Abstract
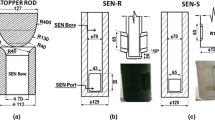
Nozzle shape plays a key role in determining the flow pattern in the mold of the continuous- casting process under both steady-state and transient conditions. This work applies computational models and experiments with a one-third scale water model to characterize flow in the nozzle and mold to evaluate well-bottom and mountain-bottom nozzle performance. Velocities predicted with the three-dimensional k-ε turbulence model agree with both particle- image velocimetry and impeller measurements in the water model. The steady-state jet velocity and angle leaving the ports is similar for the two nozzle-bottom designs. However, the results show that nozzles with a mountain-shaped bottom are more susceptible to problems from asymmetric flow, low-frequency surface-flow variations, and excessive surface velocities. The same benefits of the well-bottom nozzle are predicted for flow in the steel caster.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.G. Thomas: in Making, Sha** and Treating of Steel, 11th ed., vol. 5, Casting volume, A. Cramb, ed., AISE Steel Foundation, Pittsburgh, PA, 2003, pp. 14.1–14.41
J. Kubota, K. Okimoto, A. Shirayama, and H. Murakami: Steelmaking Conf. Proc., Iron and Steel Society, Warrendale, PA, 1991, vol. 74, pp. 233–41
M.B. Assar, P.H. Dauby, G.D. Lawson: Steelmaking Conf. Proc., ISS, Warrendale, PA, 2000, pp. 397–411
D. Gupta, A.K. Lahiri: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1996, vol. 27B, pp. 757–64
D. Gupta, A.K. Lahiri: Steel Res., 1992, vol. 63 (5), pp. 201–04
B.G. Thomas, X. Huang, R.C. Sussman: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1994, vol. 25B, pp. 527–47
B.G. Thomas, L. Zhang: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41 (10), pp. 1181–93
T. Honeyands, J. Herbertson: Steel Res., 1995, vol. 66 (7), pp. 287–93
N.J. Lawson, M.R. Davidson: J. Fluids Eng., 2002, vol. 124 (2), pp. 535–43
D. Xu, W.K. Jones, J.W. Evans: in Processing of Metals and Advanced Materials: Modeling, Design and Properties, B.Q. Li, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1998, pp. 3–14
S. Sivaramakrishnan, B.G. Thomas, S.P. Vanka: in Materials Processing in the Computer Age, V. Voller, H. Henein, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2000, pp. 189–98
H. Bai, B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 253–67
H. Bai, B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32B, pp. 269–84
D.E. Hershey, B.G. Thomas, F.M. Najjar: Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids, 1993, vol. 17 (1), pp. 23–47
F.M. Najjar, B.G. Thomas, D.E. Hershey: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1995, vol. 26B, pp. 749–65
B.G. Thomas, L.J. Mika, F.M. Najjar: Metall. Trans. B, 1990, vol. 21B, pp. 387–400
X. Huang, B.G. Thomas: Can. Metall. Q., 1998, vol. 37 (3–4), pp. 197–212
K. Takatani, Y. Tanizawa, H. Mizukami, and K. Nishimura: ISIJ Int.., 2001, vol. 41 (10), pp. 1252–61
Q. Yuan, B.G. Thomas, S.P. Vanka: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 685–702
Q. Yuan, S. Sivaramakrishnan, S.P. Vanka, and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B (5), pp. 967–82
B.G. Thomas, Q. Yuan, S. Sivaramakrishnan, T. Shi, S.P. Vanka, and M.B. Assar: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41 (10), pp. 1262–71
H. Versteeg, W. Malalasekra: An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Finite Volume Method Approach, Longman Scientific Technical, Essex, United Kingdom, 1995
B.E. Launder, D.B. Spalding: Mathematical Models of Turbulence, Academic Press, London, 1972
B.G. Thomas: in Making, Sha** and Treating of Steel, A.W. Cramb, ed., AISE Steel Foundation, Pittsburgh, PA, 2003
Y.A. Meng, B.G. Thomas: Metall. Trans. B, 2003, vol. 34B, pp. 685–705
B.T. Rietow: Master’s Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, Urbana, IL, 2007
D. Creech: Master’s Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, Urbana, IL, 1999
FLUENT6.3-Manual, ANSYS Inc., Lebanon, NH, 2007
G.A. Panaras, A. Theodorakakos, G. Bergeles: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1998, vol. 29B, pp. 1117–26
B.E. Launder, D.B. Spalding: Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng., 1974, vol. 3 (2), pp. 269–89
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Young-** Jeon and Professor Hyung-** Sung, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KAIST (South Korea), and Seong-Mook Cho, POSTECH (South Korea), for help with the PIV measurements. They also thank POSCO, Oh-Duck Kwon, Shin-Eon Kang, and POSCO Technical Research Laboratories for relevant data and providing the water model and ANSYS Inc. for supplying FLUENT. Support from the Continuous Casting Consortium, University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, POSCO, South Korea (Grant No. 4.0002397.01) and the National Science Foundation (Grant No. DMI 05-00453) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 17, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, R., Lee, GG., Thomas, B. et al. Transient Mold Fluid Flow with Well- and Mountain-Bottom Nozzles in Continuous Casting of Steel. Metall Mater Trans B 39, 870–884 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9192-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-008-9192-0