F, Zheng A, Huang K, Shen L, Au C, Jiang L (2019) Nitrogen-decorated, ordered mesoporous carbon spheres as high-efficient catalysts for selective capture and oxidation of H2S. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:7609–7618. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b05852
Kim et al (2018) Development of high performance catalytic filter of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 supported-SiC for NOx reduction. Powder Technol 327:282–290
Ku BJ, Lee JK, Park D, Rhee H-K (1994) Treatment of activated carbon to enhance catalytic activity for reduction of nitric oxide with ammonia. Ind Eng Chem Res 33:2868–2874. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00035a042
Lei B, Liu B, Zhang H, Yan L, **e H, Zhou G (2020) CuO-modified activated carbon for the improvement of toluene removal in air. J Environ Sci 88:122–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.07.001
Lei G, Fan Z, Hou Y, Liu F, Wang S, Shen L, Zhan Y, Jiang L (2023) Facile template-free synthesis of 3D cluster-like nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon as metal-free catalyst for selective oxidation of H2S. J Environ Chem Eng 11:109095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.109095
Li Q, Hou Y, Han X, Huang Z, Guo Q, Sun D, Liu J (2014) Selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over activated carbon impregnated with melamine at low temperature. J Fuel Chem Technol 42:487–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5813(14)60025-6
Li G, Shen B, Wang Y, Yue S, ** Y, An M, Ren K (2015a) Comparative study of element mercury removal by three bio-chars from various solid wastes. Fuel 145:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.12.083
Li W, Tan S, Shi Y, Li S (2015b) Utilization of sargassum based activated carbon as a potential waste derived catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxides. Fuel 160:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.07.045
Li B, **ong H, **ao Y, Hu J, Zhang X, Li L, Wang R (2020a) Efficient toluene adsorption on metal salt-activated porous carbons derived from low-cost biomass: a discussion of mechanism. ACS Omega 5:13196–13206. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c01230
Li J-R, Wang F-K, He C, Huang C, **ao H (2020b) Catalytic total oxidation of toluene over carbon-supported Cu Co oxide catalysts derived from Cu-based metal organic framework. Powder Technol 363:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.12.060
Li Q, Hou Y, Wang J, Liu Y, ** of carbon for NH3-SCR reaction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:11308–11316. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c03193
Li Q, Hou Y, ** in activated carbon for selective catalytic reduction of NOX with NH3. Sci Total Environ 740:140158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140158
Li W, ** S, Zhang R, Wei Y, Wang J, Yang S, Wang H, Yang M, Liu Y, Qiao W, Ling L, ** M (2020e) Insights into the promotion role of phosphorus do** on carbon as a metal-free catalyst for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. RSC Adv 10:12908–12919. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA01654C
Li Y, Liu Y, Yang W, Liu L, Pan J (2021) Adsorption of elemental mercury in flue gas using biomass porous carbons modified by microwave/hydrogen peroxide. Fuel 291:120152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120152
Li D, Yang J, Zhao Y, Yuan H, Chen Y (2022a) Ultra-highly porous carbon from Wasted soybean residue with tailored porosity and doped structure as renewable multi-purpose absorbent for efficient CO2, toluene and water vapor capture. J Clean Prod 337:130283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130283
Li Q, Liang M, Han X, Hou Y, Huang Z (2022b) Insight into the enhancing activity and stability of Ce modified V2O5/AC during cyclic desulfurization-regeneration-denitrification. J Hazard Mater 424:127397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127397
Li Y, Yu J, Liu Y, Huang R, Wang Z, Zhao Y (2022c) A review on removal of mercury from flue gas utilizing existing air pollutant control devices (APCDs). J Hazard Mater 427:128132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.128132
Li S, Huang Y, Zhu H, Long J, **ao L, Li P, Zhao L, Zhang J (2023a) Dual improvement in acid and redox properties of the FeO/OAC catalyst via APS oxygen-functionalization: high low-temperature NH3-SCR activity, SO2 and H2O tolerance. Fuel 341:127716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127716
Li X, Sun F, Qu Z, Zhu X, Gao J, Zhao G, Zhang L (2023b) Insight into synergistic effects of oxygen and nitrogen dual-dopants in carbon catalysts on selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: a combined computational and experimental verification. Chem Eng J 454:140098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140098
