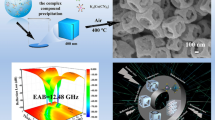
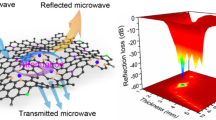
Abstract
Integrating heterogeneous interface through nanostructure design and interfacial modification is essential to realize strengthened interfacial polarization relaxation in electromagnetic wave absorption. However, an in-depth comprehension of the interfacial polarization behavior at hetero-junction/interface is highly desired but remains a great challenge. Herein, a Mott—Schottky heterojunction consisting of honeycomb-like porous N-doped carbon confined CoP nanoparticles (CoP@HNC) is designed to elevate the interfacial polarization strength. Simultaneously, corresponding electron migration and redistribution between the heterointerface of defective carbon and CoP nanoparticles are revealed. The significant difference in the work function on both sides of heterogeneous interface boosts the interfacial polarization in high frequency region. Furthermore, the relevant spectroscopic characterizations demonstrate that electron spontaneously migrates from CoP to N-doped carbon at the heterointerface, thereby contributing to the accumulation of electron on defective carbon side and the distribution of hole on CoP side. Impressively, benefitting from the synergistic effects of three-dimensional porous conductive carbon skeleton, foreign N heteroatoms, special CoP nanoparticles, and the resultant CoP/N-doped carbon Mott—Schottky heterojunction, the CoP@HNC exhibits remarkable electromagnetic wave absorption performances with minimum reflection loss up to −60.8 dB and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth of 4.96 GHz, which is superior to most of recently reported transition metal phosphides microwave absorbing composites. The present work opens a new avenue for designing heterogeneous interface to realize strengthened microwave absorption capability and also reveals the in-depth influence of interface structure on electromagnetic wave absorption.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, Z. C.; Cheng, H. W.; **, C.; Yang, B. T.; Xu, C. Y.; Pei, K.; Zhang, H. B.; Yang, Z. Q.; Che, R. C. Dimensional design and core-shell engineering of nanomaterials for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107538.
Shu, J. C.; Cao, W. Q.; Cao, M. S. Diverse metal-organic framework architectures for electromagnetic absorbers and shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100470.
Wei, Q. W.; Pei, S. F.; Qian, X. T.; Liu, H. P.; Liu, Z. B.; Zhang, W. M.; Zhou, T. Y.; Zhang, Z. C.; Zhang, X. F.; Cheng, H. M. et al. Super high electromagnetic interference shielding of ultrathin aligned pristine graphene nanosheets film. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907411.
Han, Y. X.; Ruan, K. P.; Gu, J. W. Janus (BNNS/ANF)-(AgNWs/ANF) thermal conductivity composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating performances. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 4747–4755.
Wang, L.; Li, X.; Li, Q. Q.; Yu, X. F.; Zhao, Y. H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Che, R. C. Oriented polarization tuning broadband absorption from flexible hierarchical ZnO arrays vertically supported on carbon cloth. Small 2019, 15, 1900900.
Liu, P. B.; Gao, S.; Zhang, G. Z.; Huang, Y.; You, W. B.; Che, R. C. Hollow engineering to Co@N-doped carbon nanocages via synergistic protecting-etching strategy for ultrahigh microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102812.
Sun, X.; Pu, Y. H.; Wu, F.; He, J. Z.; Deng, G.; Song, Z. M.; Liu, X. F.; Shui, J. L.; Yu, R. H. 0D-1D-2D multidimensionally assembled Co9S8/CNTs/MoS2 composites for ultralight and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130132.
Li, T.; Zhi, D. D.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, Z. W.; Meng, F. B. Multiaxial electrospun generation of hollow graphene aerogel spheres for broadband high-performance microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 477–484.
Qin, M.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105553.
Liu, Y.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhan, Q. Q.; Dong, Y. H.; Xu, Q. M.; Wu, G. L. Magnetic manganese-based composites with multiple loss mechanisms towards broadband absorption. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5590–5600.
Lv, H. P.; Wu, C.; Tang, J.; Du, H. F.; Qin, F. X.; Peng, H. X.; Yan, M. Two-dimensional SnO/SnO2 heterojunctions for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128445.
Wang, L.; Du, Z.; Bai, X. Y.; Lin, Y. Constructing macroporous C/Co composites with tunable interfacial polarization toward ultra-broadband microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 591, 76–84.
Liang, D.; Lian, C.; Xu, Q. C.; Liu, M. M.; Liu, H. L.; Jiang, H.; Li, C. Z. Interfacial charge polarization in Co2P2O7@N, P co-doped carbon nanocages as Mott-Schottky electrocatalysts for accelerating oxygen evolution reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 268, 118417.
