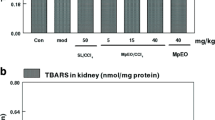
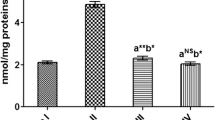
Abstract
Ethanol consumption can generate free radicals and cause oxidative stress, tissue inflammation, and kidney impairment. It has long been known that saponins from natural sources have numerous therapeutic benefits in African herbal and traditional medicine. However, the study aimed to the study aimed to evaluate the ameliorative effect of saponin-rich extract of Citrullus lanatus seed against ethanol-induced kidney injury. Rats were divided into six groups: a normal control, an ethanol control (10 ml/kg of 50% ethanol), a saponin control (100 mg/kg/day), an ethanol plus low and high doses of saponin (ET + 50 and 100 mg/kg SCL), and an ethanol plus Silymarin (ET + 100 mg/kg SLY) group. Serum urea, creatinine, and uric acid were measured, as were oxidative stress markers and renal tissue inflammatory markers. The ethanol-induced increases in creatinine, urea, and uric acid were significantly (p < 0.05) mitigated by Citrullus lanatus seed saponins (SCL). When rats administered SCL were compared to untreated ethanol rats, CAT, SOD, and GPx levels increased significantly (p < 0.05), whereas MDA decreased. Likewise, SCL dramatically lowered IL-1β and TNF-α levels in ethanol-treated rats. A histopathological study strongly supported the result of the biochemical assay. The results of this study reveal that by reducing the rise in renal function, inflammatory markers, and oxidative stress, the saponin-rich fraction of Citrullus lanatus seed has therapeutic potential against ethanol-induced kidney damage. SCL may therefore act as a plant-based natural remedy to reduce kidney damage.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The raw data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- CKD:
-
Chronic Kidney Disease
- CL:
-
Cittrulus lanatus
- ET:
-
Ethanol
- FeCl3 :
-
Iron (III) Chloride
- GSH:
-
Reduced Glutathione
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin 1 Beta
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MgCO3 :
-
Magnesium Carbonate
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- NC:
-
Normal Control
- NO:
-
Nitrite Oxide
- RAS:
-
Renin-Angiotensin System
- RNS:
-
Reactive Nitrogen Species
- ROS:
-
Reactive Oxygen Species
- SCL:
-
Saponin-rich Fraction of Citrullus lanatus Seed
- SLY:
-
Silymarin
- SOD:
-
Superoxide Dismutase
- TNF-α:
-
Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha
References
Bingqian Z, Wen Z, Yujia W, Ying Y, Na W, Junsong L, Tingming F, Lingchong W, Liuqing D (2021) Improved efficacy of Panax notoginseng saponin loaded into BSP/alginate microspheres for the treatment of alcoholic gastric ulcers. Int J Pharm 596:120218
Bulle S, Reddy VD, Hebbani AV, Padmavathi P, Challa C, Puvvada PK, Repalle E, Nayakanti D, Aluganti Narasimhulu C, Nallanchakravarthula V (2016) Nephro-protective action of P. santalinus against alcohol-induced biochemical alterations and oxidative damage in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 84:740–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.103 (PMID: 27710898)
Ceni E, Mello T, Galli A (2014) Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: role of oxidative metabolism. World J Gastroenterol 20(47):17756–17772. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17756 (PMID: 25548474)
Claereboudt EJS, Caulier G, Decroo C, Colson E, Gerbaux P, Claereboudt MR, Schaller H, Flammang P, Deleu M, Eeckhaut I (2019) Triterpenoids in echinoderms: fundamental differences in diversity and biosynthetic pathways. Drugs 17:E352
Cohen JI, Chen X, Nagy LE (2011) Redox signalling and the innate immune system in alcoholic liver disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 15(2):523–534. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3746 (PMCID: PMC3118704)
Cohen JM, Langer WD, Rosen LC, Cameron AGW (1970) Neutron star models based on an improved equation of state. Astrophys Space Sci 6:228–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00651224
Comporti M, Signorini C, Leoncini S, Gardi C, Ciccoli L, Giardini A, Vecchio D, Arezzini B (2010) Ethanol-induced oxidative stress: basic knowledge. Genes Nutr 5(2):101–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-009-0159-9
Costa-Valle MT, Tonieto BD, Altknecht L, Cunha CD, Fão N, Cestonaro LV, Göethel G, Garcia SC, Leal MB, Dallegrave E, Arbo MD (2018) Energy drink and alcohol combination leads to kidney and liver alterations in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 15(355):138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.06.024 (PMID: 29959998)
De Groot C, Muller-Goymann CC (2016) Saponin interactions with model membrane systems - Langmuir monolayer studies, hemolysis and formation of ISCOMs. Planta Med 28:1496–1512
Donnahoo KK, Shames BD, Harken AH, Meldrum DR (1999) Review article: the role of tumor necrosis factor in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Urol 162(1):196–203
Ejelonu OC, Oluba SO, Awolokun BO, Elekofehint OO, Adanlawo IG (2021) Saponin-rich extracts reverse obesity and offer protecton against obesity-induced inflammaton in high-fat diet mice. J Med Plants Econ Dev 5(1):a101. https://doi.org/10.4102/jomped.v5i1.101
