Abstract
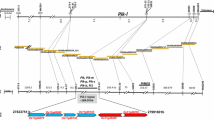
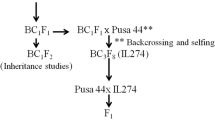
Epidemics of blast disease, also called grey leaf spot (GLS), in ryegrass species have recently become a serious problem in Japan and the USA. GLS causes serial growth inhibition and the abnormal morphology of withering in ryegrass seedlings. If the lesions expand they can completely destroy the plant at several growth stages. We attempted to construct a partial genetic linkage map around the LmPi1 locus, which confers resistance to GLS and is located on linkage group (LG) 5 of Italian ryegrass, by using synteny with rice. Because LG5 of Italian ryegrass is syntenic with rice chromosome (Chr) 9, we designed intron-scanning primers with alignment between the rice genome sequence and expressed sequence tag (EST) information on rice Chr 9. These primers were used to genotype an F1 map** population, which had been used for detection of the LmPi1 locus, by detecting single-strand conformation polymorphisms (SSCPs). We successfully constructed a partial genetic linkage map around the LmPi1 locus, spanning 66.3 cM. A comparative genomic analysis between the partial genetic linkage map and the rice Chr 9 genetic linkage map revealed that the LmPi1 locus was a candidate for orthology to the Pi5 locus or Pi15 locus, both of which are co-located in a resistance gene cluster on rice Chr 9 and are associated with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast.

Similar content being viewed by others

References
Armstead, I. P., Skøt, L., Turner, L. B., Skøt, K., Donnison, I. S., Humphreys, M. O., et al. (2005). Identification of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne (L.)) and meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis (Huds.)) candidate orthologous sequences to the rice Hd1(Se1) and barley HvCO1 CONSTANS-like genes through comparative map** and microsynteny. New Phytologist, 167, 239–247.
Armstead, I. P., Turner, L. B., Marshall, A. H., Humphreys, M. O., King, I. P., & Thorogood, D. (2008). Identifying genetic components controlling fertility in the outcrossing grass species perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) by quantitative trait loci analysis and comparative genetics. New Phytologist, 178, 559–571.
Ballini, E., Morel, J. B., Droc, G., Price, A., Courtois, B., Notteghem, J. L., et al. (2008). A genome-wide meta-analysis of rice blast resistance genes and quantitative trait loci provides new insights into partial and complete resistance. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 21, 859–868.
Bertin, I., Zhu, J. H., & Gale, M. D. (2005). SSCP-SNP in pearl millet—a new marker system for comparative genetics. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 110, 1467–1472.
Brueggeman, R., Rostoks, N., Kudrna, D., Kilian, A., Han, F., Chen, J., et al. (2002). The barley stem rust-resistance gene Rpg1 is a novel disease-resistance gene with homology to receptor kinases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99, 9328–9333.
Couch, B. C., & Kohn, L. M. (2002). A multilocus gene genealogy concordant with host preference indicates segregation of a new species, Magnaporthe oryzae, from M. grisea. Mycologia, 94, 683–693.
Curley, J., Sim, S. C., Warnke, S., Leong, S., Barker, R., & Jung, G. (2005). QTL map** of resistance to gray leaf spot in ryegrass. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 111, 1107–1117.
Farman, M. L. (2002). Pyricularia grisea isolates causing gray leaf spot on perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) in the United States: relationship to P. grisea isolates from other host plants. Phytopathology, 92, 245–254.
Feltus, F. A., Singh, H. P., Lohithaswa, H. C., Schulze, S. R., Silva, T. D., & Paterson, A. H. (2006). A comparative genomics strategy for targeted discovery of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and conserved-noncoding sequences in orphan crops. Plant Physiology, 140, 1183–1191.
Han, Y., Bonos, S. A., Clarke, B. B., & Meyer, W. A. (2006). Inheritance of resistance to gray leaf spot disease in perennial ryegrass. Crop Science, 46, 1143–1148.
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project. (2005). The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature, 436, 793–800.
Jena, K. K., & Mackill, D. J. (2008). Molecular markers and their use in marker-assisted selection in rice. Crop Science, 48, 1266–1276.
Jeon, J.-S., Chen, D., Yi, G.-H., Wang, G. L., & Ronald, P. C. (2003). Genetic and physical map** of Pi5(t), a locus associated with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 269, 280–289.
Jo, Y.-K., Barker, R., Pfender, W., Warnke, S., Sim, S.-C., & Jung, G. (2008). Comparative analysis of multiple disease resistance in ryegrass and cereal crops. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 117, 531–543.
Jones, E. S., Mahoney, N. L., Hayward, M. D., Armstead, I. P., Jones, J. G., Humphreys, M. O., et al. (2002). An enhanced molecular marker based genetic map of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) reveals comparative relationships with other Poaceae genomes. Genome, 45, 282–295.
