Abstract
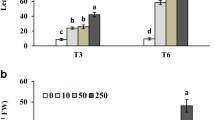
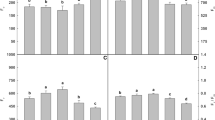
The effects of Zinc (Zn) on lipid peroxidation, antioxidative enzymes, growth, Zn accumulation, and leaf chlorophyll of Phyllostachys pubescens (Pradelle) Mazel ex J.Houz. were investigated in two greenhouse experiments. Hydroponics experiment with Zn application of 0, 20, 100, and 400 μM revealed that lower concentration of Zn in solution led to increased malondialdehyde (MDA) and proline contents but inhibited SOD activity in all treatments. P. pubescens had showed strong ability to accumulate Zn in stems and reached maximum level at 100 μM with 7.91-fold increase compared with control. In pot experiment, treatment with Zn ranged from 0, 200, 400, 800, 1,600, to 3,200 mg kg−1. Application of 800 mg kg−1 revealed 116, 24.6, and 28.3 times increase in Zn concentration of roots, stems, and leaves, respectively. Growth and chlorophyll contents of plants in pots were better promoted at 400 mg kg−1 Zn, with 60.5 and 30.9 % enhanced roots and shoot compared with control. The bioaccumulation factor (BAF) was in the sequence of stem > roots > leaves. The translocation factor (TF) of stem was higher than leaves.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aibibu N, Liu Y, Zeng G et al (2010) Cadmium accumulation in Vetiveria zizanioides and its effects on growth, physiological and biochemical characters. Bioresour Technol 101:6297–6303
Andrade SA, Gratão PL, Schiavinato MA et al (2009) Zn uptake, physiological response and stress attenuation in mycorrhizal jack bean growing in soil with increasing Zn concentration. Chemosphere 75:1363–1370
Baccouch S, Chaoui A, Ferjani EE et al (1998) Nickel-induced oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in Zea mays shoots. Plant Physiol Biochem 36:689–694
Cambrollé J, MancillaLeytón JM, MuñozVallés S et al (2012) Zinc tolerance and accumulation in the salt-marsh shrub Halimione portulacoides. Chemosphere 86:867–874
Candan N, Tarhan L (2003) The correlation between antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation levels in Mentha pulegium organs grown in Ca2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ and Mn2+ stress conditions. Plant Sci 165:769–776
Choudhary M, Jetley UK, Abash KM et al (2007) Effect of heavy metal stress on proline, malondialdehyde, and superoxide dismutase activity in the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis-S5. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66:204–209
Dazy M, Masfaraud JF, Férard JF (2009) Induction of oxidative stress biomarkers associated with heavy metal stress in Fontinalis antipyretica Hedw. Chemosphere 75:297–302
Dinh NT, Vu DT, Mulligan D, Nguyen AV (2015) Accumulation and distribution of zinc in the leaves and roots of the hyperaccumulator Noccaea caerulescens. Environ Exp Bot 110:85–95
Environmental Protection Report to the 11th National People’s Congress of China (2011): Environmental Protection Report to the 11th National People’s Congress of China
Fridovich I (1986) Biological effects of the superoxide radical. Arch Biochem Biophys 247:1–11
Gajewska E, Skłodowska M (2005) Antioxidative responses and proline level in leaves and roots of pea plants subjected to nickel stress. Acta Physiol Plant 27:329–340
Garbisu C, Alkorta I (2001) Phytoextraction: a cost-effective plant-based technology for the removal of metals from the environment. Bioresour Technol 77:229–236
Giannopolits CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Hu P-J, Qiu R-L, Senthilkumar P et al (2009) Tolerance, accumulation and distribution of zinc and cadmium in hyperaccumulator Potentilla griffithii. Environ Exp Bot 66:317–325
Islam E, Liu D, Li T-Q et al (2008) Effect of Pb toxicity on leaf growth, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. J Hazard Mater 154:914–926
Islam F, Yasmeen T, Riaz M et al (2014) Proteus mirabilis alleviates zinc toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in maize (Zea mays) plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 110:143–152
Israr M, Jewell A, Kumar D, Sahi SV (2011) Interactive effects of lead, copper, nickel and zinc on growth, metal uptake and antioxidative metabolism of Sesbania drummondii. J Hazard Mater 186:1520–1526
Jain R, Srivastava S, Solomon S et al (2010) Impact of excess zinc on growth parameters, cell division, nutrient accumulation, photosynthetic pigments and oxidative stress of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). Acta Physiol Plant 32:979–986
Jiang H-M, Yang J-C, Zhang J-F (2007) Effects of external phosphorus on the cell ultrastructure and the chlorophyll content of maize under cadmium and zinc stress. Environ Pollut 147:750–756
Jiang J, Zhuang J-Y, Fan Y-Y, Shen B (2009) Map** of qtls for leaf malondialdehyde content associated with stress tolerance in rice. Rice Sci 16:72–74
Lasat MM, Pence NS, Garvin DF et al (2000) Molecular physiology of zinc transport in the Zn hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. J Exp Bot 51:71–79
Li M, Hu C-W, Zhu Q et al (2006) Copper and zinc induction of lipid peroxidation and effects on antioxidant enzyme activities in the microalga pavlova viridis (prymnesiophyceae). Chemosphere 62:565–572
Li J, Huang Z, Hu Y, Yang H (2013) Potential risk assessment of heavy metals by consuming shellfish collected from **amen, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2937–2947
Liu D, Chen J-R, Mahmood Q et al (2014) Effect of Zn toxicity on root morphology, ultrastructure, and the ability to accumulate Zn in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:13615–13624