Li Y, Wang Y, Dou Z, Liu Y (2023c) Removal of gaseous Hg0 using biomass porous carbons modified by an environmental-friendly photochemical technique. Chem Eng J 457:141152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.141152
Liang S, Mi J, Liu F, Zheng Y, ** ordered mesoporous carbons with versatile base N sites via a calcination induced self-assembly route. Chem Eng Sci 221:115714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2020.115714
Lin Y, Li Y, Xu Z, **ong J, Zhu T (2018) Transformation of functional groups in the reduction of NO with NH3 over nitrogen-enriched activated carbons. Fuel 223:312–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.01.092
Liu Z, Adewuyi YG, Shi S, Chen H, Li Y, Liu D, Liu Y (2019) Removal of gaseous Hg0 using novel seaweed biomass-based activated carbon. Chem Eng J 366:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.025
Liu L, Wang B, Yao X, Yang L, Jiang W, Jiang X (2021) Highly efficient MnOx/biochar catalysts obtained by air oxidation for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO. Fuel 283:119336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119336
Liu S, Feng X, Liu Z, Zhao W, Li Y, Zhang J (2023a) Nitrogen do** in porous biochar from cotton stalk with H3PO4 activation for reduction of NOx with NH3-SCR at low temperatures: Characteristics and catalytic activity analysis. Fuel 332:126256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126256
Liu Y, Cui S, Wu P, Liu L, Dou Z, Wang Y (2023b) Removal of gaseous elemental mercury using corn stalk biochars modified by a green oxidation technology. Fuel Process Technol 242:107621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2022.107621
Ma Z, Zhang H, Yang Z, Ji G, Yu B, Liu X, Liu Z (2016) Mesoporous nitrogen-doped carbons with high nitrogen contents and ultrahigh surface areas: synthesis and applications in catalysis. Green Chem 18:1976–1982. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC01920F
Ma Q, Chen W, ** Z, Chen L, Zhou Q, Jiang X (2021) One-step synthesis of microporous nitrogen-doped biochar for efficient removal of CO2 and H2S. Fuel 289:119932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.119932
Mohammed J, Nasri NS, Ahmad Zaini MA, Hamza UD, Ani FN (2015) Adsorption of benzene and toluene onto KOH activated coconut shell based carbon treated with NH3. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 102:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.02.012
Murindababisha D, Yusuf A, Sun Y, Wang C, Ren Y, Lv J, **ao H, Chen GZ, He J (2021) Current progress on catalytic oxidation of toluene: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:62030–62060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16492-9
Nicolae SA, Louis-Therese J, Gaspard S, Szilágyi PÁ, Titirici MM (2022) Biomass derived carbon materials: synthesis and application towards CO2 and H2S adsorption. Nano Sel 3:165–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/nano.202100099
Pan J, Wang L, Shi Y, Li L, Xu Z, Sun H, Guo F, Shi W (2022) Construction of nanodiamonds/UiO-66-NH2 heterojunction for boosted visible-light photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics. Sep Purif Technol 284:120270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120270
Panwar NL, Pawar A (2022) Influence of activation conditions on the physicochemical properties of activated biochar: a review. Biomass Convers Biorefin 12:925–947. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00870-3
Rubel AM, Stencel JM (1997) The effect of low-concentration SO2 on the adsorption of NO from gas over activated carbon. Fuel 76:521–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-2361(96)00221-9
Shi W, Shi C, Sun W, Liu Y, Guo F, Lin X (2021) Dual enhancement of photooxidation and photoreduction activity by coating CdS nanoparticles on lignin-based biomass carbon with irregular flower-like structure. J Mater Sci 56:19452–19465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06589-4
Shi R, Liu K, Liu B, Chen H, Xu X, Ren Y, Qiu J, Zeng Z, Li L (2022a) New insight into toluene adsorption mechanism of melamine urea-formaldehyde resin based porous carbon: experiment and theory calculation. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 632:127600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127600
Shi W, Hao C, Fu Y, Guo F, Tang Y, Yan X (2022b) Enhancement of synergistic effect photocatalytic/persulfate activation for degradation of antibiotics by the combination of photo-induced electrons and carbon dots. Chem Eng J 433:133741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133741
Shi W, Liu Y, Sun W, Hong Y, Li X, Lin X, Guo F, Shi J (2022c) Improvement of synergistic effect photocatalytic/peroxymonosulfate activation for degradation of amoxicillin using carbon dots anchored on rod-like CoFe2O4. Chin J Chem Eng 52:136–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2021.10.030
Shi W, Hao C, Shi Y, Guo F, Tang Y (2023) Effect of different carbon dots positions on the transfer of photo-induced charges in type I heterojunction for significantly enhanced photocatalytic activity. Sep Purif Technol 304:122337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122337
