Abstract
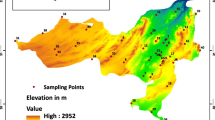
Currently, groundwater contamination has become a challenging problem, because of its susceptibility to pollution both by natural and anthropogenic processes. The study focused on the appraisal of vulnerability chances of shallow aquifers of Kandaihimmat watershed. Employing the DRASTIC model which is based on seven hydrogeological data layers viz.: depth to water table, net recharge, aquifer media, soil media, topography, impact of the vadose zone and hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer. By integrating all these data layers within GIS environment vulnerability index of groundwater was prepared. The estimated vulnerability index varies between 121 and 206 and was divided into three vulnerable zones namely high, moderate and low. The results of the study reveal that 38.28 % area of the watershed is coming under low risk, 34.32 % under medium risk and 27.39 % to high risk. Furthermore, validation of the model was done by nitrate contamination in groundwater of the watershed. Results have shown that in high vulnerable zone nitrate was found >10 mg/l, in moderate zone 5–10 mg/l, while in low vulnerable zone 0–5 mg/l. The model has been found applicable for the existing watershed and will help local authorities for managing the groundwater resources of the studied area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller, L., Bennet, T., Lehr, J.H. and Petty, R.J. (1987) DRASTIC: A standardized system for evaluating groundwater pollution potential using hydro geologic settings. USEPA document no. EPA/600/2–85–018.
Atkinson, S.F., and Thomlinson, J.R. (1994) An Examination of Ground Water Pollution Potential through GIS Modeling, ASPRS/ACSM Annual Convention and Exposition: Technical Papers, Reno, Nevada.
Adamat, R., Foster, I., and Baban, S. (2003) Groundwater vulnerability and risk map** for the Basaltic aquifer of the Azraq basin of Jordan using GIS, remote sensing and DRASTIC. Appld. Geograp., v.23, pp.303–324.
Almasri, M.N. (2008) Assessment of intrinsic vulnerability to contamination for Gaza coastal aquifer Palestine. Jour. Environ. Managmt., v.88(4), pp.577–593.
Akhtar Malik Muhammad, Tang Zhonghua, Ammar Salman Dawood and Bailey, Earl (2015) Evaluation of local groundwater vulnerability based on DRASTIC index method in Lahore, Pakistan. Geofísica Internacional v.54(1), pp.67–81.
Burkart, M.R., Kolpin, D.W. and James, D.E. (1999) Assessing groundwater vulnerability to agrichemical contamination in the Midwest US, Water Sci. Tech., v.39(3), pp.103–112.
Babiker, I.S., Mohamed, A.A., Hiyama, T. and Kato, K. (2005) A GIS–based DRASTIC model for assessing aquifer vulnerability in Kakamigahara Heights, Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. Sci. Total Environ., v.345, pp.127–14.
Becker, M. (2006) Potential for satellite remote sensing of ground water. Ground Water, v.44(2), pp.306–31.
Brindha, K. and Elango, L. (2015) Cross comparison of five popular groundwater pollution vulnerability index approaches. Jour. Hydrol., v.524, pp.595–613.
Chandrashekhar, H., Adiga, S., Lakshminarayana, V., Jagdeesha, C.J. and Nataraju, C. (1999) A case study using the model ‘DRASTIC’ for assessment of groundwater pollution potential. In: Proceedings of the ISRS national symposium on remote sensing applications for natural resources, June 19–21.
Bangalore Chitsazan, M. and Akhtari, Y. (2009) A GIS–based DRASTIC Model for Assessing Aquifer Vulnerability in Kherran Plain, Khuzestan, Iran, Water Resour. Managmt., v.23, pp.1137–1155.
Chonattu Jaseela, Kavya Prabhakar, Puthenveedu Sadasivan and Pillai Harikumar (2016) Application of GIS and DRASTIC Modeling for Evaluation of Groundwater Vulnerability near a Solid Waste Disposal Site. Internat. Jour. Geosci., v.7, pp.558–571.
Fritch, T.G., McKnight, C.L., Yelderman, J.C. and Arnold, J.G. (2000) Environmental auditing: An aquifer vulnerability assessment of the Paluxy aquifer, Central Texas, USA, using GIS and a modified DRASTIC approach. Jour. Environ. Managmt., v.25(3), pp.337–345.
Fred W., Besien, T. and Kolpin, D.W. (2002) Groundwater vulnerability: interactions of chemical and site properties. Sci. Total Environ. v.299(1), pp.131–14.
Foster, SSD., and Chilton, P.J. (2003) Groundwater: the processes and global significance of aquifer degradation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, B, 358, 1957–1972.
Ghosh, A., Tiwari, A.K. and Das, S. (2015) A GIS based DRASTIC model for assessing groundwater vulnerability of Katri Watershed, Dhanbad, India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, v.1(3), pp.11.
Hrkal, Z. (2001) Vulnerability of groundwater to acid deposition, Jizerske Mountains, northern Czech Republic: construction and reliability of a GIS–based vulnerability map. Jour. Hydrogeol., v.9, pp.348–357.
