Abstract
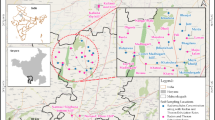
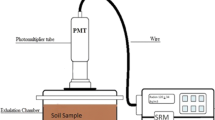
The measurements of primordial radionuclides (226Ra, 232Th and 40K) and radon exhalation rates in soil samples were performed in Bageshwar region of Kumaun Himalaya, India using gamma-ray spectrometry and scintillation detector based radon monitor, respectively. The average concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K in the investigated region were found to be 36 Bq kg−1, 50 Bq kg−1 and 1595 Bq kg−1, respectively. The average values of radon and thoron mass exhalation rates were observed to be 29 mBq−1 kg−1 s−1 and 256 mBq−1 kg−1 s−1, respectively. The average value of thoron surface exhalation rates was observed to be 2281 mBq−1 m−2 s−1. The external exposure to 226Ra, 232Th and 40K is estimated in terms of different hazard assessment indices and dose quantities. The high values of 232Th content in soil samples indicate the presence of thorium mineralization in the vicinity of study area. The methodology adopted and results obtained are discussed in details.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar A, Singh P, Agarwal T, Joshi M, Semwal P, Singh K, Pathak PP, Ramola RC (2020) Statistical inferences from measured data on concentrations of naturally occurring radon, thoron and decay products in Kumaun Himalayan belt. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:40229–40243
Flores OB, Estrada AM, Suarez RR, Zerquera JT, Pérez AH (2008) Natural radionuclide content in building materials and gamma dose rate in dwellings in Cuba. J Envir Radioact 99(12):1834–1837
Prasad M, Ranga V, Kumar GA, Ramola RC (2020) Radiological impact assessment of soil and groundwater of Himalayan regions in Uttarakhand, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 323(3):1269–1282
UNSCEAR (1982) United nations scientific committee on the effects of atomic radiation. Exposures resulting from nuclear explosions, New York
Johner HU, Surbeck H (2001) Soil gas measurements below foundation depth improve indoor radon prediction. Sci Total Environ 272(1–3):337–341
Yadav M, Rawat M, Dangwal A, Prasad M, Gusain GS, Ramola RC (2014) Levels and effects of natural radionuclides in soil samples of Garhwal Himalaya. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 302:869–873
Yadav M, Rawat M, Dangwal A, Prasad M, Gusain GS, Ramola RC (2015) Analysis of natural radionuclides in soil samples of Purola area of Garhwal Himalaya, India. Rad Prot Dosim 167:215–218
Kandari T, Prasad M, Pant P, Semwal P, Bourai AA, Ramola RC (2018) Study of radon flux and natural radionuclides (226Ra, 232Th and 40K) in the main boundary thrust region of Garhwal Himalaya. Acta Geophys 66:1243–1248
Ramola RC, Gusain GS, Badoni M, Prasad Y, Prasad G, Ramachandran TV (2008) 226Ra, 232Th and 40K contents in soil samples from Garhwal Himalaya, India and its radiological implications. J Radiol Prot 28:379–385
Ramola RC, Yadav M, Gusain GS (2019) Distribution of natural radionuclide along main central thrust in Garhwal Himalaya. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:614–619
CGWB (2009) District ground water brochure of Bageshwar district, Uttarakhand Bageshwar district at a glance. Central Ground Water Board. http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/Uttarakhand/Bageshwar.pdf
Semwal P, Singh K, Agarwal TK, Joshi M, Pant P, Kandari T, Ramola RC (2018) Measurement of 222 Rn and 220 Rn exhalation rate from soil samples of Kumaun Hills, India. Acta Geophys 66(5):1203–1211
UNSCEAR (2000) United nations scientific committee on the effects of atomic radiation. Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. Report to the general assembly, annexe B. United Nations Publication, United Nations, New York
UNSCEAR (2008) Sources, effects and risks of ionizing radiation. United nations scientific committee on the effects of atomic radiation (report to the general assembly, with Annexes)
ICRP (1990) International commission on radiological protection. Recommendations of the international commission on radiological protection. Publication 60 Ann. 21, pp 1–3
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to BRNS, Department of Atomic Energy, Government of India for providing financial support in the form of a research Project (Ref. 2013/36/61-BRNS/2470).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Singh, P., Semwal, P. et al. Study of primordial radionuclides and radon/thoron exhalation rates in Bageshwar region of Kumaun Himalaya, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 328, 1361–1367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07582-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07582-y