Song G, Deng R, Yao Z, Chen H, Romero C, Lowe T, Driscoll G, Kreglow B, Schobert H, Baltrusaitis J (2020) Anthracite coal-based activated carbon for elemental Hg adsorption in simulated flue gas: preparation and evaluation. Fuel 275:117921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117921
Su L, Chen M, Zhuo G, Ji R, Wang S, Zhang L, Zhang M, Li H (2021) Comparison of biochar materials derived from coconut husks and various types of livestock manure, and their potential for use in removal of H2S from biogas. Sustainability 13:6262. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116262
Tang T, Wang Z, Guan J (2022) Electronic structure regulation of single-site M-N-C electrocatalysts for carbon dioxide reduction. Acta Phys Chim Sin 39:2208033. https://doi.org/10.3866/PKU.WHXB202208033
Tang T, Duan Z, Baimanov D, Bai X, Liu X, Wang L, Wang Z, Guan J (2023a) Synergy between isolated Fe and Co sites accelerates oxygen evolution. Nano Res 16:2218–2223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5001-3
Tang T, Wang Y, Han J, Zhang Q, Bai X, Niu X, Wang Z, Guan J (2023b) Dual-atom Co-Fe catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chin J Catal 46:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(22)64189-5
Tang T, Wang Z, Guan J (2023c) Structural optimization of carbon-based diatomic catalysts towards advanced electrocatalysis. Coord Chem Rev 492:215288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215288
Tian W et al (2001) Heteroatom (N or N-S)-do** induced layered and honeycomb microstructures of porous carbons for CO2 capture and energy applications. Adv Funct Mater 26(47):8651–8661
Tuerhong T, Kuerban Z (2022) Preparation and characterization of cattle manure-based activated carbon for hydrogen sulfide removal at room temperature. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107177
Vakili F, Rashidi A, Taghavi L, Mansouri N (2021) Single-step synthesis of N, S co-doped waste-derived nanoporous carbon sorbent for mercury vapor removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:17265–17274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12075-2
Wang M-X, Huang Z-H, Shimohara T, Kang F, Liang K (2011) NO removal by electrospun porous carbon nanofibers at room temperature. Chem Eng J 170:505–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.01.017
Wang J, Yan Z, Liu L, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Wang X (2014) In situ DRIFTS investigation on the SCR of NO with NH3 over V2O5 catalyst supported by activated semi-coke. Appl Surf Sci 313:660–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.06.043
Wang M, Guo Z, Huang Z, Kang F (2016) Preparation of porous carbon nanofibers with controllable pore structures for low-concentration NO removal at room temperature. New Carbon Mater 31:277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5805(16)60013-6
Wang T, Wu J, Zhang Y, Liu J, Sui Z, Zhang H, Chen W-Y, Norris P, Pan W-P (2018a) Increasing the chlorine active sites in the micropores of biochar for improved mercury adsorption. Fuel 229:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.05.028
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Shen Y, Zhu S (2018b) Pyridinic N: a special group for enhancing direct decomposition reaction of NO over N-doped porous carbon. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 265:98–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.02.006
Wang A, Chen W, Liu S, Lin W, Tian C (2023a) Layered porous carbon material derived from food residues and its application for elemental mercury adsorption in flue gas. Fuel 335:126876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126876
Wang H, Wu F, Wu L, Guan J, Niu X (2023b) Nanozyme colorimetric sensor array based on monatomic cobalt for the discrimination of sulfur-containing metal salts. J Hazard Mater 456:131643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131643
Wu J, Chen W, Chen L, Jiang X (2022) Super-high N-do** promoted formation of sulfur radicals for continuous catalytic oxidation of H2S over biomass derived activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 424:127648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127648
Xu X, Guo Y, Shi R, Chen H, Du Y, Liu B, Zeng Z, Yin Z, Li L (2021) Natural Honeycomb-like structure cork carbon with hierarchical micro-mesopores and N-containing functional groups for VOCs adsorption. Appl Surf Sci 565:150550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150550
Xue Y, Guo Y, Zhang Z, Guo Y, Wang Y, Lu G (2008) The role of surface properties of activated carbon in the catalytic reduction of NO by carbon. Appl Surf Sci 255:2591–2595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.07.167
Yang W, Liu Z, Xu W, Liu Y (2018) Removal of elemental mercury from flue gas using sargassum chars modified by NH4Br reagent. Fuel 214:196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.11.004
