Abstract
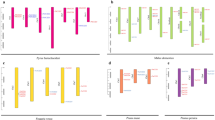
Novel expressed and genomic members in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis [L.] Osbeck) carotenoid biosynthesis gene families have been identified through mining of an expressed sequence tags (ESTs) database and hybridization with a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library. These new expressed members included one phytoene synthase (PSY), one phytoene desaturase (PDS), ten zeta-carotene desaturases (ZDS), one lycopene beta-cyclase (LCYB), one lycopene epsilon-cyclase (LCYE), four carotenoid beta-ring hydroxylases (CHYB), and one capsanthin/capsorubin synthase (CCS). Most unigenes with multiple ESTs, including the ones containing the known genes and these new members, were heterozygous, in which putative single nucleotide polymorphisms distinguished two alleles. According to digital gene expression profiling, fruit was the primary tissue where at least one member of each gene family was specifically or highly expressed. Digital expression levels varied among the members and tissues. According to Southern hybridization of the identified BAC clones, genomic members of the families were either clustered in a single BAC contig or distributed in several different contigs. PSY has four members in one contig, PDS two in one, ZDS 12 in three, LCYB 11 in three, LCYE three in two, CHYB eight in one, and CCS 14 in four, respectively. The number of the genomic members in most families tended to be more than that of the expressed members, suggesting that some genomic members may not be expressed or structurally functional. These new carotenoid gene members, along with much first-hand genomic information, can be used further for functional genomics and genetic map**.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alquezar B, Zacarias L, Rodrigo MJ (2009) Molecular and functional characterization of a novel chromoplast-specific lycopene beta-cyclase from Citrus and its relation to lycopene accumulation. J Exp Bot 60:1783–1797
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bartley GE, Scolnik PA (1993) cDNA cloning, expression during development, and genome map** of PSY2, a second tomato gene encoding phytoene synthase. J Biol Chem 268:25718–25721
Busch M, Seuter A, Hain R (2002) Functional analysis of the early steps of carotenoid biosynthesis in tobacco. Plant Physiol 128:439–453
Cai WW, Reneker J, Chow CW, Vaishnav M, Bradley A (1998) An anchored framework BAC map of mouse chromosome 11 assembled using multiplex oligonucleotide hybridization. Genomics 54:387–397
Close TJ, Wanamaker S, Lyon M, Mei GW, Davies C, Mikeal L Roose ML (2006) A GeneChip For Citrus. In: Plant & Animal Genomes XIV Conf, San Diego, CA, USA, W82
Cunningham FX, Gantt E (1998) Genes and enzymes of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:557–583
Deng Z, Tao Q, Chang Y-L, Huang S, Ling P, Yu C, Chen C, Gmitter FG Jr, Zhang H-B (2001) Construction of a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library for citrus and identification of BAC contigs containing resistance gene candidates. Theor Appl Genet 102:1177–1184
Ewing B, Green P (1998) Basecalling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res 8:186–194
Fanciullino A-L, Dhuique-Mayer C, Luro F, Casanova J, Morillon R, Ollitrault P (2006) Carotenoid diversity in cultivated citrus is highly influenced by genetic factors. J Agric Food Chem 54:4397–4406
Fanciullino A-L, Dhuique-Mayer C, Luro F, Morillon R, Ollitrault P (2007) Carotenoid biosynthetic pathway in the Citrus genus: number of copies and phylogenetic diversity of seven genes. J Agric Food Chem 55:7405–7417
Fanciullino A-L, Cercos M, Dhuique-Mayer C, Froelicher Y, Talon M, Ollitrault P, Morillon R (2008) Changes in carotenoid content and biosynthetic gene expression in juice sacs of four orange varieties (Citrus sinensis) differing in flesh fruit color. J Agric Food Chem 56:3628–3638
