Abstract
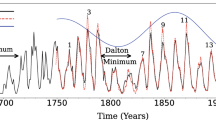
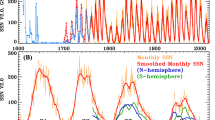
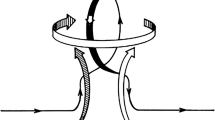
Reconstructions of past solar activity based on cosmogenic radioisotopes have reavealed that the Sun spends a significant fraction (\({\approx}\, 20\)%) of its time in aperiodically recurring states of so-called Grand Minima or Grand Maxima, namely epochs of strongly supressed and markedly above-average levels of magnetic activity, respectively. The physical origin of these episodes is not yet understood. In this article we present a dual-dynamo model of the solar cycle, combining a dominant dynamo based on differential-rotation shear and surface decay of bipolar active regions, and a weak, deep-seated turbulent dynamo. The resulting dynamo simulations are found to exhibit the equivalent of observed Grand Minima and Maxima. By adjusting the magnitude and saturation level of the secondary turbulent dynamo, we can reproduce well the duration and waiting-time distributions of Grand Minima and Maxima inferred from the cosmogenic-isotope record. The exit from Grand Minima episodes is typically characterized by strong hemispheric asymmetries, in agreement with sunspot observations during the 1645 – 1715 Maunder Minimum. In these simulations, Grand Maxima can be unambiguously identified as a distinct dual-dynamo state resulting from constructive interference between the two dynamos mechanisms operating within the simulation. This interaction leads to the autonomous production of long quasi-periodicities in the millennial range, commensurate with the Halstatt cycle. Such a quasi-periodic modulation, readily produced through dynamical backreaction on large-scale flows in non-kinematic dynamo models, is quite uncommon in a purely kinematic solar-cycle model such as the one developed herein. We argue that these long periodicities are set by the long diffusion time of magnetic field accumulating in the stable layers underlying the turbulent convection zone.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augustson, K., Brun, A.S., Miesch, M., Toomre, J.: 2015, Grand minima and equatorward propagation in a cycling stellar convective dynamo. Astrophys. J. 809, 149. DOI . ADS .
Baumann, I., Schmitt, D., Schüssler, M., Solanki, S.K.: 2004, Evolution of the large-scale magnetic field on the solar surface: a parameter study. Astron. Astrophys. 426, 1075. DOI . ADS .
Beer, J., Tobias, S., Weiss, N.: 1998, An active sun throughout the maunder minimum. Solar Phys. 181, 237. DOI . ADS .
Beer, J., Blinov, A., Bonani, G., Finkel, R.C., Hofmann, H.J., Lehmann, B., Oeschger, H., Sigg, A., Schwander, J., Staffelbach, T., Stauffer, B., Suter, M., Wötfli, W.: 1990, Use of Be-10 in polar ice to trace the 11-year cycle of solar activity. Nature 347, 164. DOI . ADS .
Bushby, P.J.: 2006, Zonal flows and grand minima in a solar dynamo model. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 371, 772. DOI . ADS .
Caligari, P., Moreno-Insertis, F., Schüssler, M.: 1995, Emerging flux tubes in the solar convection zone. 1: asymmetry, tilt, and emergence latitude. Astrophys. J. 441, 886. DOI . ADS .
Calim Costa, M.: 2013, WAIPY, wavelet analysis in Python.
Cameron, R.H., Schüssler, M.: 2012, Are the strengths of solar cycles determined by converging flows towards the activity belts? Astron. Astrophys. 548, A57. DOI . ADS .
Cameron, R.H., Schüssler, M.: 2017, Understanding solar cycle variability. Astrophys. J. 843, 111. DOI . ADS .
Cameron, R.H., Jiang, J., Schmitt, D., Schüssler, M.: 2010, Surface flux transport modeling for solar cycles 15 – 21: effects of cycle-dependent tilt angles of sunspot groups. Astrophys. J. 719, 264. DOI . ADS .
Charbonneau, P.: 2010, Dynamo models of the solar cycle. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys. 7, 3. DOI . ADS .