Yang W, Li Y, Shi S, Chen H, Shan Y, Liu Y (2019) Mercury removal from flue gas by magnetic iron-copper oxide modified porous char derived from biomass materials. Fuel 256:115977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115977
Yang C, Florent M, de Falco G, Fan H, Bandosz TJ (2020a) ZnFe2O4/activated carbon as a regenerable adsorbent for catalytic removal of H2S from air at room temperature. Chem Eng J 394:124906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124906
Yang C, Wang Y, Fan H, de Falco G, Yang S, Shangguan J, Bandosz TJ (2020b) Bifunctional ZnO-MgO/activated carbon adsorbents boost H2S room temperature adsorption and catalytic oxidation. Appl Catal B Environ 266:118674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118674
Yang M, Wang H, ** S, Zhang R, Wang Y, Huo W, Wang X, ** M, Qiao W, Ling L (2021) Insight into the mechanism of boron-do** of carbon aerogel for enhancing the activity of low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Catal Sci Technol 11:2057–2072. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CY02006K
Yao L, Liu Q, Mossin S, Nielsen D, Kong M, Jiang L, Yang J, Ren S, Wen J (2020) Promotional effects of nitrogen do** on catalytic performance over manganese-containing semi-coke catalysts for the NH3-SCR at low temperatures. J Hazard Mater 387:121704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121704
Zhang Z, Wang J, Li W, Wang M, Qiao W, Long D, Ling L (2016) Millimeter-sized mesoporous carbon spheres for highly efficient catalytic oxidation of hydrogen sulfide at room temperature. Carbon 96:608–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.10.001
Zhang X, Gao B, Creamer AE, Cao C, Li Y (2017) Adsorption of VOCs onto engineered carbon materials: a review. J Hazard Mater 338:102–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.013
Zhang X, Ren K, Wang Y, Shen B, Shen F, Shang Y (2021) Solvent-free synthesis of MnOx-FeOx/biochar for Hg 0 and o -xylene removal from flue gas. Energy Fuels 35:15969–15977. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.1c02508
Zhou K, Ma W, Zeng Z, Ma X, Xu X, Guo Y, Li H, Li L (2019) Experimental and DFT study on the adsorption of VOCs on activated carbon/metal oxides composites. Chem Eng J 372:1122–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.218
Zhou M, Xu Y, Luo G, Zhang Q, Du L, Cui X, Li Z (2022a) Facile synthesis of phosphorus-doped porous biochars for efficient removal of elemental mercury from coal combustion flue gas. Chem Eng J 432:134440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.134440
Zhou Q, Di G, Song T, Lu P, Xu G (2022b) Template synthesis of sulfur-doped mesoporous carbon for efficiently removing gas-phase elemental mercury from flue gas. Fuel 321:124112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124112
Zhu Z, Liu Z, Liu S, Niu H (1999) A novel carbon-supported vanadium oxide catalyst for NO reduction with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl Catal B Environ 23:L229–L233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(99)00085-5
Zhu L, Huang B, Wang W, Wei Z, Ye D (2011) Low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over CeO2 supported on modified activated carbon fibers. Catal Commun 12:394–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2010.10.028
Zhu X, Zhang L, Zhang M, Ma C (2019) Effect of N-do** on NO2 adsorption and reduction over activated carbon: an experimental and computational study. Fuel 258:116109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116109
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2021R1I1A3050146 & RS-2023-00249553), the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (No. RS-2023-00218203), and Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) as Waste to energy recycling Human resource development Project.
Funding
This research was financially supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2021R1I1A3050146 & RS-2023-00249553), the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (No. RS-2023-00218203), and Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) as Waste to energy recycling Human resource development Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jae Hwan Yang: Conceptualization, review, editing, and supervision. Ajit Dattatray Phule: Conceptualization, writing-original draft preparation, writing-review and editing. Md. Wahad Uz Zaman: writing-review and editing. Sahar Elkaee: writing-review and editing. Seul Yi Kim: writing-review and editing. Sang Gyu Lee: writing-review and editing. Gibeom Park: writing-review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial or non-financial interest that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Phule, A.D., Zaman, M.W.U., Elkaee, S. et al. Carbon-Based Catalysts for Clean Environmental Remediation. Int J Environ Res 18, 3 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-023-00554-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-023-00554-6