Le Cunff, L., Garsmeur, O., Raboin, L. M., Pauquet, J., Telismart, H., Selvi, A., et al. (2008). Diploid/polyploid syntenic shuttle map** and haplotype-specific chromosome walking toward a rust resistance gene (Bru1) in highly polyploid sugarcane (2n ∼ 12x ∼ 115). Genetics, 180, 649–660.
Lee, S.-K., Song, M.-Y., Seo, Y.-S., Kim, H.-K., Ko, S., Cao, P.-J., et al. (2009). Rice Pi5-mediated resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae requires the presence of two coiled-coil-nucleotide-binding-leucine-rich repeat genes. Genetics, 181, 1627–1638.
Lin, F., Liu, Y., Wang, L., Liu, X., & Pan, Q. (2007). A high-resolution map of the rice blast resistance gene Pi15 constructed by sequence-ready markers. Plant Breeding, 126, 287–290.
Mammadov, J. A., Steffenson, B. J., & Saghai Maroof, M. A. (2005). High-resolution map** of the barley leaf rust resistance gene Rph5 using barley expressed sequence tags (ESTs) and synteny with rice. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 111, 1651–1660.
Miura, Y., Ding, C., Ozaki, R., Hirata, M., Fujimori, M., Takahashi, W., et al. (2005). Development of EST-derived CAPS and AFLP markers linked to a gene for resistance to ryegrass blast (Pyricularia sp.) in Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 111, 811–818.
Miura, Y., Hirata, M., & Fujimori, M. (2007). Map** of EST-derived CAPS markers in Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.). Plant Breeding, 126, 353–360.
Pan, Q.-H., Hu, Z.-D., Tanisaka, T., & Wang, L. (2003). Fine map** of the blast resistance gene Pi15, linked to Pii, on rice chromosome 9. Acta Botanica Sinica, 45, 871–877.
Perovic, D., Stein, N., Zhang, H., Drescher, A., Prasad, M., Kota, R., et al. (2004). An integrated approach for comparative map** in rice and barley with special reference to the Rph16 resistance locus. Functional and Integrative Genomics, 4, 74–83.
Reith, P. E., Prine, G. M., & Blount, A. R. (2003). Selection for gray leaf spot disease resistance in annual ryegrass. Soil and Crop Science Society of Florida Proceedings, 62, 69–73.
Sim, S., Chang, T., Curley, J., Warnke, S. E., Barker, R. E., & Jung, G. (2005). Chromosomal rearrangements differentiating the ryegrass genome from the Triticeae, oat, and rice genomes using common heterologous RFLP probes. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 110, 1011–1019.
Sim, S., Diesburg, K., Casler, M., & Jung, G. (2007). Map** and comparative analysis of QTL for crown rust resistance in an Italian x perennial ryegrass population. Phytopathology, 97, 767–776.
Takahashi, W., Miura, Y., & Sasaki, T. (2009). A novel inoculation method for evaluation of grey leaf spot resistance in Italian ryegrass. Journal of Plant Pathology, 91, 171–176.
Tamura, K., Yonemaru, J., Hisano, H., Kanamori, H., King, J., King, I. P., et al. (2009). Development of intron-flanking EST markers for the Lolium/Festuca complex using rice genomic information. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 118, 1549–1560.
The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. (2000). Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature, 408, 796–815.
Tosa, Y., Uddin, W., Viji, G., Kang, S., & Mayama, S. (2007). Comparative genetic analysis of Magnaporthe oryzae isolates causing gray leaf spot of perennial ryegrass turf in the United States and Japan. Plant Disease, 91, 517–524.
Trevathan, L. E. (1982). Response of ryegrass plant introductions to artificial inoculation with Pyricularia grisea under greenhouse conditions. Plant Disease, 66, 696–697.
Viji, G., Wu, B., Kang, S., & Uddin, W. (2001). Pyricularia grisea causing gray leaf spot of perennial ryegrass turf: population structure and host specificity. Plant Disease, 85, 817–826.
Voorrips, R. E. (2002). MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. The Journal of Heredity, 93, 77–78.
Wu, J., Maehara, T., Shimokawa, T., Yamamoto, S., Harada, C., Takazaki, Y., et al. (2002). A comprehensive rice transcript map containing 6591 expressed sequence tag sites. The Plant Cell, 14, 525–535.
Yi, G., Lee, S.-K., Hong, Y.-K., Cho, Y.-C., Nam, M.-H., Kim, S.-C., et al. (2004). Use of Pi5(t) markers in marker-assisted selection to screen for cultivars with resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 109, 978–985.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms K. Akimoto (Japan Grassland Agriculture and Forage Seed Association) for her superior assistance throughout this study. This work was funded by a research grant from the Japan Racing Association (JRA) and supported by National Agriculture and Food Research Organisation (NARO), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, W., Miura, Y., Sasaki, T. et al. Targeted map** of rice ESTs to the LmPi1 locus for grey leaf spot resistance in Italian ryegrass. Eur J Plant Pathol 126, 333–342 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-009-9549-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-009-9549-5