Charbonneau, P.: 2014, Solar dynamo theory. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 52, 251. DOI . ADS .
Charbonneau, P., Blais-Laurier, G., St-Jean, C.: 2004, Intermittency and phase persistence in a Babcock–Leighton model of the solar cycle. Astrophys. J. Lett. 616, L183. DOI . ADS .
Clauset, A., Shalizi, C.R., Newman, M.E.J.: 2009, Power-law distributions in empirical data. SIAM Rev. 51, 661. DOI . ADS .
Clette, F., Svalgaard, L., Vaquero, J.M., Cliver, E.W.: 2014, Revisiting the sunspot number. A 400-year perspective on the solar cycle. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 35. DOI . ADS .
Dikpati, M., Charbonneau, P.: 1999, A Babcock–Leighton flux transport dynamo with solar-like differential rotation. Astrophys. J. 518, 508. DOI . ADS .
D’Silva, S., Howard, R.F.: 1993, Limits on the magnetic field strength at the base of the solar convection zone. Solar Phys. 148, 1. DOI . ADS .
Eddy, J.A.: 1976, The Maunder minimum. Science 192, 1189. DOI . ADS .
Fan, Y.: 2009, The emergence of a twisted flux tube into the solar atmosphere: sunspot rotations and the formation of a coronal flux rope. Astrophys. J. 697, 1529. DOI . ADS .
Gibson, S.E., Zhao, L., Fisk, L.A.: 2011, The solar wind structure and heliospheric magnetic field in the solar Cycle 23 – 24 minimum and in the increasing phase of Cycle 24. In: AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, SH31D. ADS .
Gleissberg, W.: 1944, A secular change in the shape of the spot-frequency curve. Observatory 65, 244. ADS .
Hathaway, D.H.: 2009, Solar cycle forecasting. Space Sci. Rev. 144, 401. DOI . ADS .
Hazra, S., Passos, D., Nandy, D.: 2014, A stochastically forced time delay solar dynamo model: self-consistent recovery from a maunder-like grand minimum necessitates a mean-field alpha effect. Astrophys. J. 789, 5. DOI . ADS .
Inceoglu, F., Arlt, R., Rempel, M.: 2017, The nature of grand minima and maxima from fully nonlinear flux transport dynamos. Astrophys. J. 848, 93. DOI . ADS .
Inceoglu, F., Simoniello, R., Knudsen, M.F., Karoff, C., Olsen, J., Turck-Chiéze, S., Jacobsen, B.H.: 2015, Grand solar minima and maxima deduced from 10Be and 14C : magnetic dynamo configuration and polarity reversal. Astron. Astrophys. 577, A20. DOI . ADS .
Jiang, J., Cameron, R.H., Schüssler, M.: 2015, The cause of the weak solar Cycle 24. Astrophys. J. 808, L28. DOI . ADS .
Jiang, J., Hathaway, D.H., Cameron, R.H., Solanki, S.K., Gizon, L., Upton, L.: 2014, Magnetic flux transport at the solar surface. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 491. DOI . ADS .
Käpylä, M.J., Käpylä, P.J., Olspert, N., Brandenburg, A., Warnecke, J., Karak, B.B., Pelt, J.: 2016, Multiple dynamo modes as a mechanism for long-term solar activity variations. Astron. Astrophys. 589, A56. DOI . ADS .
Karak, B.B., Miesch, M.: 2017, Solar cycle variability induced by tilt angle scatter in a Babcock–Leighton solar dynamo model. Astrophys. J. 847, 69. DOI . ADS .
Karak, B.B., Miesch, M.: 2018, Recovery from Maunder-like grand minima in a Babcock–Leighton solar dynamo model. Astrophys. J. Lett. 860, L26. DOI . ADS .
Karak, B.B., Jiang, J., Miesch, M.S., Charbonneau, P., Choudhuri, A.R.: 2014, Flux transport dynamos: from kinematics to dynamics. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 561. DOI . ADS .