Elkomy NMIM, Ibrahim IAAE, Elshazly SM, El-Fayoumi HM (2018) Ameliorative effects of clonidine on ethanol induced kidney injury in rats: potential role for imidazoline-1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 5(824):148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.02.001 (PMID: 29452086)
Fan Z, Yun J, Yu S, Yang Q, Song L (2019) Alcohol consumption can be a “double-edged sword” for chronic kidney disease patients. Med Sci Monit 25:7059–7072. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.916121
Gao Y, Jiang X, Yang D, Wang D, Gong K, Peng Y, Jiang H, Shi C, Duan Y, Chen Y, Han J, Yang X (2022) Roxadustat, a hypoxiainducible factor 1α activator, attenuates both long- and shortterm alcohol-induced alcoholic liver disease. Front Pharmacol 13:895710. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.895710
Gholami A, De Geyter N, Pollier J, Goormachtig S, Goossens A (2014) Natural product biosynthesis in Medicago species. Nat Prod Rep 31:356–380
Gyamfi MA, Wan YJ (2010) Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: the role of nuclear receptors. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 235(5):547–560. https://doi.org/10.1258/ebm.2009.009249 (PMID: 20463294; PMCID: PMC3908670)
Harris PS, Roy SR, Coughlan C, Orlicky DJ, Liang Y, Shearn CT, Roede JR, Fritz KS (2015) Chronic ethanol consumption induces mitochondrial protein acetylation and oxidative stress in the kidney. Redox Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.06.021 (PMCID: PMC4511634)
Hong MY, Beidler J, Hooshmand S, Figueroa A, Kern M (2018) Watermelon and L-argine consumption improve serum lipid profile and reduce inflammation and oxidative stress by altering gene expression in rats fed an atherogenic diet. Nutr Res 58:46–54
Hosseini SM, Taghiabadi E, Abnous K, Hariri AT, Pourbakhsh H, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Protective effect of thymoquinone, the active constituent of Nigella sativa fixed oil, against ethanol toxicity in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 20(8):927–939. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2017.9116 (PMID: 29085585)
Ikram M, Jo MH, Choe K, Khan A, Ahmad S, Saeed K, Kim MW, Kim MO (2021) Cycloastragenol, a triterpenoid saponin, regulates oxidative stress, neurotrophic dysfunctions, neuroinflammation and apoptotic cell death in neurodegenerative conditions. Cells 10(10):2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102719 (PMID: 34685699; PMCID: PMC8534642)
Jiang Z, Wang J, Xue H, Wang M, Jiang H, Liang Y, Dias AC, Gregory M, Chen C, Zhang X (2016) Protective effect of wild Corni fructus methanolic extract against acute alcoholic liver injury in mice. Redox Rep 22(6):338–345. https://doi.org/10.1080/13510002.2016.1239867 (PMID: 27712564)
Kar M, Mishra D (1976) Catalase, peroxidase and polyphenoloxidase activities during rice leaf senescence. Plant Physiol 57:315–319
Kępka A, Chojnowska S, Śnitko R, Zwierz K, Waszkiewicz N (2016) Renal carnitine excretion following abstinence after chronic drinking. Adv Med Sci 61(1):160–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advms.2015.11.002 (PMID: 26774267)
Kishi S, Campanholle G, Gohil VM, Perocchi F, Brooks CR, Morizane R, Sabbisetti V, Ichimura T, Mootha VK, Bonventre JV (2015) Meclizine preconditioning protects the kidney against ischemia-reperfusion injury. EBioMedicine 2(9):1090–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.07.035 (PMID: 26501107)
Kooti W, Daraei N (2017) A review of the antioxidant activity of celery (Apium graveolens L). J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 22(4):1029–1034. https://doi.org/10.1177/2156587217717415 (PMCID: PMC5871295)
Kothavade PS, Bulani VD, Nagmoti DM, Deshpande PS, Gawali NB, Juvekar AR (2015) Therapeutic effect of saponin rich fraction of achyranthes aspera linn. on adjuvant-induced arthritis in sprague-dawley rats. Autoimmune Dis 2015:943645. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/943645 (PMCID: PMC4529882)
Latchoumycandane C, Nagy LE, McIntyre TM (2014) Chronic ethanol ingestion induces oxidative kidney injury through taurine-inhibitable inflammation. Free Radic Biol Med 69:403–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.01.001 (PMID: 24412858; PMCID: PMC3960325)
Leal S, Ricardo Jorge DO, Joana B, Maria SS, Isabel SS (2017) Heavy alcohol consumption effects on blood pressure and on kidney structure persist after long-term withdrawal. Kidney Blood Press Res 42(4):664–675. https://doi.org/10.1159/000482022 (PMID: 29145198)
Ma Q, Jiang JG, Yuan X, Qiu K, Zhu W (2019) Comparative antitumor and anti-in§ammatory effects of savonoids, saponins, polysaccharides, essential oil, coumarin and alkaloids from Cirsium japonicum DC. Food Chem Toxicol 125:422–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.01.020
Mahmoudzadeh L, Najafi H, Ashtiyani SC, Yarijani ZM (2017) Anti-inflammatory and protective effects of saffron extract in ischaemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrology (carlton) 22(10):748–754. https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.12849 (PMID: 27381453)
