Abstract
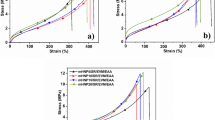
Blends of silicone rubber (SR) and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) are immiscible due to different polarity and poor interfacial surface tension between their rubber chains. In this study, compatibilizing effect of a nanoclay addition in SR/EPDM blends was investigated. Viscoelasticity and morphology of nanocomposites based on SR and EPDM, containing 10, 20 and 30 wt% of EPDM and 3, 6 and 9 phr of nanoclay (Cloisite 15A), were studied. The curing behavior of the samples showed that the vulcanization rate and cross-link density of the blends increased with increases in SR content. Morphological study was conducted by XRD, SEM and EDX analyses and they indicated that the nanoparticles tended to disperse in the EPDM phase and consequently caused hardness and the elasticity of this phase in nanocomposites increased. Tensile properties of the samples showed a good fitting between that of experiments and the Maxwell model at initial time of testing (1.5 s) for all the blends. Sample parameters including modulus (E), viscosity (η) and relaxation time (τ) calculated by the Maxwell model revealed that those samples with higher content of nanoparticles exhibit higher modulus and lower relaxation time. The good match in tensile properties based on Maxwell model and those of the experimental data was attributed to good dispersion of nanoclay in the blends.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Dimethyl, dehydrogenated, tallow quaternary ammonium chloride.
References
Das A, Mahaling R, Stöckelhuber K, Heinrich G (2011) Reinforcement and migration of nanoclay in polychloroprene/ethylene–propylene–diene-monomer rubber blends. Compos Sci Technol 71:276–281
Krajnc M, Karger Kocsis J, Sebenik U (2013) Grafting of maleic anhydride onto an ethylene-propylene-diene terpolymer and concurrent organoclay nanocomposite preparation in solution and melt. J Appl Polym Sci 127:950–958
Ebadi Dehaghani H, Khonakdar HA, Barikani M, Jafari SH (2015) Experimental and theoretical analyses of mechanical properties of PP/PLA/clay nanocomposites. Compos Part B Eng 69:133–144
Le Baron PC, Wang Z, Pinnavaia TJ (1999) Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: an overview. Appl Clay Sci 15:11–29
Ma J, Yu ZZ, Kuan HC, Dasari A, Mai YW (2005) A new strategy to exfoliate silicone rubber/clay nanocomposites. Macromol Rapid Commun 26:830–833
Chang YW, Yang Y, Ryu S, Nah C (2002) Preparation and properties of EPDM/organomontmorillonite hybrid nanocomposites. Polym Int 51:319–324
Sinha Ray S, Okamoto M (2003) Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: a review from preparation to processing. Prog Polym Sci 28:1539–1641
Kang D, Kim D, Yoon SH, Kim D, Barry C, Mead J (2007) Properties and dispersion of EPDM/modified-organoclay nanocomposites. Macromol Mater Eng 292:329–338
Ghasemi I, Karrabi M, Mohammadi M, Azizi H (2010) Evaluating the effect of processing conditions and organoclay content on the properties of styrene-butadiene rubber/organoclay nanocomposites by response surface methodology. Express Polym Lett 4:62–70
Ra**i V, Deepalaxmi R (2012) Property modification of SiR-EPDM blends by electron beam irradiation. In: 2012 IEEE international conference on condition monitoring and diagnosis (CMD), pp 1071–1076. doi:10.1109/CMD.2012.6416342
Bagheri Kazemabad S, Khavandi A, Chen B (2012) Evaluation of toughening mechanisms of polypropylene/ethylene–octene copolymer/maleic anhydride-grafted poly (ethylene-co-octene)/clay nanocomposite. Polym Int 62:566–572
Ock HG, Kim DH, Ahn KH, Lee SJ, Maia JM (2016) Effect of organoclay as a compatibilizer in poly (lactic acid) and natural rubber blends. Eur Polym J 76:216–227
Acharya H, Kumar Srivastava S (2014) EPDM/silicone blend layered silicate nanocomposite by solution intercalation method: morphology and properties. Polym Compos 35:1834–1841
Li Y, Shimizu H (2004) Novel morphologies of poly (phenylene oxide)(PPO)/polyamide 6 (PA6) blend nanocomposites. Polymer 45:7381–7388
Asaad JN, El-Nashar DE, Mansour SH (2014) Effect of modified clay and Mg (OH)2 on the properties of ethylene propylene diene monomer/silicon rubber nanocomposites. Proc Int Mech Eng NJ Nano 229:121–130
Sengupta R, Chakraborty S, Bandyopadhyay S, Dasgupta S, Mukhopadhyay R, Auddy K, Deuri A (2007) A short review on rubber/clay nanocomposites with emphasis on mechanical properties. Polym Eng Sci 47:1956–1974
Maiti M, Bhattacharya M, Bhowmick AK (2008) Elastomer nanocomposites. Rubber Chem Technol 81:384–469