Knudsen, M.F., Riisager, P., Jacobsen, B.H., Muscheler, R., Snowball, I., Seidenkrantz, M.-S.: 2009, Taking the pulse of the Sun during the Holocene by joint analysis of 14C and 10Be. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L16701. DOI . ADS .
Krause, F., Rädler, K.-H.: 1980, Mean-Field Magnetohydrodynamics and Dynamo Theory. Pergamon, Oxford. ADS .
Küker, M., Arlt, R., Rüdiger, G.: 1999, The Maunder minimum as due to magnetic Lambda -quenching. Astron. Astrophys. 343, 977. ADS .
Lemerle, A., Charbonneau, P.: 2017, A coupled \(2\times 2\)D Babcock–Leighton solar dynamo model. II. Reference dynamo solutions. Astrophys. J. 834, 133. DOI . ADS .
Lemerle, A., Charbonneau, P., Carignan-Dugas, A.: 2015, A coupled \(2\times 2\)D Babcock–Leighton solar dynamo model. I. Surface magnetic flux evolution. Astrophys. J. 810, 78. DOI . ADS .
Lepreti, F., Carbone, V., Veltri, P.: 2001, Solar flare waiting time distribution: varying-rate Poisson or Lévy function? Astrophys. J. 555, L133. DOI . ADS .
McClintock, B.H., Norton, A.A.: 2013, Recovering joy’s law as a function of solar cycle, hemisphere, and longitude. Solar Phys. 287, 215. DOI . ADS .
Moss, D., Brooke, J.: 2000, Towards a model for the solar dynamo. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 315, 521. DOI . ADS .
Mursula, K., Ulich, T.: 1998, A new method to determine the solar cycle length. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 1837. DOI . ADS .
Nagy, M., Lemerle, A., Labonville, F., Petrovay, K., Charbonneau, P.: 2017, The effect of “rogue” active regions on the solar cycle. Solar Phys. 292, 167. DOI . ADS .
Ossendrijver, M.A.J.H.: 2000, Grand minima in a buoyancy-driven solar dynamo. Astron. Astrophys. 359, 364. ADS .
Parker, E.N.: 1955, Hydromagnetic dynamo models. Astrophys. J. 122, 293. DOI . ADS .
Passos, D., Nandy, D., Hazra, S., Lopes, I.: 2014, A solar dynamo model driven by mean-field alpha and Babcock–Leighton sources: fluctuations, grand-minima-maxima, and hemispheric asymmetry in sunspot cycles. Astron. Astrophys. 563, A18. DOI . ADS .
Petrovay, K.: 2010, Solar cycle prediction. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys. 7, 6. DOI . ADS .
Pipin, V.V., Kosovichev, A.G.: 2011, Mean-field solar dynamo models with a strong meridional flow at the bottom of the convection zone. Astrophys. J. 738, 104. DOI . ADS .
Ribes, J.C., Nesme-Ribes, E.: 1993, The solar sunspot cycle in the Maunder minimum AD1645 to AD1715. Astron. Astrophys. 276, 549. ADS .
Sanchez, S., Fournier, A., Aubert, J.: 2014, The predictability of advection-dominated flux-transport solar dynamo models. Astrophys. J. 781, 8. DOI . ADS .
Sokoloff, D., Nesme-Ribes, E.: 1994, The Maunder minimum: a mixed-parity dynamo mode? Astron. Astrophys. 288, 293. ADS .
Solanki, S.K., Usoskin, I.G., Kromer, B., Schüssler, M., Beer, J.: 2004, Unusual activity of the Sun during recent decades compared to the previous 11,000 years. Nature 431, 1084. DOI . ADS .
Steinhilber, F., Abreu, J.A., Beer, J., Brunner, I., Christl, M., Fischer, H., Heikkila, U., Kubik, P.W., Mann, M., McCracken, K.G., Miller, H., Miyahara, H., Oerter, H., Wilhelms, F.: 2012, 9,400 years of cosmic radiation and solar activity from ice cores and tree rings. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. 109, 5967. DOI . ADS .