Hamza, M.H., Added, A., Rodriguez, R., Abdeljaoued, S., and Mammou, B. (2007) A GIS–based DRASTIC vulnerability and net recharge reassessment in an aquifer of a semi–arid region (Metline–Ras Jebel–Raf Raf aquifer, Northern Tunisia). Jour. Environ. Managmt., v.84, pp.12–19.
Iqbal, J., Pathak, G., and Gorai, A.K. (2015) Development of hierarchical fuzzy model for groundwater vulnerability to pollution assessment; Arab Jour. Geosci., v.8, pp.2713–2728.
Jamrah, A., Futaisi, A.A., Rajmohan, N. and Al–Yaroubi, S. (2008) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability in the coastal region of Oman using DRASTIC index method in GIS environment. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.147(1–3), pp.125–138.
Knox, R.C., Sabatini, D.A. and Canter, L.W. (1993)subsurface transport and fate processes. Lewis publishers, USA. Boca Raton, FL, 430p.
Kalinski, R.J., Kelly, W.E., Bogardi, I., Ehrman, R.L. and Yamamoto, P.D. (1994) Correlation between DRASTIC vulnerabilities and incidents of VOC contamination of municipal wells in Nebraska. Ground Water, v.32(1), pp.31–34.
Kimand, Y.J. and Hamm, S. (1999) Assessment of the potential for groundwater contamination using the DRASTIC/EGIS technique, Cheongju area, South Korea. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.7(2), pp.227–235.
Khan, A., Khan, H.H., Umar, R. and Khan, M.H. (2014) An integrated approach for aquifer vulnerability map** using GIS and rough sets: Study from an alluvial aquifer in north India; Hydrogeol. Jour., v.22, pp.1561–1572.
Kumar, P., Debnath, S.K., Thakur, P.K. and Bansod, B.K.S. (2016) Assessment of the effectiveness of DRASTIC in predicting the vulnerability of groundwater to contamination: A case study from Fatehgarh Sahib district in Punjab, India. Environ. Earth Sci., v.75, pp.879.
Lowe M. and Butler, M. (2003) Groundwater sensitivity and vulnerability to pesticides, Herber and Round Valleys, Wasatch County; Utah Geological Survey; Salt Lake City, UT: USA.
Leone, A., Ripa, M.N., Uricchio, V., Deak, J., and Vargay, Z. (2009) Vulnerability and risk evaluation of agricultural nitrogen pollutionfor Hungary’s main aquifer using DRASTIC and GLEAMS models. Jour. Environ. Managmt., v.90, pp.2969–297.
Lathamani, R., Janardhana, M.R., Mahalingam, B. and Suresha S. (2015) Evaluation of aquifer vulnerability using Drastic Model and GIS: A case study of Mysore City, Karnataka, India; Aquatic Procedia, v.4, pp.1031–1038.
Margat, J. (1968) Vulnerabilite desnappes d’eau souterraineala pollution. Basede lacartographie, Doc. BRGM, 68 SGL 198 HYD. Orlean, France.
Mehra, M., Oinam B. and Singh C.K. (2016) Integrated assessment of groundwater for agricultural use in Mewat district of Haryana, India using geographical information system (GIS); Jour. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. v.44(5), pp.747–758.
Mondal, N.C., Adike, S., Singh, V.S. Ahmed, S. and Jayakumar, K.V. (2017) Determining shallow aquifer vulnerability by the DRASTIC model and hydrochemistry in granitic terrain, southern India. Jour. Earth System Sci., v.126, pp.89
Navada, S.V., Nair, A.R., Rao, S.M., Paliwall, B.L. and Doshi C.S. (1993) Groundwater recharge studies in arid region of Jalore, Rajasthan using isotope techniques. Jour. Arid Environ., v.24, pp.125–133.
National Bureau of Soil Sciences & Land use Planning NBSS&LUP, ICAR, Nagpur (1996). Soils of Madhya Pradesh, NBSS Publ.59
Nasri, N., Chebil, M., Guellouz L., Bouhlila, R., Maslouhi, A., Ibnoussina, M. (2015) Modelling nonpoint source pollution by nitrate of soil in the Mateur plain, northeast of Tunisia. Arab Jour. Geosci., v.8, pp.1057–107.
Pathak, D. R., Hiratsuka, A., Awata, I. and Chen, L. (2009) Groundwater vulnerability assessment in shallow aquifer of Kathmandu Valley using GIS–based DRASTIC model, Environ. Geol., v.57, pp.1569–157.
Prasad, K. and Shukla, J. P. (2014) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability using GIS–based DRASTIC technology for the basaltic aquifer of Burhner watershed, Mohgaon block, Mandla (India), Curr. Sci., v.107(10), pp.1649–1656.
Rosen, L. (1994) Study of the DRASTIC methodology with the emphasis onSwedish conditions. In Program and abstracts of the 37th conference of the International Association for Great Lakes Research and Estuarine Research Federation, Buffalo, NY: IAGLR, pp.166
Rao, S.M., and Mamatha, P. (2004) Water quality in sustainable water management. Curr. Sci., v.87(7), pp.942–94.
