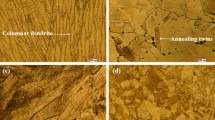
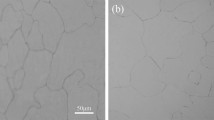
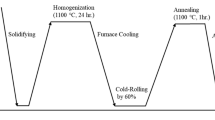
Abstract
Cold-rolling with subsequent annealing was carried out to produce recrystallized structures with different grain sizes in an Al0.5CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy to systematically investigate the grain growth behavior and varying properties. The results show that recrystallized microstructures can be achieved through an annealing process at 1200 °C for 75 min to 16 h, and the average grain size in this study ranges from 5.33 to 30.03 µm. The hardness shown to be affected through grain coarsening was then measured as a function of the grain size, and it is found to follow the classical Hall–Petch strengthening.
Graphic abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantor B, Chang ITH, Knight P, Vincent AJB. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2004;375–377:213.
Yeh JW, Sk Chen, Lin SJ, Gan JY, Chin TS. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv Eng Mater. 2004;6(5):299.
Lu YP, Gao XX, Dong Y, Wang TM, Chen HL, Mao HH, Zhao YH, Jiang H, Cao ZQ, Li TJ, Guo S. Preparing bulk ultrafine-microstructure high-entropy alloys via direct solidification. Nanoscale. 2018;10(4):1912.
Yuan Y, Wu Y, Tong X, Zhang H, Wang H, Liu XJ, Ma L, Suo HL, Lu ZP. Rare-earth high-entropy alloys with giant magnetocaloric effect. Acta Mater. 2017;125:481.
Senkov ON, Wilks GB, Miracle DB, Chuang CP, Liaw PK. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics. 2010;18(9):1758.
Hy YM, Liu XD, Guo NN, Wang L, Su YQ, Guo JJ. Microstructure and mechanical properties of NbZrTi and NbHfZrTi alloys. Rare Met. 2019;38(9):840.
Jiang SY, Lin ZF, Xu HM. Microstructure and properties of as-cast and annealed AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. Chin J Rare Met. 2018;42(12):1241.
Huang HL, Wu Y, He JY, Wang H, Liu XJ, An K, Wu W, Lu ZP. Phase-transformation ductilization of brittle high-entropy alloys via metastability engineering. Adv Mater. 2017;29(30):7.
Shun TT, Hsieh CY, Hung WJ, Lee CF. Age heat treatment of the CoCrFeNiTi0.3 high-entropy alloy. Mater Trans. 2018;59(5):730.
Wu CL, Zhang S, Zhang CH, Zhang H, Dong SY. Phase evolution and cavitation erosion-corrosion behavior of FeCoCrAlNiTix high entropy alloy coatings on 304 stainless steel by laser surface alloying. J Alloys Compd. 2017;698:761.
Chen MR, Lin SJ, Yeh JW, Chuang MH, Chen SK, Huang YS. Effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure hardness, and wear resistance of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2006;37(5):1363.
Laplanche G, Gadaud P, Horst O, Otto F, Eggeler G, George EP. Temperature dependencies of the elastic moduli and thermal expansion coefficient of an equiatomic, single-phase CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2015;623:348.
Zhang AJ, Han JS, Su B, Meng JH. A promising new high temperature self-lubricating material: CoCrFeNiS0.5 high entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2018;731:36.
Satake M, Bitoh T. Synthesis of Fe-Co-Ni-(B, Si, C) ferromagnetic high entropy amorphous alloys and their thermal and magnetic properties. J Jpn Soc Powder Powder Metall. 2018;65(7):401.
Lim KR, Lee KS, Lee JS, Kim JY, Chang HJ, Na YS. Dual-phase high-entropy alloys for high-temperature structural applications. J Alloys Compd. 2017;728:1235.
Li ZM, Tasan CC, Pradeep KG, Raabe D. A TRIP-assisted dual-phase high-entropy alloy: grain size and phase fraction effects on deformation behavior. Acta Mater. 2017;131:323.
