Abstract
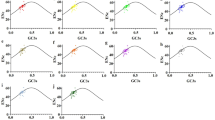
Gynostemma plants are important Chinese medicinal material and economic crops. Codon usage analysis is a good way to understand organism evolution and phylogeny. There is no report yet about analysis of codon usage bias of chloroplast genomes in Gynostemma species. In this study, the chloroplast genomes in nine Gynostemma species were analyzed systematically to explore the factors affecting the formation of codon usage bias. The codon usage indicators were analyzed. Multivariate statistical analysis including analysis of neutrality plot, effective number of codons plot, parity rule 2 plot and correspondence were performed. Composition analysis of codons showed that the frequency of GC in chloroplast genes of all nine Gynostemma species was less than 50%, and the protein-coding sequences of chloroplast genes preferred to end with A/T at the third codon position. The chloroplast genes had an overall weak codon usage bias. A total of 29 high frequency codons and 12 optimal codons were identified. These could provide useful information in optimizing and modifying codons thus improving the gene expression of Gynostemma species. The results of multivariate analysis showed that the codon usage patterns were not only affected by single one factor but multiple factors. Mutation pressure, natural selection and base composition might have an influence on the codon usage patterns while natural selection might be the main determinant. The study could provide a reference for organism evolution and phylogeny of Gynostemma species and help to understand the patterns of codons in chloroplast genomes in other plant species.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharyya D, Uddin A, Das S, Chakraborty S (2019) Mutation pressure and natural selection on codon usage in chloroplast genes of two species in Pisum L (Fabaceae: Faboideae). Mitochondr DNA A 30:664–673. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701394.2019.1616701
Blake WJ, Kaern M, Cantor CR, Collins JJ (2003) Noise in eukaryotic gene expression. Nature 422:633–637. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01546
Chakraborty S, Yengkhom S, Uddin A (2020) Analysis of codon usage bias of chloroplast genes in Oryza species: Codon usage of chloroplast genes in Oryza species. Planta 252:67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-020-03470-7
Das S, Paul S, Dutta C (2006) Synonymous codon usage in adenoviruses: influence of mutation, selection and protein hydropathy. Virus Res 117:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2005.10.007
Du N, Wang L, Bai G, Zhang MX, **ao YP, Zhang K, Wang P, Wang XB, Liu QH (2018) Food safety toxicology evaluation and anti-aging analysis of Gynostemma pentaphyllum seed oil. J Northwest A F Univ (nat Sci Ed) 46:131–140
Duret L, Mouchiroud D (1999) Expression pattern and surprisingly, gene length shape codon usage in Caenorhabditis, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4482–4487. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.8.4482
Editorial Committee of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2011) Flora of China. Science Press, Bei**g 19:11–15
Galtier N, Lobry JR (1997) Relationships between genomic G+C content, RNA secondary structures, and optimal growth temperature in prokaryotes. J Mol Evol 44:632–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006186
Gu WJ, Zhou T, Ma JM, Sun X, Lu ZH (2003) Folding type specific secondary structure propensities of synonymous codons. IEEE T Nanobiosci 2:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2003.817024
Huang XF, Song Y, Song CW, Wang MY, Liu HX, Yu SG, Fang NB (2013) Study on the hypoglycemic activity of different components of Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Hubei J Trad Chinese Med 35:67–69
James FC, McCulloch CE (1990) Multivariate analysis in ecology and systematics: panacea or Pandora’s box? Annu Rev Ecol Syst 21:129–166. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.21.110190.001021
Jia J, Xue Q (2009) Codon usage biases of transposable elements and host nuclear genes in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa. Genom Proteom Bioinf 7:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-0229(08)60047-9
Jiang Y, Deng F, Wang HL, Hu ZH (2008) An extensive analysis on the global codon usage pattern of baculoviruses. Arch Virol 153:2273–2282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-008-0260-1
Kawabe A, Miyashita NT (2003) Patterns of codon usage bias in three dicot and four monocot plant species. Genes Genet Syst 78:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1266/ggs.78.343
Kwak SY, Lew TTS, Sweeney CJ, Koman VB, Wong MH, Bohmert-Tatarev K, Snell KD, Seo JS, Chua NH, Strano MS (2019) Chloroplast-selective gene delivery and expression in planta using chitosan-complexed single-walled carbon nanotube carriers. Nat Nanotechnol 14:447–455. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0375-4
Li GL, Pan ZL, Gao SC, He YY, **a QY, ** Y, Yao HP (2019) Analysis of synonymous codon usage of chloroplast genome in Porphyra umbilicalis. Genes Genom 41:1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00847-1