Feng J, Vick BA, Lee M-K, Zhang H-B, Jan CC (2006) Construction of BAC and BIBAC libraries from sunflower and identification of linkage group-specific clones by overgo hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 113:23–32
Fraser PD, Bramley PM (2004) The biosynthesis and nutritional uses of carotenoids. Prog Lipid Res 43:228–265
Galpaz N, Ronen G, Khalfa Z, Zamir D, Hirschberg J (2006) A chromoplast-specific carotenoid biosynthesis pathway is revealed by cloning of the tomato white-flower locus. Plant Cell 18:1947–1960
Gardiner J, Schroeder S, Polacco ML, Sanchez-Villeda H, Fang ZW, Morgante M, Landewe T, Fengler K, Useche F, Hanafey M, Tingey S, Chou H, Wing R, Soderlund C, Coe EH Jr (2004) Anchoring 9, 371 maize expressed sequence tagged unigenes to the bacterial artificial chromosome contig map by two-dimensional overgo hybridization. Plant Physiol 134:1317–1326
Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P (1998) Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res 8:195–202
Gross J (1987) Carotenoids: pigments in fruits. Academic Press, London
Inoue K, Furbee KJ, Uratsu S, Kato M, Dandekar AM, Ikoma Y (2006) Catalytic activities and chloroplast import of carotenogenic enzymes from citrus. Physiol Plant 127(4):561–570
Just BJ, Santos CAF, Fonseca MEN, Boiteux LS, Oloizia BB, Simon PW (2007) Carotenoid biosynthesis structural genes in carrot (Daucus carota): isolation, sequence-characterization, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers and genome map**. Theor Appl Genet 114:693–704
Kato M, Ikoma Y, Matsumoto H, Sugiura M, Hyodo H, Yano M (2004) Accumulation of carotenoids and expression of carotenoid biosynthetic genes during maturation in citrus fruit. Plant Physiol 134:824–837
Keilin T, Pang X, Venkateswari J, Halaly T, Crane O, Keren A, Ogrodovitch A, Ophir R, Volpin H, Galbraith D, Or E (2007) Digital expression profiling of a grape-bud EST collection leads to new insight into molecular events during grape-bud dormancy release. Plant Sci 173:446–457
Lange BM, Ghassemian M (2003) Genome organization in Arabidopsis thaliana: a survey for genes involved in isoprenoid and chlorophyll metabolism. Plant Mol Biol 51:925–948
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Li F, Vallabhaneni R, Wurtzel ET (2008) PSY3, a new member of phytoene synthase gene family conserved in the Poaceae and regulator of abiotic stress-induced root carotenogenesis. Plant Physiol 146:1333–1345
Livingstone K, Anderson S (2009) Patterns of variation in the evolution of carotenoid biosynthetic pathway enzymes of higher plants. J Hered. doi:10.1093/jhered/esp026
Lu Y, Rausher MD (2003) Evolutionary rate variation in anthocyanin pathway genes. Mol Biol Evol 20:1844–1853
Luo M-C, Thomas C, You FM, Hsiao J, Ouyang S, Buell CR, Malandro M, McGuire PE, Anderson OD, Dvorak J (2003) High-throughput fingerprinting of bacterial artificial chromosomes using the SNaPshot labeling kit and sizing of restriction fragments by capillary electrophoresis. Genomics 82:378–389
Matthews PD, Luo RB, Wurtzel ET (2003) Maize phytoene desaturase and ζ-carotene desaturase catalyse a poly-Z desaturation pathway: implications for genetic engineering of carotenoid content among cereal crops. J Exp Bot 54:2215–2230
Nickerson DA, Tobe VO, Taylor SL (1997) PolyPhred: automating the detection and genoty** of single nucleotide substitutions using fluorescence-based resequencing. Nucleic Acids Res 25:2745–2751
Page RDM (1996) TREEVIEW: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Pozniak CJ, Knox RE, Clarke FR, Clarke JM (2007) Identification of QTL and association of a phytoene synthase gene with endosperm colour in durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 114:525–537
Rodrigo M-J, Marcos JF, Zacarias L (2004) Biochemical and molecular analysis of carotenoid biosynthesis in flavedo of orange (Citrus sinensis L.) during fruit development and maturation. J Agric Food Chem 52:6724–6731