Manios T, Stentiford EI, Millner PA (2003) The effect of heavy metals accumulation on the chlorophyll concentration of Typha latifolia plants, growing in a substrate containing sewage sludge compost and watered with metaliferus water. Ecol Eng 20:65–74
Meng Q-M, Zou J, Zou J-H et al (2007) Effect of Cu2+ concentration on growth, antioxidant enzyme activity and malondialdehyde content in garlic (Allium sativum L.). Acta Biol Cracov Bot 49:95–101
Nyitrai P, Bóka K, Gáspár L et al (2003) Characterization of the stimulating effect of low-dose stressors in maize and bean seedlings. J Plant Physiol 160:1175–1183
Ozdener Y, Aydin BK (2010) The effect of zinc on the growth and physiological and biochemical parameters in seedlings of Eruca sativa (L.) (Rocket). Acta Physiol Plant 32:469–476
Pence NS, Larsen PB, Ebbs SD et al (2000) The molecular physiology of heavy metal transport in the Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4956–4960
Porra RJ, Thompson WA, Kriedemann PE (1989) Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Res Gate 975:384–394
Robinson BH, Ieblanc M, Petit D et al (1998) The potential of Thlaspi caerulescens for phytoremediation of contaminated soils. Plant Soil 203:47–56
Rossi G, Figliolia A, Socciarelli S et al (2002) Capability of brassica napus to accumulate cadmium, zinc and copper from soil. Acta Biotechnol 22:133–140
Saison C, PerrinGanier C, Amellal S et al (2004) Effect of metals on the adsorption and extractability of 14C-phenanthrene in soils. Chemosphere 55:477–485
Saradhi PP (1991) Proline accumulation under heavy metal stress. J Plant Physiol 138:554–558
Scalet M, Federico R, Guido MC et al (1995) Peroxidase activity and polyamine changes in response to ozone and simulated acid rain in Aleppo pine needles. Environ Exp Bot 35:417–425
Schat H, Sharma SS, Vooijs R (1997) Heavy metal-induced accumulation of free proline in a metal-tolerant and a nontolerant ecotype of Silene vulgaris. Physiol Plant 101:477–482
Schneider T, Persson DP, Husted S et al (2013) A proteomics approach to investigate the process of Zn hyperaccumulation in Noccaea caerulescens (J & C. Presl) F.K. Meyer. Plant J 73:131–142
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2009) The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci 14:43–50
Song X-Z, Peng C-H, Zhou G-M et al (2013) Climate warming-induced upward shift of Moso bamboo population on Tianmu Mountain, China. J Mt Sci 10:363–369
Sun Y-B, Zhou Q-X, Wei S-H et al (2007) Growth responses of the newly-discovered Cd-hyperaccumulator Rorippa globosa and its accumulation characteristics of Cd and as under joint stress of Cd and As. Front Environ Sci Eng China 1:107–113
Tang Y-T, Qiu R-L, Zeng X-W et al (2009) Lead, zinc, cadmium hyperaccumulation and growth stimulation in Arabis paniculata Franch. Environ Exp Bot 66:126–134
Teng Y-G, Wu J, Lu S-J et al (2014) Soil and soil environmental quality monitoring in China: a review. Environ Int 69:177–199
Upadhyay R, Panda SK (2010) Zinc reduces copper toxicity induced oxidative stress by promoting antioxidant defense in freshly grown aquatic duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza L. J Hazard Mater 175:1081–1084
Van AF, Clijsters H (1990) A biological test system for the evaluation of the phytotoxicity of metal-contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 66:157–172
Verma S, Dubey RS (2003) Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Sci 164:645–655
Wenzel WW, Jockwer F (1999) Accumulation of heavy metals in plants grown on mineralized soils of the Austrian Alps. Environ Pollut 104:145–155
Xu Q-S, Qiu H, Chu W-Y et al (2013) Copper ultrastructural localization, subcellular distribution, and phytotoxicity in Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8672–8679
Yang X-E, Long X-X, Ni W-Z et al (2002) Sedum alfredii H: a new Zn hyperaccumulating plant first found in China. Chin Sci Bull 47:1634–1637
Yang B, Shu W-S, Ye Z-H et al (2003) Growth and metal accumulation in vetiver and two Sesbania species on lead/zinc mine tailings. Chemosphere 52:1593–1600
Zhang L, Ye Z-Q, Li T-Q, Yang X-E (2006) Studies on soil microbial activity in areas contaminated by tailings from Pb/Zn mine. J Soil Water Conserv 20:136–140
Zhang F-Q, Wang Y-S, Lou Z-P et al (2007) Effect of heavy metal stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of two mangrove plant seedlings (Kandelia candel and Bruguiera gymnorrhiza). Chemosphere 67:44–50
Zhong B-Q, Liang T, Wang L-Q et al (2014) Applications of stochastic models and geostatistical analyses to study sources and spatial patterns of soil heavy metals in a metalliferous industrial district of China. Sci Total Environ 490:422–434
Zhuang P, McBride MB, **a H-P et al (2009) Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Sci Total Environ 407:1551–1561
Acknowledgements
The study was financially supported through a grant from the Natural Science Foundation of China (31300520), Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province (2014C33043), Science Technology department of Zhejiang province (2013C33016), and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY12C16004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, D., Shafi, M., Wang, Y. et al. Effect of Zn stresses on physiology, growth, Zn accumulation, and chlorophyll of Phyllostachys pubescen s . Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 14983–14992 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4692-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4692-3