Abstract
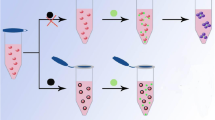
We have developed an ultrasensitive homogeneous fluorometric assay for Hg(II) ion. It is based on the different affinities of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for unfolded and folded aptamers. AuNPs are capable of recognizing conformational changes of aptamers under conditions of high ionic strength. A highly Hg(II)-specific T-rich aptamer was selected and adsorbed on the surface of AuNPs. This prevents the salt-induced aggregation of AuNPs. The red AuNP/aptamer system reduces the green fluorescence of cysteamine-capped CdTe quantum dots (CA-CdTe QDs). However, in the presence of Hg(II), the aptamer specifically reacts with Hg(II) to form a “T-Hg(II)-T” structure, and the AuNPs therefore form blue aggregates because they are not protected by the aptamer under conditions of high ionic strength. The blue aggregates cannot quench the fluorescence of the CA-CdTe QDs. Therefore, on addition of Hg(II), the fluorescence of the CdTe QDs is recovered. Fluorescence intensity is linearly proportional to the concentration of Hg(II) in the 50 pM to 1.0 nM concentration range, with a 2.5 pM detection limit. This ultrasensitive method in our eyes holds a large potential for environmental monitoring Hg(II) ion, and of other ions if respective aptamers are available.

An aptamer-based aggregation assay is developed for ultrasensitive detection of mercury ions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao J, Zhang YY, Li HT, Wen YQ, Fan XY, Lin FB, Tan L, Yao SZ (2011) Ultrasensitive electrochemical aptasensor for thrombin based on the amplification of aptamer-AuNPs-HRP conjugates. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2297–2303
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–840
Zhu ZY, Schmidt T, Mahrous M, Guieu V, Perrier S, Ravelet C, Peyrin E (2011) Optimization of the structure-switching aptamer-based fluorescence polarization assay for the sensitive tyrosinamide sensing. Anal Chim Acta 70:191–196
Zhao Q, Lv Q, Wang HL (2015) Aptamer fluorescence anisotropy sensors for adenosine triphosphate by comprehensive screening tetramethylrhodamine labeled nucleotides. Biosens Bioelectron 70:188–193
Bai YF, Feng F, Zhao L, Wang CY, Wang HY, Tian MZ, Qin J, Duan YL, He XX (2013) Aptamer/thrombin/aptamer-AuNPs sandwich enhanced surface plasmon resonance sensor for the detection of subnanomolar thrombin. Biosens Bioelectron 47:265–270
Hansen JA, Wang J, Kawde AN, **ang Y, Gothelf KV, Collins G (2006) Quantum-dot/aptamer-based ultrasensitive multi-analyte electrochemical biosensor. J Am Chem Soc 128:2228–2229
Li BL, Wang YL, Wei H, Dong SJ (2008) Amplified electrochemical aptasensor taking AuNPs based sandwich sensing platform as a model. Biosens Bioelectron 23:965–970
Fu AH, Gu WW, Larabell C, Alivisatos AP (2005) Semiconductor nanocrystals for biological imaging. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:568–575
Dai Z, Zhang JM, Dong QX, Guo N, Xu SC, Sun B, Bu YH (2007) Adaption of Au nanoparticles and CdTe quantum dots in DNA detection. J Chin Inst Chem Eng 15:791–794
Oh E, Hong MY, Lee DH, Nam SH, Yoon HC, Kim HS (2005) Inhibition assay of biomolecules based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 127:3270–3271
Yang WH, Li WW, Dou HJ, Sun K (2008) Hydrothermal synthesis for high-quality CdTe quantum dots capped by cysteamine. Mater Lett 62:2564–2566
Wang X, Guo XQ (2009) Ultrasensitive Pb2+ detection based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Analyst 134:1348–1354
Cao XY, Shen F, Zhang MW, Guo JJ, Luo YL, Li X, Liu H, Sun CY, Liu JB (2013) Efficient inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles on the fluorescence of CdS quantum dots for sensitive detection of melamine in raw milk. Food Control 34:221–229
Maxwell DJ, Taylor JR, Nie SM (2002) Self-assembled nanoparticle probes for recognition and detection of biomolecules. J Am Chem Soc 124:9606–9612
Liu JW, Lu Y (2006) Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat Protoc 1:246–252
Zhang J, Wang LH, Pan D, Song SP, Freddy YCB, Zhang H, Fan CH (2008) Visual cocaine detection with gold nanoparticles and rationally engineered aptamer structures. Small 4:1196–1200
Yi YH, Huang Y, Zhu GB, Lin FB, Zhang LL, Li HT, Zhang YY, Yao SZ (2013) A colorimetric and fluorescence sensing platform for two analytes in homogenous solution based on aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles. Anal Methods 5:2477–2484
