Abstract
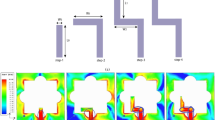
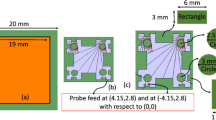
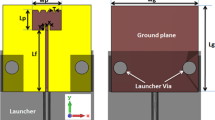
In this paper, a novel design for a 5G base station (BS) antenna is proposed. The proposed antenna consists of two orthogonally polarized antennas. The two antennas are modified compact Vivaldi antennas operating in the two recommended 5G operating bands; 28 and 38 GHz with measured impedance bandwidth of 26.5–40 GHz. The orthogonality of the two antennas allows the use of two antennas on the same substrate within one enclosure to serve two sectors separately. So, instead of using two enclosures to serve two sectors, only one enclosure is required. The two elements may be part of two separate MIMO distributions. To minimize the isolation between the MIMO antennas elements with low complexity and low cost, the antenna elements have been distributed along the z-direction with half-wavelength spacing between elements including Electromagnetic band-gap (EBG) structure in between them. The simulation results have been shown that the measured mutual coupling between the array elements is improved from − 32 to − 45 dB at 28 GHz and from − 22 to − 59 at 38 GHz. The envelope correlation coefficient (ECC) is enhanced and the diversity gain (DG) is improved simultaneously. The suggested structure has been designed on CST Microwave Studio 2019. The two orthogonal antennas’ overall size approaches 34 mm × 55.8 mm × 0.203 mm3. The measured gain of the suggested design is enhanced from 10.4 to 12.8 dB at 28 GHz whereas a minor change is noticed at 38 GHz. The maximum simulated radiation efficiency approaches 96%. The antenna is fabricated and tested where good experimental results are noticed compared to the simulation results.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Wu, B. Wu, Z. Su and X. Zhang, 2018 International Workshop on Antenna Technology (iWAT), Nan**g, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1109/IWAT.2018.8379163
D.J.Zhang, IMT-2020(5G) Summit, (2017).
M. Alibakhshikenari, B. S. Virdee, C. H. See, R. A. Abd-Alhameed and E. Limiti, 2019 44th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves (IRMMW-THz), Paris, France, 2019, pp. 1-2, https://doi.org/10.1109/IRMMW-THz.2019.8874127.
W. Hong, Z. H. Jiang, C. Yu, J. Zhou, P. Chen, Z Yu, H. Zhang, and B Yang, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 65(12), 6231(2017).
S. Zhu, H. Liu, P. Wen, and Z. Chen, IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. , 17(5), 776 (2018).
Y. Liu, W. Zhou, S. Yang, W. Li, P.Li, and S. Yang, IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett. , 1536 (2015).
E. W. Reid , L. Ortiz-Balbuena , A. Ghadiri and K. Moez, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag, 61(1), 241 (2012).
J. Wu, Z. Zhao, Z. Nie, and Q. Liu, IEEE Antennas Wireless Propag. Lett, 13(1), 698 (2014).
R. Sturdivant, and E. K.P. Chong, 2017 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), (2017), pp.197-200. https://doi.org/10.1109/RWS.2017.7885986
P.J. Gibson, Proc. of the 9th European Microwave Conference, (1979), pp.101–105. https://doi.org/10.1109/EUMA.1979.332681
E. Gazit. IEE Proc., no.135 (2), 89 (1988).
J.D.S. Langley, P.S. Hall, and P. Newham, IEE Proc. Microw. Antennas Propag. , (143), 97 (1996).
J. Bai, S. Shi, and D. W. Prather, IEEE trans. on microwave theory and techniques, 59(4), (2011).
M. Alibakhshikenari, B. S. Virdee, IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 5182-51840, April 29, 2019.
M. Alibakhshikenari, B. S. Virdee, IEEE Access, vol. 7, Page(s): 23606 - 23614, March 5, 2019.
I. Nadeem and D.-U. Choi, IEEE Access, 7, 563(2019).
M. S. Khan, A. D. Capobianco, A. Iftikhar, R. M. Shubair, D. E. Anagnostou, and B. D. Braaten, IET Microw, Antennas Propag., 11( 7), 997(2017).
S. Koziel, A. Bekasiewicz, and Q. S. Cheng, IET Microw., Antennas Propag., 11(8), 1162 (2017).
X. Zhao, S. P. Yeo, and L. C. Ong IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 66(1), 420 (2018).
H.-X. Xu, G.-M. Wang, and M.-Q. Qi, IEEE Trans. Magn., 49(4), 1526 (2013).
J.-Y. Lee, S.-H. Kim, and J.-H. Jang, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 63(9), 4194 (2015).
H. Y. Qi, L. L. Liu, X. X. Yin, H. X. Zhao, and W. J. Kulesza, IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett 15, 191(2016).
Z. Briqech, A.-R. Sebak, and Tayeb A. Denidni, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 65(12), 6403(2017).
S. Sharma, Mainuddin, B. K. Kanaujia, M. K. Khandelwal, Microsyst Technol., (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04574-1, 2019
A. Kumar, C.S. Rai, K. Elwal MK, BK. Kanaujia, Microsyst Technol., 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04513-0
Z. Li, C. Yin , and X. Zhu, IEEE Access , 7 , 38696 (2019).
D. H. Li, F. Zhang, L. Cao, and Y. Zhao, Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, 86, 97( 2019).
R. Natarajan, M. G. Alsath, M. Kanagasabai, S, Bilvam, and Sh. Meiyalagan, Int J RF Microw Comput Aided Eng. 2019 https://doi.org/10.1002/mmce.21989
Haythem H. Abdullah, AA Megahed, M.EA Abo-Elsoud, IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 13( 9), 345(2019).
K. R. Jha and S. K. Sharma, IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag., 60(1), 118 (2018)
K.S. Sultan, H.H. Abdullah, E. A. Abdallah and H. S. El-Hennawy , IEEE Access , 8, 37250 ( 2020)
L. Malviya, R. K. Panigrahi, M. V. Kartikeyan, Micro. Optical and Comm. Eng. (ICMOCE), 61, 91 ( 2016).
K. S. Sultan and H. H. Abdullah, Progress in electromagnetics Research C, 93, 119(2019).
M. Manteghi, and R.Samii, "EEE Trans Antennas Propag, 53(1), 466 (2005).
SH. Chae, S. Oh, S-O. , IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett, 6, 122 (2007).
A. Mahmoud, and A.A.Ibrahim, IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett, 12(5), 1452 (2013).
M. Abdullah, S. H. Kiani, L. F. Abdulrazak , A. Iqbal, M. A. Bashir , Sh. Khan and S. Kim, Electronics, 8, 1090 (2019)
R. Herzi, H. Zairi, A. Gharsallah , 16th international conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic control & computer engineering - STA' 2015, Monastir, Tunisia, Dec. (2015), pp. 21-23. https://doi.org/10.1109/STA.2015.7505195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elabd, R.H., Abdullah, H.H. & Abdelazim, M. Compact Highly Directive MIMO Vivaldi Antenna for 5G Millimeter-Wave Base Station. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 42, 173–194 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-020-00765-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-020-00765-4