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Meza V, Arnold J, Díaz LA, Ayala Valverde M, Idalsoaga F, Ayares G, Devuni D, Arab JP (2022) Alcohol consumption: medical implications, the liver and beyond. Alcohol Alcohol 57(3):283–291. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agac013 (PMID: 35333295)
Montgomery HAC, Dymock JE (1961) The determination of nitrite in water. Analyst 86:414–416
Osbourn A, Goss RJ, Field RA (2011) The saponins: polar isoprenoids with important and diverse biological activities. Nat Prod Rep 28:1261–1268
Perera T, Ranasinghe S, Alles N, Wadug R (2020) Experimental rat model for acute tubular injury induced by high water hardness and high-water fluoride: efficacy of primary preventive intervention by distilled water administration. BMC Nephrol 21:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-020-01763-3
Pourbakhsh H, Taghiabadi E, Abnous K, Hariri AT, Hosseini SM, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) Effect of Nigella sativa fixed oil on ethanol toxicity in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 17(12):1020–1031
Shahani S, Behzadfar F, Jahani D, Ghasemi M, Shaki F (2017) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Nasturtium officinale involved in attenuation of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Mech Methods 27(2):107–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2016.1258748
Shanmugam KR, Ramakrishna CH, Mallikarjuna K, Reddy KS (2010) Protective effect of ginger against alcohol-induced renal damage and antioxidant enzymes in male albino rats. Indian J Exp Biol 48:143–149
Shi Z, Long X, Li Y, ** J, Li J, Yuan C, ** R (2022) Protective effect of tea saponins on alcohol-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice. ACS Omega 8(1):673–681. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c05880 (Article ASAP)
Top H, Sarikahya NB, Nalbantsoy A, Kirmizigul S (2017) Immunomodulatory, hemolytic properties and cytotoxic activity potent of triterpenoid saponins from Cephalaria balansae. Phytochemistry 137:139–147
Varga ZV, Matyas C, Paloczi J, Pacher P (2017) Alcohol misuse and kidney injury: epidemiological evidence and potential mechanisms. Alcohol Res 38(2):283–288 (PMCID: PMC5513691)
Vo NN, Fukushima EO, Muranaka T (2017) Structure and hemolytic activity relationships of triterpenoid saponins and sapogenins. J Nat Med 71:50–58
Wahid M, Saqib F, Qamar M, Ziora ZM (2022) Antispasmodic activity of the ethanol extract of Citrullus lanatus seeds: justifying ethnomedicinal use in Pakistan to treat asthma and diarrhea. J Ethnopharmacol 295:115314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2022.115314
Wang L, Zhu Y, Wang L, Hou J, Gao Y, Shen L, Zhang J (2017) Effects of chronic alcohol exposure on ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in mice: the role of β-arrestin 2 and glycogen synthase kinase 3. Exp Mol Med 49(6):e347. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2017.76 (PMID: 28642577; PMCID)
Xu L, Yu Y, Sang R, Li J, Ge B, Zhang X (2018) Protective effects of taraxasterol against ethanol-induced liver injury by regulating CYP2E1/Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev 23(2018):8284107. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8284107 (PMID: 30344887; PMCID: PMC6174809)
Yao F, Xue Q, Li K, Cao X, Sun L, Liu Y (2019) Phenolic compounds and ginsenosides in ginseng shoots and their antioxidant and anti-in§ammatory capacities in LPS-induced RAW264.7 mouse macrophages. Int J Mol Sci 20(12):2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122951
Zhang F, Xu Z, Gao J, Xu B, Deng Y (2008) In vitro effect of manganese chloride exposure on energy metabolism and oxidative damage of mitochondria isolated from rat brain. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 26(2):232–236
Zhong Y, Luo R, Liu Q, Zhu J, Lei M, Liang X, Wang X, Peng X (2022) Jujuboside a ameliorates high fat diet and streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropathy via suppressing oxidative stress, apoptosis, and enhancing autophagy. Food Chem Toxicol 159:112697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112697 (PMID: 34826549)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SAB and WM conceptualised and designed the study; HBR, OBO, HSB, and VKJ carried out the experiments and analysed the data; SAB and HBR visualised and interpreted the histological slides. WM was responsible for drafting the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors declare no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The research was approved by ABU Directorate of Academic Planning and Monitoring (Approval No: ABUCAUC/2022/088) and was conducted according to the ARRIVE Guidelines.
Informed consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bazabang, S.A., Makena, W., Rilwan, H.B. et al. Citrullus lanatus methanol seed extract exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential against ethanol-induced kidney damage in Wistar rats. Comp Clin Pathol 32, 733–742 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03479-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03479-w