Sriharitha R, Murty BS, Kottada RS. Phase formation in mechanically alloyed AlxCoCrCuFeNi (x = 0.45, 1, 2.5, 5 mol) high entropy alloys. Intermetallics. 2013;32:119.
Guo S, Chun N, Lu J, Liu CT. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys. J Appl Phys. 2011;109(10):103505.
Ogura M, Fukushima T, Zeller R, Dederichs PH. Structure of the high-entropy alloy AlxCrFeCoNi: fcc versus bcc. J Alloys Compd. 2017;715:454.
Rao JC, Diao HY, Ocelik V, Vainchtein D, Zhang C, Kuo C, Tang Z, Guo W, Poplawsky JD, Zhou Y, Liaw PK, De Hosson JTM. Secondary phases in AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys: an in situ TEM heating study and thermodynamic appraisal. Acta Mater. 2017;131:206.
Sheng WJ, Yang X, Zhu J, Wang C, Zhang Y. Amorphous phase stability of NbTiAlSiNx high-entropy films. Rare Met. 2018;37(8):682.
Zhu JM, Meng JL, Liang JL. Microstructure and mechanical properties of multi-principal component AlCoCrFeNiCux alloy. Rare Met. 2016;35(5):385.
Yang TF, **a SQ, Liu S, Wang CX, Liu SS, Zhang Y, Xue JM, Yan S, Wang YG. Effects of Al addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxCoCrFeNi High-entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2015;648:15.
Hou JX, Zhang M, Ma SG, Liaw PK, Qiao JW. Strengthening in Al0.25CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys by cold rolling. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2017;707:593.
Wang Z, Gao MC, Ma SG, Yang HJ, Wang ZH, Ziomek-Moroz M, Qiao JW. Effect of cold rolling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al0.25CoCrFe1.25Ni1.25 high-entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2015;645:163.
Nourbakhsh S, Nutting J. The high strain deformation of an aluminium-4% copper alloy in the supersaturated and aged conditions. Acta Metall. 1980;28(3):357.
Guo T, Li JS, Wang J, Wang WY, Liu Y, Luo XM, Kou HC, Beaugnon E. Microstructure and properties of bulk Al0.5CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy by cold rolling and subsequent annealing. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2018;729:141.
Ma LL, Wang L, Nie ZH, Wang FC, Xue YF, Zhou JL, Cao TQ, Wang YD, Ren Y. Reversible deformation-induced martensitic transformation in Al0.6CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy investigated by in situ synchrotron-based high-energy X-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 2017;128:12.
Ma SG, Qiao JW, Wang ZH, Yang HJ, Zhang Y. Microstructural features and tensile behaviors of the Al0.5CrCuFeNi2 high-entropy alloys by cold rolling and subsequent annealing. Mater Des. 2015;88:1057.
Zener C, Smith CS. Grains, phases and interfaces: an interpretation of microstructure. Trans Metall Soc AIME. 1948;175:11.
Nishizawa T, Ohnuma I, Ishida K. Examination of the Zener relationship between grain size and particle dispersion. Mater Trans, JIM. 1997;38(11):950.
Li DY, Gao MC, Hawk JA, Zhang Y. Annealing effect for the Al0.3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy fibers. J Alloys Compd. 2019;778:23.
Hall EO. The deformation and ageing of mild steel: III discussion of results. Proc Phys Soc B. 1951;64:747.
Sriharitha R, Murt BS, Kottada RS. Alloying, thermal stability and strengthening in spark plasma sintered AlxCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2014;583:419.
Gwalani B, Soni V, Lee M, Mantri S, Ren Y, Banerjee R. Optimizing the coupled effects of Hall-Petch and precipitation strengthening in a Al0.3CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater Des. 2017;121:254.
Wu Z, Bei H, Otto F, Pharr GM, George EP. Recovery, recrystallization, grain growth and phase stability of a family of FCC-structured multi-component equiatomic solid solution alloys. Intermetallics. 2014;46:131.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51571161 and 51774240).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, HX., Li, JS., Guo, T. et al. Evolution of microstructure and hardness in a dual-phase Al0.5CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy with different grain sizes. Rare Met. 39, 156–161 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01320-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01320-4