Romer S, Hugueney P, Bouvier F, Camara B, Kuntz M (1993) Expression of the genes encoding the early carotenoid biosynthetic enzymes in Capsicum annuum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 196:1414–1421
Ronen G, Cohen M, Zamir D, Hirschberg J (1999) Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis during tomato fruit development: expression of the gene for lycopene epsilon-cyclase is down-regulated during ripening and is elevated in the mutant Delta. Plant J 17:341–351
Ronen G, Carmel-Goren L, Zamir D, Hirschberg J (2000) An alternative pathway to beta-carotene formation in plant chromoplasts discovered by map-based cloning of beta and old-gold color mutations in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11102–11107
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols in the Series Methods in Molecular Biology. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 365–386
Song WY, Pi LY, Wang GL, Gardner J, Holsten T, Ronald PC (1997) Evolution of the rice Xa21 disease resistance gene family. Plant Cell 9:1279–1287
Stephens M, Sloan JS, Robertson PD, Scheet P, Nickerson DA (2006) Automating sequence-based detection and genoty** of SNPs from diploid samples. Nat Genet 38:375–381
Tao N-G, Xu J, Cheng Y-J, Deng X-X (2005) Lycopene-ε-cyclase pre-mRNA is alternatively spliced in Cara Cara navel orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck). Biotechnol Lett 27:779–782
The French-Italian Public Consortium for Grapevine Genome Characterization (2007) The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 449:463–467
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney RK, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:411–422
Velculescu VE, Kinzler KW (2007) Gene expression analysis goes digital. Nat Biotechnol 25:878–880
Welsch R, Wust F, Bar C, Al-Babili S, Beyer P (2008) A third phytoene synthase is devoted to abiotic stress-induced abscisic acid formation in rice and defines functional diversification of phytoene synthase genes. Plant Physiol 147:367–380
Wong JC, Lambert RJ, Wurtzel ET, Rocheford TR (2004) QTL and candidate gene phytoene synthase and ζ-carotene desaturase associated with the accumulation of carotenoids in maize. Theor Appl Genet 108:349–359
Wu X, Walker MG, Luo J, Wei L (2005) GBA server: EST-based digital gene expression profiling. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W673–W676
Xu CJ, Chen DM, Zhang SL (2001) Molecular cloning of full length capsanthin/capsorubin synthase homologous gene from orange (Citrus sinensis). Shi Yan Sheng Wu Xue Bao 34:147–150
Zhang Y, Luoh S-M, Hon LS, Baertsch R, Wood WI, Zhang ZM (2007) GeneHub-GEPIS: digital expression profiling for normal and cancer tissues based on an integrated gene database. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W152–W158
Zelena K, Hardebusch B, Hlsdau B, Berger RG, Zorn H (2009) Generation of norisoprenoid flavors from carotenoids by fungal peroxidases. J Agric Food Chem 57:9951–9955
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Drs. R. Niedz and M. Bausher (USDA-ARS, Fort Pierce) for access to the selected clones from the BAC library, Drs. M.-C. Luo and J. Dvorak (University of California, Davis) for access to the BAC library physical map, and Mrs. M. Wendell and M. Holt for their technical assistance. This research was supported in part by grants from the State of Bahia Research Foundation (FAPESB), Salvador, Brazil (to MGCC) and from the Florida Citrus Production Research Advisory Council (FCPRAC), Peter McClure, Chairman (to FGG). We gratefully acknowledge the ‘International Cooperation’ scholarship to MGCC by FAPESB (INT007/2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E. Dirlewanger
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 771 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Costa, M.G.C., Yu, Q. et al. Identification of novel members in sweet orange carotenoid biosynthesis gene families. Tree Genetics & Genomes 6, 905–914 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0300-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0300-3