Abstract
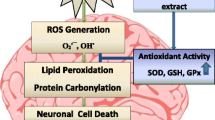
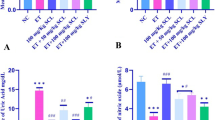
We investigated the effect of Syzygium cumini(L.) Skeels seed extract on the oxidative stress of brain cortical tissues of alcohol-treated rats. The in vitro antioxidative effect of methnolic S. cumini seed extract was initially compared with those of the buytylated hydroxyl toluene (BHT) and Vitamin C, by determining their DPPH-free radical scavenging activity. The S. cumini seed extract exhibited stronger free radical scavenging activity than those of the BHT and Vitamin C. Cortex homogenates were then directly incubated with 15% ethanol and/or Fenton’s reagent (H2O2 + Fe2SO4) to induce in vitro oxidative stress in the absence or presence of S. cumini seed extract . The S. cumini seed extract significantly reduced the levels of lipid peroxide (LPO) in the cortical homogenates. Twenty four rats were then divided into four groups: Control, S. cumini seed extract (SE)-administered, 15% ethanol-fed (EtOH) and EtOH + SE rats. The oral administration of the extract (400 mg/kg BW.day) for 8 weeks significantly (P < 0.05) decreased the levels of LPO in the cortex of the EtOH + SE rats, suggesting that S. cumini seed not only scavenged the DPPH-free radicals and obstructed the ethanol/Fenton’s reagents-induced in vitro oxidative stress of the cortical tissues but also reduced their in vivo formation. These results suggest that S. cumini seed could be used as a potential antioxidant therapy for alcoholics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adibhatla RM, Hatcher JF (2007) Role of lipids in brain injury and diseases. Future Lipidol 2:403–422
Bhuyan ZA, Rokeya B, Masum N, Hossain S, Mahmud I (2010) Antidiabetic effect of Syzygium cumini (L) seed on type II diabetic rats. Dhaka Univ J Biol Sci 19:157–164
Block GD, Yamamoto ME, Mallick E, Styche A (1993) Effects on pubertal hormones by ethanol abuse in adolescents. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 17:505–511
Bopp A, De Bona KS, Bellé LP, Moresco RN, Moretto MB (2009) Syzygium cumini inhibits adenosine deaminase activity and reduces glucose levels in hyperglycemic patients. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 23:501–507
Crews FT, Nixon K (2009) Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in alcoholism. Alcohol Alcohol 44:115–127
de la Monte SM (1988) Disproportionate atrophy of cerebral white matter in chronic alcoholics. Arch Neurol 45:990–992
Dees WL, Dissen GA, Hiney JK (2000) Alcohol ingestion inhibits the increased secretion of puberty-related hormones in the develo** female rhesus monkey. Endocrinology 141:1325–1331
Evert DL, Oscar-Berman M (1995) Alcohol related cognitive impairments: an overview of how alcoholism may affect the workings of the brain. Alcohol Health Res World 19:89–96
Evert DL, Oscar-Berman M, Land C, Ne S (2004) Ethanol impairs memory of a simple discrimination in adolescent rats at doses that leave adult memory unaffected. Neurobiol Learn Mem 81:75–81
Frias J, Torres JM, Rodriguez R (2000) Effects of acute alcohol intoxication on growth axis in human adolescents of both sexes. Life Sci 67:2691–2697
Harper C (1998) The neuropathology of alcohol-specific brain damage, or does alcohol damage the brain? J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:101–110
Harper C, Dixon G, Sheedy D, Garrick T (2003) Neuropathological alterations in alcoholic brains. Studies arising from the New South Wales tissue resource centre. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiat 27:951–961
Hatano T, Edamatsu R, Hiramatsu M, Mori A, Fujita Y, Yasuhara T, Yoshida T, Okuda T (1989) Effect of interaction of tannins with co-existing substances vs. effect of tannins and related polyphenols on superoxide anion radical and on DPPH radical. Chem Pharm Bull 37:2016–2021
Hossain S, Chowdhury IM, Basunia MA, Nahar T, Rahaman A, Choudhury BK, Choudhuri SK, Mahmud I, Uddin B (2011) Syzygium cumini seed extract protects the liver against lipid peroxidation with concurrent amelioration of hepatic enzymes and lipid profile of alcoholic rats. J Compl Integr Med 8:1–17
ISO. ISO 14502–1 (2005) Determination of substances characteristic of green and blck tea. Part 1: content of total polyphenols in tea. Colorimetric method using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent
Lang AR (1993) Alcohol-related violence: psychological perspectives. In: Martin SE (ed) Alcohol and interpersonal violence. NIAAA research monograph No. 24. NIH Pub. No. 93–3496. NIAAA, Rockville, pp 121–148
Lowry DH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mandal S, Barik B, Mallick C, De D, Ghosh D (2008) Therapeutic effect of ferulic acid, an ethereal fraction of ethanolic extract of seed of Syzygium cumini against streptozotocin-induced diabetes in male rat. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 30:121–128
Namasivayam R, Ramachandran B, Munuswamy D (2008) Effect of aqueous extract of Syzygium cumini pulp on antioxidant defense system in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Iranian J Pharmacol Therap 1735- 2657/08/72-137-145
Ohkawa H, Ohnishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissue by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Oscar-Berman M, Hutner N (1993) Frontal lobe changes after chronic alcohol ingestion. In: Hunt WA, Nixon SJ (eds) Alcohol induced brain damage. Washington, DC: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, pp 121–156
Pandey M, Khan A (2002) Hypoglycaemic effect of defatted seeds and water soluble fibre from the seeds of Syzygium cumini (Linn.) Skeels in alloxan diabetic rats. Indian J Exp Biol 40:1178–1182
Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV, Mathalon DH, Shear PK, Rosenbloom MJ, Lim KO (1995) Longitudinal changes in magnetic resonance imaging brain volumes in abstinent and relapsed alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 19:1177–1191
Polidori MC, Mecocci P, Frei B (2001) Plasma vitamin c levels are decreased and correlated with brain damage in patients with intracranial Hemorrhage or head trauma. Stroke 32:898–902
Rahmatullah M, Mollik MAH, Azam ATMA, Islam MR, Chowdhury MAM, Jahan R, Chowdhury MH, Rahman T (2009) Ethnobotanical Survey of the Santal tribe residing in Thakurgaon District, Bangladesh. Am Eur J Sust Agric 3:889–898
Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventós RM (1999) Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol 299:152–178
Slawecki CJ, Betancourt M, Cole M, Ehlers CL (2001) Periadolescent alcohol exposure has lasting effects on adult neurophysiological function in rats. Dev Brain Res 128:63–72
Sun AY, Sun GY (2001) Ethanol and oxidative mechanisms in the brain. J Biomed Sci 8:37–43
White AM, Ghia AJ, Levin ED, Swartzwelder HS (2000) Binge pattern ethanol exposure in adolescent and adult rats: differential impact on subsequent responsiveness to ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:1251–1256
Wu A, Ying Z, Gomez-Pinilla F (2010) Vitamin E protects against oxidative damage and learning disability after mild traumatic brain injury in rat. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 24:290–298
Acknowledgements
This work was partly funded by the University Grant Commission (6/75/UGC/Biol.18/2008-09), Bangladesh.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, S., Rahaman, A., Nahar, T. et al. Syzygium cumini (L.) skeels seed extract ameliorates in vitro and in vivo oxidative potentials of the brain cerebral cortex of alcohol-treated rats. Orient Pharm Exp Med 12, 59–66 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-011-0044-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-011-0044-0