Pasbakhsh P, Ismail H, Fauzi MA, Bakar AA (2009) Influence of maleic anhydride grafted ethylene propylene diene monomer (MAH-g-EPDM) on the properties of EPDM nanocomposites reinforced by halloysite nanotubes. Polym Test 28:548–559
Ehsani M, Borsi H, Gockenbach E, Morshedian J, Bakhshandeh G (2004) An investigation of dynamic mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of housing materials for outdoor polymeric insulators. Eur Polym J 40:2495–2503
Mansor NS, Hamzah MS, Kamarol M, Mariatti MA (2014) Comparative study of dielectric strength between SiR/EPDM and PP/EPDM blends with various type of nanofillers. Adv Mater Res 832:483–487
Dang ZM, **a YJ, Zha JW, Yuan JK, Bai J (2011) Preparation and dielectric properties of surface modified TiO2/silicone rubber nanocomposites. Mater Lett 65:3430–3432
Jung SY, Kim BK (2009) Preparation and characteristics of high voltage liquid silicone rubber by modified cross-linking agent. Trans Electr Electron Mater 10:9–15
Kole S, Srivastava S, Tripathy D, Bhowmick A (1994) Accelerated hydrothermal weathering of silicone rubber, EPDM, and their blends. J Appl Polym Sci 54:1329–1337
Yang L, Hu Y, Lu H, Song L (2006) Morphology, thermal, and mechanical properties of flame-retardant silicone rubber/montmorillonite nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 99:3275–3280
Raja Prabu R, Udayakumar K, Abdullah Khan M, Abdul Majeed S (2007) Electrical insulation characteristics of silicone and EPDM polymeric blends. I. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 14:1207–1214
Kole S, Chaki T, Bhowmick AK, Tripathy D (1993) Effect of compatibiliser, curing sequence and ageing on the thermal stability of silicone rubber, EPDM rubber and their blends. Polym Degrad Stabil 41:109–116
Xu G, Qin S, Yu J, Huang Y, Zhang M, Ruan W (2015) Effect of migration of layered nanoparticles during melt blending on the phase morphology of poly (ethylene terephthalate)/polyamide 6/montmorillonite ternary nanocomposites. RSC Adv 5:29924–29930
Zhang C, Pal K, Byeon JU, Han SM, Kim JK (2011) A study on mechanical and thermal properties of silicone rubber/EPDM dam** materials. J Appl Polym Sci 119:2737–2741
Bagheri Kazemabad S, Fox D, Chen Y, Geever LM, Khavandi A, Bagheri R, Higginbotham CL, Zhang H, Chen B (2012) Morphology, rheology and mechanical properties of polypropylene/ethylene–octene copolymer/clay nanocomposites: effects of the compatibilizer. Compos Sci Technol 72:1697–1704
Kooshki RM, Ghasemi I, Karrabi M, Azizi H (2013) Nanocomposites based on polycarbonate/poly (butylene terephthalate) blends effects of distribution and type of nanoclay on morphological behavior. J Vinyl Addit Technol 19:203–212
Li Y, Wei GX, Sue HJ (2002) Morphology and toughening mechanisms in clay-modified styrene-butadiene-styrene rubber-toughened polypropylene. J Mater Sci 37:2447–2459
Mirabedini AS, Karrabi M, Ghasemi I (2013) Viscoelastic behavior of NBR/phenolic compounds. Iran Polym J 22:25–32
Fried JR (2005) Polymer science and technology. In: Viscoelasticity and rubber elasticity, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, New Delhi
Bonnerup C, Gatenholm P (1993) The effect of surface energetics and molecular interdiffusion on adhesion in multicomponent polymer systems. J Adhes Sci Technol 7:247–262
Roe RJ (1965) Parachor and surface tension of amorphous polymers. J Phys Chem 69:2809–2810
Fenouillot F, Cassagnau P, Majeste JC (2009) Uneven distribution of nanoparticles in immiscible fluids: morphology development in polymer blends. Polymer 50:1333–1350
Elias L, Fenouillot F, Majesté JC, Martin G, Cassagnau P (2008) Migration of nanosilica particles in polymer blends. J Polym Sci Pol Phys 46:1976–1983
Van Puyvelde P, Moldenaers P (2005) Rheology and morphology development in immiscible polymer blends. Rheology Rev 2005:101
Song K, Zhang Y, Meng J, Minus ML (2015) Spectral analysis of lamellae evolution and constraining effects aided by nano-carbons: a coupled experimental and simulation study. Polymer 75:187–198
Kole S, Bhattacharya A, Tripathy D, Bhowmick AK (1993) Influence of curative, filler, compatibilizer, domain size, and blend ratio on the dynamic mechanical properties of silicone–EPDM blends. J Appl Polym Sci 48:529–545
Song K, Zhang Y, Minus ML (2015) Polymer interphase self-reinforcement and strengthening mechanisms in low-loaded nanocomposite fibers. Macromol Chem Phys 216:1313–1320
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bazli, L., Khavandi, A., Boutorabi, M.A. et al. Morphology and viscoelastic behavior of silicone rubber/EPDM/Cloisite 15A nanocomposites based on Maxwell model. Iran Polym J 25, 907–918 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-016-0477-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-016-0477-x