Svalgaard, L., Cliver, E.W., Kamide, Y.: 2005, Sunspot cycle 24: smallest cycle in 100 years? Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L01104. DOI . ADS .
Tobias, S.M.: 1997, The solar cycle: parity interactions and amplitude modulation. Astron. Astrophys. 322, 1007. ADS .
Usoskin, I.G.: 2013, A history of solar activity over millennia. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys. 10, 1. DOI . ADS .
Usoskin, I.G.: 2017, A history of solar activity over millennia. Liv. Rev. Solar Phys. 14, 3. DOI . ADS .
Usoskin, I.G., Mursula, K., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2000, Regular and random components of sunspot activity during active sun and great minima: model simulation. In: Wilson, A. (ed.) The Solar Cycle and Terrestrial Climate, Solar and Space Weather, SP-463, ESA, Noordwijk, 447. ADS .
Usoskin, I.G., Mursula, K., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2003, Reconstruction of monthly and yearly group sunspot numbers from sparse daily observations. Solar Phys. 218, 295. DOI . ADS .
Usoskin, I.G., Solanki, S.K., Kovaltsov, G.A.: 2007, Grand minima and maxima of solar activity: new observational constraints. Astron. Astrophys. 471, 301. DOI . ADS .
Usoskin, I.G., Hulot, G., Gallet, Y., Roth, R., Licht, A., Joos, F., Kovaltsov, G.A., Thébault, E., Khokhlov, A.: 2014, Evidence for distinct modes of solar activity. Astron. Astrophys. 562, L10. DOI . ADS .
Usoskin, I.G., Kovaltsov, G.A., Lockwood, M., Mursula, K., Owens, M., Solanki, S.K.: 2016a, A new calibrated sunspot group series since 1749: statistics of active day fractions. Solar Phys. 291, 2685. DOI . ADS .
Usoskin, I.G., Gallet, Y., Lopes, F., Kovaltsov, G.A., Hulot, G.: 2016b, Solar activity during the Holocene: the Hallstatt cycle and its consequence for grand minima and maxima. Astron. Astrophys. 587, A150. DOI . ADS .
Vecchio, A., Lepreti, F., Laurenza, M., Alberti, T., Carbone, V.: 2017, Connection between solar activity cycles and grand minima generation. Astron. Astrophys. 599, A58. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y.-M., Lean, J., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 2002, Role of a variable meridional flow in the secular evolution of the Sun’s polar fields and open flux. Astrophys. J. Lett. 577, L53. DOI . ADS .
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R. Jr.: 1991, Magnetic flux transport and the sun’s dipole moment – new twists to the Babcock–Leighton model. Astrophys. J. 375, 761. DOI . ADS .
Wheatland, M.S.: 2000, The origin of the solar flare waiting-time distribution. Astrophys. J. Lett. 536, L109. DOI . ADS .
Wheatland, M.S.: 2003, The coronal mass ejection waiting-time distribution. Solar Phys. 214, 361. DOI . ADS .
Whitbread, T., Yeates, A.R., Muñoz-Jaramillo, A., Petrie, G.J.D.: 2017, Parameter optimization for surface flux transport models. Astron. Astrophys. 607, A76. DOI . ADS .
Yeates, A.R., Baker, D., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L.: 2015, Source of a prominent poleward surge during solar Cycle 24. Solar Phys. 290, 3189. DOI . ADS .
Yeates, A.R., Muñoz-Jaramillo, A.: 2013, Kinematic active region formation in a three-dimensional solar dynamo model. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 436, 3366. DOI . ADS .
Ziȩba, S., Nieckarz, Z.: 2014, Sunspot time series: passive and active intervals. Solar Phys. 289, 2705. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Discovery Grant Program of Canada’s Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council. Special thanks to Ilya G. Usoskin for kindly providing their most recent reconstructed solar-activity time series based on 10Be and 14C cosmogenic radioisotopes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ölçek, D., Charbonneau, P., Lemerle, A. et al. Grand Activity Minima and Maxima via Dual Dynamos. Sol Phys 294, 99 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1492-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1492-9