Li HS, Ying H, Hu AR, Hu YR, Li DZ (2017) Therapeutic effect of gypenosides on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via regulating hepatic lipogenesis and fatty acid oxidation. Bio Pharm Bull 40:650–657. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b16-00942
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Beiles A, Nevo E (2002) Microsatellites: genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: a review. Mol Ecol 11:2453–2465. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01643.x
Liu HB, Lu YZ, Lan BL, Xu JC (2020a) Codon usage by chloroplast gene is bias in Hemiptelea davidii. J Genet 99:8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-019-1167-1
Liu XY, Li Y, Ji KK, Zhu J, Ling P, Zhou T, Fan LY, **e SQ (2020b) Genome-wide codon usage pattern analysis reveals the correlation between codon usage bias and gene expression in Cuscuta australis. Genomics 112:2695–2702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.03.002
Lu YL, Du YM, Qin L, Ma FF, Ling L, Wu D, Zhou XM, He YQ (2018) Hypolipemic mechanism of saponins from Gynostemma pentaphylla based on analysis of bile acids. Nat Prod Res Dev 30:1143–1148
Mcclellan DA (2000) The codon-degeneracy model of molecular evolution. J Mol Evol 50:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002399910015
Morton BR (1998) Selection on the codon bias of chloroplast and cyanelle genes in different plant and algal lineages. J Mol Evol 46:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006325
Morton BR (2003) The role of context-dependent mutations in generating compositional and codon usage bias in grass chloroplast DNA. J Mol Evol 56:616–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-002-2430-1
Nie XJ, Deng PC, Feng KW, Liu PX, Du XH, You FM, Song WM (2014) Comparative analysis of codon usage patterns in chloroplast genomes of the Asteraceae family. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:828–840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-013-0691-z
Prabha R, Singh DP, Gupta SK, Farooqi S, Rai A (2012) Synonymous codon usage in Thermosynechococcus elongatus (cyanobacteria) identifies the factors sha** codon usage variation. Bioinformation 8:622–628. https://doi.org/10.6026/97320630008622
Qi YY, Xu WJ, **ng T, Zhao MM, Li NN, Yan L, **a GM, Wang MC (2015) Synonymous codon usage bias in the plastid genome is unrelated to Gene structure and shows evolutionary heterogeneity. Evol Bioinform 2015:65–77. https://doi.org/10.4137/EBO.S22566
Rao YS, Wu GZ, Wang ZF, Chai XW, Nie QH, Zhang XQ (2011) Mutation bias is the driving force of codon usage in the Gallus gallus genome. DNA Res 18:499–512. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsr035
Ruf S, Forner J, Hasse C, Kroop X, Seeger S, Schollbach L, Schadach A, Bock R (2019) High-efficiency generation of fertile transplastomic Arabidopsis plants. Nat Plants 5:282–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-019-0359-2
Sharp PM, Cowe E (1991) Synonymous codon usage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 7:657–678
Sharp PM, Cowe E, Higgins DG, Shields DC, Wolfe KH, Wright F (1988) Codon usage patterns in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens; a review of the considerable within-species diversity. Nucleic Acids Res 16:8207–8711. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/16.17.8207
Sharp PM, Devine KM (1989) Codon usage and gene expression level in Dictyostelium discoideum highly expressed genes do ‘prefer’ optimal codons. Nucleic Acids Res 17:5029–5039
Sharp PM, Emery LR, Zeng K (2010) Forces that influence the evolution of codon bias. Philos Trans R Soc B 365:1203–1212
Sharp PM, Li WH (1986) An evolutionary perspective on synonymous codon usage in unicellular organisms. J Mol Evol 24:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02099948
Sharp PM, Li WH (1987) The codon adaptation index - a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res 15:1281–1295. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/15.3.1281
Sharp PM, Stenico M, Peden JF, Lloyd AT (1993) Codon usage: mutational bias, translational selection, or both? Biochem Soc Trans 21:835–841. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0210835
Shields DC, Sharp PM (1987) Synonymous codon usage in Bacillus subtil and reflects both translational selection and multational biases. Nucleic Acids Res 15:8023–8040
Singh ND, Davis JC, Petrov DA (2005) X-linked genes evolve higher codon bias in Drosophila and Caenorhabditis. Genetics 171:145–155. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.105.043497
Sueoka N (1988) Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2653–2657. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.85.8.2653
Sueoka N (1999a) Translation-coupled violation of Parity Rule 2 in human genes is not the cause of heterogeneity of the DNA G+C content of third codon position. Gene 238:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00320-0
Sueoka N (1999b) Two aspects of DNA base composition: G+ C content and translation-coupled deviation from intra-strand rule of A=T and G=C. J Mol Evol 49:49–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006534