Wu, Z. C.; **, C.; Yang, Z. Q.; Che, R. C. Integrating hierarchical interfacial polarization in yeast-derived Mo2C/C nanoflower/microsphere nanoarchitecture for boosting microwave absorption performance. Carbon 2022, 189, 530–538.
Ding, J. J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y. H.; **ng, L. S.; Yu, X. F.; Chen, G. Y.; Zhang, J.; Che, R. C. Boosted interfacial polarization from multishell TiO2@Fe3O4@PPy heterojunction for enhanced microwave absorption. Small 2019, 15, 1902885.
Zhao, Z. H.; Kou, K. C.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Optimal particle distribution induced interfacial polarization in bouquet-like hierarchical composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2022, 186, 323–332.
Liang, L. L.; Song, G.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J. P.; **e, L. J.; Jia, H.; Kong, Q. Q.; Sun, G. H.; Chen, C. M. Constructing Ni12P5/Ni2P heterostructures to boost interfacial polarization for enhanced microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 52208–52220.
Huang, W. H.; Gao, W. M.; Zuo, S. W.; Zhang, L. X.; Pei, K.; Liu, P. B.; Che, R. C.; Zhang, H. B. Hollow MoC/NC sphere for electromagnetic wave attenuation: Direct observation of interfacial polarization on nanoscale hetero-interfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 1290–1298.
Li, Z. H.; Xu, B. G.; Han, J.; Huang, J. X.; Chung, K. Y. Interfacial polarization and dual charge transfer induced high permittivity of carbon dots-based composite as humidity-resistant tribomaterial for efficient biomechanical energy harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101294.
Yang, H. Q.; Wang, B. D.; Kou, S. Q.; Lu, G. L.; Liu, Z. N. Mottschottky heterojunction of Co/Co2P with built-in electric fields for bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis and zinc-air battery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131589.
Sun, Y. K.; Liu, T.; Li, Z. J.; Meng, A. L.; Li, G. C.; Wang, L.; Li, S. X. Morphology and interfacial charge regulation strategies constructing 3D flower-like Co@CoP2 heterostructure electrocatalyst for efficient overall water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133684.
Liang, L. Y.; Li, Q. M.; Yan, X.; Feng, Y. Z.; Wang, Y. M.; Zhang, H. B.; Zhou, X. P.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y.; **e, X. L. Multifunctional magnetic Ti3C2Tx MXene/graphene aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6622–6632.
Zeng, Z. H.; Wang, C. X.; Siqueira, G.; Han, D. X.; Huch, A.; Abdolhosseinzadeh, S.; Heier, J.; Nüesch, F.; Zhang, C. F.; Nyström, G. Nanocellulose-MXene biomimetic aerogels with orientationtunable electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000979.
Li, Y.; Liu, X. F.; Nie, X. Y.; Yang, W. W.; Wang, Y. D.; Yu, R. H.; Shui, J. L. Multifunctional organic-inorganic hybrid aerogel for self-cleaning, heat-insulating, and highly efficient microwave absorbing material. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807624.
Huang, W. H.; Zhang, X. X.; Zhao, Y. N.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P. B. Hollow N-doped carbon polyhedra embedded Co and Mo2C nanoparticles for high-efficiency and wideband microwave absorption. Carbon 2020, 167, 19–30.
Quan, B.; Liang, X. H.; Ji, G. B.; Zhang, Y. N.; Xu, G. Y.; Du, Y. W. Cross-linking-derived synthesis of porous CoxNiy/C nanocomposites for excellent electromagnetic behaviors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 38814–38823.
Chen, T.; Guo, S. Q.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y. D.; Sun, J.; Wei, D. L.; Chen, Z. X.; Zhao, B.; Ding, W. P. Nitrogen-doped carbon activated in situ by embedded nickel through the Mott—Schottky effect for the oxygen reduction reaction. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 3454–3461.
Sun, Z. H.; Wang, Y. K.; Zhang, L. B.; Wu, H.; **, Y. C.; Li, Y. H.; Shi, Y. C.; Zhu, T. X.; Mao, H.; Liu, J. M. et al. Simultaneously realizing rapid electron transfer and mass transport in jellyfish-like Mott-Schottky nanoreactors for oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910482.
Wu, Z. C.; Pei, K.; **ng, L. S.; Yu, X. F.; You, W. B.; Che, R. C. Enhanced microwave absorption performance from magnetic coupling of magnetic nanoparticles suspended within hierarchically tubular composite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901448.
