Abstract
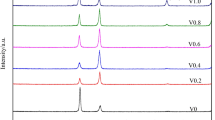
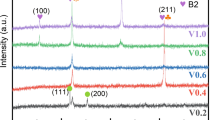
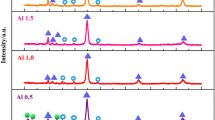
The authors studied the effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure and properties of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. The microstructure of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNiV x (x=0 to 2.0 in molar ratio) alloys was investigated by scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectrometry, and X-ray diffraction. With little vanadium addition, the alloys are composed of a simple fcc solid-solution structure. As the vanadium content reaches 0.4, a BCC structure appears with spinodal decomposition and envelops the FCC dendrites. From x=0.4 to 1.0, the volume fraction of bcc structure phase increases with the vanadium content increase. When x=1.0, fcc dendrites become completely replaced by bcc dendrites. Needle-like σ-phase forms in bcc spinodal structure and increases from x=0.6 to 1.0 but disappears from x=1.2 to 2.0. The hardness and wear resistance of the alloys were measured and explained with the evolution of the microstructure. The hardness values of the alloys increase when the vanadium content increases from 0.4 to 1.0 and peak (640 HV) at a vanadium content of 1.0. The wear resistance increases by around 20 pct as the content of vanadium increases from x=0.6 to 1.2 and levels off beyond x=1.2. The optimal vanadium addition is between x=1.0 and 1.2. Compared with the previous investigation of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi alloy, the vanadium addition to the alloy promotes the alloy properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Handbook Committee: Metals Handbook, 10th ed., vol. 1, ASM International, Metals Park, OH, 1990.
Handbook Committee: Metals Handbook, 10th ed., vol. 2, ASM International, Metals Park, OH, 1990.
A.L. Greer: Nature, 1993, vol. 366, pp. 303–04.
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, vol. 6, pp. 299–303.
S. Ranganathan: Curr. Sci., 2003, vol. 85, pp. 1404–06.
R.A. Swalin: Thermodynamics of Solids, 2nd ed., E. Burke, B. Chalmers, J.A. Krumhansl, eds., John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1991, pp. 21–87.
P.K. Huang, J.W. Yeh, T.T. Shun, and S.K. Chen: Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, vol. 6, pp. 74–78.
C.Y. Hsu, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, and T.T. Shun: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 1465–69.
C.J. Tong, Y.L. Chen, S.K. Chen, J.W. Yeh, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, S.J. Lin, and S.Y. Chang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 881–93.
C.J. Tong, M.R. Chen, S.K. Chen, J.W. Yeh, T.T. Shun, S.J. Lin, and S.Y. Chang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, vol. 36A, pp. 1263–71.
F.R. de Boer, R. Boom, W.C.M. Mattens, A.R. Miedema, and A.K. Nissen: Cohesion in Metals, Elsevier Science Publishing Company, 1989.
M.M. Khruschov: Wear, 1974, vol. 28, pp. 69–88.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, MR., Lin, SJ., Yeh, JW. et al. Effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure, hardness, and wear resistance of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 37, 1363–1369 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0081-3
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0081-3