Qiang WB, Liu HP, Li W, Chen X, Xu DK (2014) Label-free detection of adenosine based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between fluorescent silica nanoparticles and unmodified gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 828:92–98
Di L, Wieckowska A, Willner I (2008) Optical analysis of Hg2+ ions by oligonucleotide gold-nanoparticle hybrids and DNA-based machines. Angew Chem 120:3991–3995
Li HX, Rothberg LJ (2004) Label-free colorimetric detection of specific sequences in genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. J Am Chem Soc 126:10958–10961
Chen YJ, Yao L, Deng Y, Pan DD, Ogabiela E, Cao JX, Adeloju SB, Chen W (2015) Rapid and ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of mercury(II) by chemically initiated aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:2147–2154
Jiang YX, Tian JN, Hu K, Zhao YC, Zhao SL (2014) Sensitive aptamer-based fluorescence polarization assay for mercury(II) ions and cysteine using silver nanoparticles as a signal amplifier. Microchim Acta 181:1423–1430
Liu F, Wang SM, Zhang M, Wang YH, Ge SG, Yu JH, Yan M (2014) Aptamer based test stripe for ultrasensitive detection of mercury(II) using a phenylene-ethynylene reagent on nanoporous silver as a chemiluminescence reagent. Microchim Acta 181:663–670
Chen ZB, Zhang CM, Tan Y, Zhou TH, Ma H, Wan CQ, Lin YQ, Li K (2015) Chitosan-functionalized gold nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of mercury ions based on chelation-induced aggregation. Microchim Acta 182:611–616
Noor AM, Rameshkumar P, Huang NM, Wei LS (2016) Visual and spectrophotometric determination of mercury(II) using silver nanoparticles modified with graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 183:597–603
Li T, Dong SJ, Wang EK (2009) Label-free colorimetric detection of aqueous mercury ion (Hg2+) using Hg2+-modulated G-quadruplex-based DNAzymes. Anal Chem 81:2144–2149
Chen QF, Wang WX, Ge YX, Li MY, Xu SK, Zhang XJ (2007) Direct aqueous synthesis of cysteamine stabilized CdTe quantum dots and its deoxyribonucleic acid bioconjugates. Chin J Anal Chem 35:135–142
Li F, Zhang J, Cao XN, Wang LH, Li D, Song SP, Ye BC, Fan CH (2009) Adenosine detection by using gold nanoparticles and designed aptamer sequences. Analyst 134:1355–1360
Balasubramanian SK, Yang LM, Yung LL, Ong CN, Ong WY, Yu LE (2010) Characterization, purification, and stability of gold nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31:9023–9030
Gurunathan S, Han J, Park JH, Kim JH (2014) A green chemistry approach for synthesizing biocompatible gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:248–259
Li L, Li BX, Qi YY, ** Y (2009) Label-free aptamer-based colorimetric detection of mercury ions in aqueous media using unmodified gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probe. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:2051–2057
Wen D, Deng L, Guo SJ, Dong SJ (2011) Self-powered sensor for trace Hg2+ detection. Anal Chem 83:3968–3972
Duan JL, Song LX, Zhan JH (2009) One-pot synthesis of highly luminescent CdTe quantum dots by microwave irradiation reduction and their Hg2+-sensitive properties. Nano Res 2:61–68
Ding XJ, Qu LB, Yang R, Zhou YC, Li JJ (2015) A highly selective and simple fluorescent sensor for mercury (II) ion detection based on cysteamine-capped CdTe quantum dots synthesized by the reflux method. Luminescence 30:465–471
Wang YW, Tang SR, Yang HH, Song HB (2016) A novel colorimetric assay for rapid detection of cysteine and Hg2+ based on gold clusters. Talanta 146:71–74
Zhu SS, Zhuo Y, Miao H, Zhong D, Yang XM (2015) Detection of mercury(II) by DNA templated gold nanoclusters based on forming thymidine-Hg2+-thymidine duplexes. Luminescence 30:631–636
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21075050, No. 21275063) and the Science and Technology Development project of Jilin province, China (No. 20150204010GX)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 119 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tianyu, H., Xu, Y., Weidan, N. et al. Aptamer-based aggregation assay for mercury(II) using gold nanoparticles and fluorescent CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta 183, 2131–2137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1831-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1831-6