**ong, Y.; Xu, L. L.; Yang, C. X.; Sun, Q. F.; Xu, X. J. Implanting FeCo/C nanocages with tunable electromagnetic parameters in anisotropic wood carbon aerogels for efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 18863–18871.
Huang, M. Q.; Wang, L.; Pei, K.; You, W. B.; Yu, X. F.; Wu, Z. C.; Che, R. C. Multidimension-controllable synthesis of MOF-derived Co@N-doped carbon composite with magnetic-dielectric synergy toward strong microwave absorption. Small 2020, 16, 2000158.
Liu, P. B.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; He, W. J.; Huang, W. H.; Luo, J. H. Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122653.
Li, M. H.; Zhu, W. J.; Li, X.; Xu, H. L.; Fan, X. M.; Wu, H. J.; Ye, F.; Xue, J. M.; Li, X. Q.; Cheng, L. F. et al. Ti3C2Tx/MoS2 self-rolling rod-based foam boosts interfacial polarization for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2201118.
Wang, H. Y.; Jiao, Y. K.; Wang, S. J.; Ye, P. C.; Ning, J. Q.; Zhong, Y. J.; Hu, Y. Accelerating triple transport in zinc-air batteries and water electrolysis by spatially confining Co nanoparticles in breathable honeycomb-like macroporous N-doped carbon. Small 2021, 17, 2103517.
Pan, J. J.; Sun, X.; **, Z. Z.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Q. L.; Qu, H. J.; He, J. P. Constructing two-dimensional lamellar monometallic carbon nanocomposites by sodium chloride hard template for lightweight microwave scattering and absorption. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2022, 228, 109422.
Liu, S. H.; Wang, Z. Y.; Zhou, S.; Yu, F. J.; Yu, M. Z.; Chiang, C. Y.; Zhou, W. Z.; Zhao, J. J.; Qiu, J. S. Metal-organic-framework-derived hybrid carbon nanocages as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700874.
Pan, Y.; Sun, K. A.; Liu, S. J.; Cao, X.; Wu, K. L.; Cheong, W. C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Q. et al. Core—shell ZIF-8@ZIF-67-derived CoP nanoparticle-embedded N-doped carbon nanotube hollow polyhedron for efficient overall water splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2610–2618.
Zhu, C. Q.; Zhao, S. F.; Fan, Z. W.; Wu, H. D.; Liu, F. Q.; Chen, Z. X.; Li, A. M. Confinement of CoP nanoparticles in nitrogen-doped yolk-shell porous carbon polyhedron for ultrafast catalytic oxidation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003947.
Zhang, C. L.; **e, Y.; Liu, J. T.; Cao, F. H.; Cong, H. P.; Li, H. 1D core-shell MOFs derived CoP nanoparticles-embedded N-doped porous carbon nanotubes anchored with MoS2 nanosheets as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129977.
Hao, Y. R.; Xue, H.; Sun, J.; Guo, N. K.; Song, T. S.; Sun, J. W.; Wang, Q. Tuning the electronic structure of CoP embedded in N-doped porous carbon nanocubes via Ru do** for efficient hydrogen evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 56035–56044.
Qian, X.; Zhang, Y. H.; Wu, Z. C.; Zhang, R. X.; Li, X. H.; Wang, M.; Che, R. C. Multi-path electron transfer in 1D double-shelled Sn@Mo2C/C tubes with enhanced dielectric loss for boosting microwave absorption performance. Small 2021, 17, 2100283.
Zhao, H. H.; Xu, X. Z.; Wang, Y. H.; Fan, D. G.; Liu, D. W.; Lin, K. F.; Xu, P.; Han, X. J.; Du, Y. C. Heterogeneous interface induced the formation of hierarchically hollow carbon microcubes against electromagnetic pollution. Small 2020, 16, 2003407.
Wang, B. J.; Li, S. K.; Huang, F. Z.; Wang, S. P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F. H.; Liu, Q. C. Construction of multiple electron transfer paths in 1D core-shell hetetrostructures with MXene as interlayer enabling efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 2022, 187, 56–66.
Huang, T.; Wu, Z. C.; Yu, Q.; Tan, D. G.; Li, L. Preparation of hierarchically porous carbon/magnetic particle composites with broad microwave absorption bandwidth. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 69–78.
Xu, J.; Shi, Y. N.; Zhang, X. C.; Yuan, H. R.; Li, B.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, X. T.; Chen, Y. J. General strategy for fabrication of N-doped carbon nanotube/reduced graphene oxide aerogels for dissipation and conversion of electromagnetic energy. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 7847–7857.
Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, H. R.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, X. T.; Chen, Y. J. N-doped reduced graphene oxide aerogels containing pod-like N-doped carbon nanotubes and FeNi nanoparticles for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2020, 159, 357–365.
Wu, F.; Yang, K.; Li, Q.; Shah, T.; Ahmad, M.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Zhang, B. L. Biomass-derived 3D magnetic porous carbon fibers with a helical/chiral structure toward superior microwave absorption. Carbon 2021, 173, 918–931.
Wang, P.; Qi, J.; Li, C.; Li, W. P.; Wang, T. H.; Liang, C. H. Hierarchical CoNi2S4@NiMn-layered double hydroxide heterostructure nanoarrays on superhydrophilic carbon cloth for enhanced overall water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 345, 136247.
Wei, Y.; Liu, H. J.; Liu, S. C.; Zhang, M. M.; Shi, Y. P.; Zhang, J. W.; Zhang, L.; Gong, C. H. Waste cotton-derived magnetic porous carbon for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 9, 70–75.
Zhang, C.; Wu, Z. C.; Xu, C. Y.; Yang, B. T.; Wang, L.; You, W. B.; Che, R. C. Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/carbon nanotubes hollow microsphere with confined magnetic nanospheres for broadband microwave absorption. Small 2022, 18, 2104380.
Wang, S. J.; Li, D. S.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L. Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/Ni chain/ZnO array hybrid nanostructures on cotton fabric for durable self-cleaning and enhanced microwave absorption. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8634–8645.
Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. C.; Deng, B. W.; Cai, L.; Dong, Y. Y.; Zhu, X. J.; Lu, W. Honeycomb-like NiCo2O4@MnO2 nanosheets array/3D porous expanded graphite hybrids for high-performance microwave absorber with hydrophobic and flame-retardant functions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129547.
Gao, Z. G.; Lan, D.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Simultaneous manipulation of interfacial and defects polarization toward Zn/Co phase and ion hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106677.
Liu, D. W.; Du, Y. C.; Wang, F. Y.; Wang, Y. H.; Cui, L. R.; Zhao, H. H.; Han, X. J. MOFs-derived multi-chamber carbon microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 2020, 157, 478–485.
Yang, K.; Cui, Y. H.; Wan, L. Y.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Zhang, B. L. MOF-derived magnetic-dielectric balanced Co@ZnO@ N-doped carbon composite materials for strong microwave absorption. Carbon 2022, 190, 366–375.
Cao, M. S.; Wang, X. X.; Cao, W. Q.; Fang, X. Y.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. Thermally driven transport and relaxation switching self-powered electromagnetic energy conversion. Small 2018, 1800987.
Xu, Z. X.; **, S.; Seo, M. H.; Wang, X. L. Hierarchical Ni-Mo2C/N-doped carbon Mott-Schottky array for water electrolysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 292, 120168.
Huang, Y.; Yan, H. T.; Zhang, C. Y.; Wang, Y. Z.; Wei, Q. H.; Zhang, R. K. Interfacial electronic effects in Co@N-doped carbon shells heterojunction catalyst for semi-hydrogenation of phenylacetylene. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2776.
Xu, X. F.; Shi, S. H.; Tang, Y. L.; Wang, G. Z.; Zhou, M. F.; Zhao, G. Q.; Zhou, X. C.; Lin, S. W.; Meng, F. B. Growth of NiAl-layered double hydroxide on graphene toward excellent anticorrosive microwave absorption application. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002658.
Xu, Z. J.; He, M.; Zhou, Y. M.; Nie, S. X.; Wang, Y. J.; Huo, Y.; Kang, Y. F.; Wang, R. L.; Xu, R.; Peng, H. et al. Spider web-like carbonized bacterial cellulose/MoSe2 nanocomposite with enhanced microwave attenuation performance and tunable absorption bands. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 738–746.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51872002 and 52172174), Open Project of Provincial and Ministerial Scientific Research Platform, and Fuyang Normal University (No. FSKFKT009D). The authors acknowledge the support from Joint Laboratory of Electromagnetic Material Structure Design and Advanced Stealth Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4779_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Enhanced interfacial polarization of defective porous carbon confined CoP nanoparticles forming Mott—Schottky heterojunction for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Huang, F., Wu, H. et al. Enhanced interfacial polarization of defective porous carbon confined CoP nanoparticles forming Mott—Schottky heterojunction for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 16, 4160–4169 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4779-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4779-3