Sueoka N, Kawanishi Y (2000) DNA G+C content of the third codon position and codon usage biases of human genes. Gene 261:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00480-7
Tang DF, Wei F, Cai ZQ, Wei YY, Khan A, Miao JH, Wei KH (2021) Analysis of codon usage bias and evolution in the chloroplast genome of Mesona chinensis Benth. Dev Genes Evol 231:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00427-020-00670-9
Tang L, Shah S, Chung L, Carney J, Katz L, Khosla C, Julien B (2000) Cloning and heterologous expression of the epothilone gene cluster. Science 287:640–642. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5453.640
Wan XF, Xu D, Leinhofs A, Zhou JZ, (2004) Quantitative relationship between synonymous codon usage bias and GC composition across unicellular genomes. BMC Evol Biol 4:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-4-19
Wang L, Lu GY, Liu H, Huang LJ, Jiang WM, Li P, Lu X (2020a) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Gynostemma yixingense and comparative analysis with congeneric species. Genet Mol Biol 43:e20200092. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2020-0092
Wang LJ, Roossinck MJ (2006) Comparative analysis of expressed sequences reveals a conserved pattern of optimal codon usage in plants. Plant Mol Biol 61:699–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-0041-8
Wang ZJ, Xu BB, Li B, Zhou QQ, Wang GY, Jiang XZ, Wang CC, Xu ZD (2020b) Comparative analysis of codon usage patterns in chloroplast genomes of six Euphorbiaceae species. Peer J 8:e8251. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8251
Wright F (1990) The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene 87:23–29
Wu YQ, Li ZY, Zhao DQ, Tao J (2018) Comparative analysis of flower-meristem-identity gene APETALA2 (AP2) codon in different plant species. J Integr Agr 17:867–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(17)61732-5
**ang H, Zhang RZ, Butler RR, Liu T, Zhang L, Pombert JF, Zhou ZY (2015) Comparative analysis of codon usage bias patterns in Microsporidian genomes. PLoS ONE 10:e0129223. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129223
**ng SF, Liu LH, Zu ML, Lin M, Zhai XF, Piao XL (2019) Inhibitory effect of damulin B from Gynostemma pentaphyllum on human lung cancer cells. Planta Med 85:394–405. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0810-7738
Yadav MK, Swati D (2012) Comparative genome analysis of six malarial parasites using codon usage biasbased tools. Bioinformation 8:1230–1239. https://doi.org/10.6026/97320630081230
Zhang WJ, Zhou J, Li ZF, Wang L, Gu X, Zhong Y (2008) Comparative analysis of codon usage patterns among mitochondrion, chloroplast and nuclear genes in Triticum aestivum L. J Integr Plant Biol 49:246–254. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00404.x
Zhang X, Zhou T, Kanwal N, Zhao YM, Bai GQ, Zhao GF (2017) Completion of Eight Gynostemma BL. (Cucurbitaceae) chloroplast genomes: characterization, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships. Front Plant Sci 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01583
Zhang YR, Nie XJ, Jia XO, Zhao CZ, Biradar SS, Wang L, Du XH, Song WM (2012) Analysis of codon usage patterns of the chloroplast genomes in the Poaceae family. Aust J Bot 60:461–470. https://doi.org/10.1071/BT12073
Zhao YC, Zheng H, Xu AX, Yan DH, Jiang ZJ, Qi Q, Sun JC (2016) Analysis of codon usage bias of envelope glycoprotein genes in nuclear polyhedrosis virus (NPV) and its relation to evolution. BMC Genomics 17:677–677. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-3021-7
Zhou M, Long W, Li X (2008a) Analysis of synonymous codon usage in chloroplast genome of Populus alba. J for Res 19:293–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-008-0052-1
Zhou M, Long W, Li X (2008b) Patterns of synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genomes of seed plants. For Stud China 10:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-008-0047-1
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFC1711000), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 81973414) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant no. BK20191319).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peipei Zhang collected, processed and analyzed data, produced charts and figures, authored and reviewed the draft manuscript, approved the final manuscript; Wenbo Xu analyzed and processed data, reviewed the manuscript, approved the final manuscript; Xu Lu conceived the project, reviewed the draft manuscript, approved the final manuscript; Long Wang conceived and designed the experiment, provided materials and analysis tools, guided the writing of the manuscript, reviewed the draft manuscript, approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or other aspects.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Xu, W., Lu, X. et al. Analysis of codon usage bias of chloroplast genomes in Gynostemma species. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27, 2727–2737 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01105-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01105-z