Ritzema, H.P. (2006) Determining the Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity (Oosterbaan R.J and Nijland H. J.) In: H. P. Ritzema (Ed) Drainage Principles and Applications (pp.283–294). ILRI Publ. 16, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Rahman, A. (2008) A GIS based DRASTIC model for assessing groundwater vulnerability in shallow aquifer in Aligarh India. Appld. Geogr., v.28(1), pp.32–5.
Smedema, L.K. and Rycroft, D.W. (1983) Land drainage: planning and design of Agricultural Drainage Systems. Batsford, London, 376p.
Smith, P. A., Scott, H. D., and Fugitt, T. (1994) Influence of geographic database scale on prediction of groundwater vulnerability to pesticides. Jour. Soil Contamination, v.3, pp.285–298.
Sadek M., and El–Samie A.S. (2001) Pollution vulnerability of the quaternary aquifer near Cairo, Egypt, as indicated by isotopes and hydrochemistry. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.9(3), pp.273–281.
Sener E., Sener S., and Davraz, A. (2009) Assessment of aquifer vulnerability based on GIS and DRASTIC methods: A case study of the Senirkent–Uluborlu Basin (Isparta, Turkey). Hydrogeol. Jour., v.17, pp.2023–203.
Saha D. and Alam F. (2014) Groundwater vulnerability assessment using DRASTIC and Pesticide DRASTIC models in intense agriculture area of the Gangetic plains India. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.186(12), pp.8741–876.
Sahu, P.C. and Nandi, D. (2015) Evaluation of Ground Water Pollution Potential Using Drastic Model: A Case Study in Berhampur City, Orissa. Internat. Jour. Geol. Earth Environ. Sci., v.5(3), pp.55–61.
Singh, A., Srivastav, S. K., Kumar, S., and Chakrapani, G. J. (2015) A modified–DRASTIC model (DRASTICA) for assessment of groundwater vulnerability to pollution in an urbanized environment in Lucknow, India, Environ. Earth. Sci., v.4, pp.5475–5490.
Sinha, M.K., Verma, M.K., Ahmad, I., Baier, K. Jha, R. and Azzam, R. (2016) Assessment of Groundwater Vulnerability Using Modified DRASTIC Model in Kharun Basin, Chhattisgarh, India. Arabian Jour. Geosci., 9, 1–22.
Todd, D. K. (1980) Groundwater hydrology (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Wiley.
US General Accounting Office (GAO). (1991). Groundwater protection: Measurement of relative vulnerability to pesticide contamination. Washington, DC: US General Accounting Office. GAO/PEMD–92–8
Tesoriero, A.J., Inkpen, E.L., Voss, F.D. (1998) Assessing groundwater vulnerability using logistic regression, Proceedings for the Source Water Assessment and Protection 98 Conference, Dallas, TX, pp.157–165.
Thapinta, A., and Hudak, P.F. (2003) Use of geographic information systems for assessing groundwater pollution potential by pesticides in Central Thailand. Environ. Internat., v.29(1), pp.87–9.
Tahlawi Mohamed, R. El., Mohamed Abo–El Kassem., Gamal Y. Baghdadi., and Hussein A. Saleem (2016) Assessment of Groundwater Vulnerability–A Case Study. Internat. Jour. Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS, v.5(2) pp.1561–157.
Tiwari, A.K., Singh, P.K., and Maio, M.D. (2016) Evaluation of aquifer vulnerability in a coal mining of India by using GIS–based DRASTIC model; Arab Jour. Geosci. v.9, pp.438.
Umar, R., and Ahmed, I., Alam, F. (2009) Map** groundwater vulnerable zones using modified DRASTIC approach of an alluvial aquifer in parts of central Ganga plain, Western Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.73(2), pp.93–20.
Varol, S.O. and Davraz, A. (2010) Hydrogeological investigation of Sarkikaraagac Basin (Isparta,Turkey) and groundwater vulnerability. Water Internat., v.35(2), pp.177–19.
Wang, Y., Merke, B.J., Li, Y., Ye, H., Fu, S. and Ihm, D. (2007) Vulnerability of groundwater in quaternary aquifers to organic contaminants: A case study in Wuhan City, China. Environ. Geol., v.53, pp.479–48.
Yeh PJF., Swenson, S.C., Famiglietti, J.S. and Rodell, M. (2006) Remote sensing of groundwater storage changes in Illinois using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE), Water Resour. Res. v.42(12), pp.W12203
Yin, Lihe., Eryong Zhang., **aoyong Wang., Jochen Wenninger., Jiaqiu Dong., Li Guo., **ting Huang (2013) GIS–based DRASTIC model for assessing groundwater vulnerability in the Ordos Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci., v.69, pp.171
Zhou J., Li G., Liu F., Wang Y. and Guo X. (2010) DRASTIC model and its application in assessing groundwater vulnerability in arid area: A case study of pore phreatic water in Tarim Basin, **njiang Northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci., v.60(5), pp.1055–1063.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, M.S., Shukla, J.P. Assessment of Groundwater Vulnerability Risk in Shallow Aquifers of Kandaihimmat Watershed, Hoshangabad, Madhya Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 93, 199–206 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1152-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1152-6