Abstract
We report here a signal amplifying strategy to construct polarization aptamer probes for small molecules. The method is based on the use of silver nanoparticles acting as a fluorescence polarization signal amplifier. It was applied to the sensitive and selective detection of the two model analytes mercury (II) and cysteine. The aptamer probes were conjugated to CdTe-CdS quantum dots and are shown to work well for both analytes. The analytical range for Hg(II) is from 10 nM to 0.4 μM, and the limit of detection is 6.6 nM. The respective range for cysteine is from 20 nM to 0.7 μM, and the LOD is 11 nM.

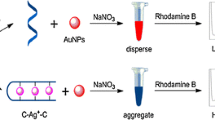
A signal polarization strategy for small molecules based on silver nanoparticles as a fluorescence polarization signal amplifier for sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions and cysteine was constructed







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tan SJ, Campolongo MJ, Luo D, Cheng WL (2011) Building plasmonic nanostructures with DNA. Nat Nanotechnol 6:268–276
Link S, Wang ZL, El-Sayed MA (1999) Size and temperature dependence of the plasmon absorption of colloidal gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 103:4212–4217
Jiang ZJ, Liu CY, Sun LW (2005) Catalytic properties of silver nanoparticles supported on silica spheres. J Phys Chem B 109:1730–1735
Braun G, Lee SJ, Dante M, Nguyen TQ, Moskovits M, Reich N (2007) Suface-enhanced raman spectroscopy for DNA detection by nanoparticle assembly onto smooth metal films. J Am Chem Soc 129:6378–6379
Wei E, Lawlor A, Whelan A, Regan F (2008) The use of nanoparticles in anti-microbial materials and their characterization. Analyst (Cambridge, U K) 133:835–845
Ye BC, Yin BC (2008) Highly sensitive detection of mercury(II) ions by fluorescence polarization enhanced by gold nanoparticles. Angew Chem, Int Ed 47:8386–8389
Huang Y, Zhao S, Chen ZF, Liu YC, Liang H (2011) Ultrasensitive endonuclease activity and inhibition detection using gold nanoparticle-enhanced fluorescence polarization. Chem Commun 47:4763–4765
Yin BC, Zuo P, Huo H, Zhong X, Ye BC (2010) DNAzyme self-assembled gold nanoparticles for determination of metal ions using fluorescence anisotropy assay. Anal Biochem 401:47–52
Smith DS, Eremin SA (2008) Fluorescence polarization immunoassays and related methods for simple, high-throughput screening of small molecules. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1499–1507
Cui L, Zou Y, Lin N, Zhu Z, Jenkins G, Yang CJ (2012) Mass amplifying probe for sensitive fluorescence anisotropy detection of small molecules in complex biological samples. Anal Chem 84:5535–5541
Zhang D, Lu M, Wang H (2011) Fluorescence anisotropy analysis for map** aptamer-protein interaction at the single nucleotide level. J Am Chem Soc 133:9188–9191
Gokulrangan G, Unruh JR, Holub DF, Ingram B, Johnson CK, Wilson GS (2005) DNA aptamer-based bioanalysis of IgE by fluorescence anisotropy. Anal Chem 77:1963–1970
Zhang D, Zhao Q, Zhao B, Huang H (2012) Fluorescence anisotropy reduction of allosteric aptamer for sensitive and specific protein signaling. Anal Chem 84:3070–3074
Li M, Wang Q, Shi X, Hornak LA, Wu N (2011) Detection of mercury(II) by quantum dot/DNA/gold nanoparticle ensemble based nanosensor via nanometal surface energy transfer. Anal Chem 83:7061–7065
Li D, Wieckowska A, Willner I (2008) Optical analysis of Hg2+ ions by oligonucleotide-gold-nanoparticle hybrids and DNA-based machines. Angew Chem, Int Ed 47:3927–3931
Zhu X, Zhou X, **ng D (2011) Ultrasensitive and selective detection of mercury(II) in aqueous solution by polymerase assisted fluoresecence amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2666–2669
Liu CW, Hsieh YT, Huang CC, Lin ZH, Chang HT (2008) Detection of mercury(II) based on Hg2+-DNA complexes inducing the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun 21:2242–2244
Choi JK, Sargsyan G, Olive AM, Balaz M (2013) Highly sensitive and selective spectroscopic detection of mercury(II) in water by using pyridylporphyrin-DNA conjugates. Chemistry 19:2515–2522
Lee JS, Ulmann PA, Han MS, Mirkin CA (2008) A DNA-gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assay for the detection of cysteine. Nano Lett 8:529–522
Stricks W, Kolthoff IM (1953) Reactions between mercuric mercury and cysteine and glutathione. Apparent dissociation constants, heats and entropies of formation of various forms of mercuric mercapto-cysteine and –glutathione. J Am Chem Soc 75:5673–5681
Tian JN, Liu RJ, Zhao YC, Xu Q, Zhao SL (2009) Controllable synthesis and cell-imaging studies on CdTe quantum dots together capped by glutathione and thioglycolic acid. J Colloid Interface Sci 336:504–509
Caswell KK, Wilson JN, Bunz UHF, Murphy CJ (2003) Preferential end-to-end assembly of gold nanorods by biotin-streptavidin connectors. J Am Chem Soc 125:13914–13915
Munro CH, Smith WE, Garner M, Clarkson J, White PC (1995) Characterization of the surface of a citrate-reduced colloid optimized for use as a substrate for surface-enhanced resonance raman scattering. Langmuir 11:3712–3720
Liu CH, Li ZP, Du BA, Duan XR, Wang YC (2006) Silver nanoparticle-based ultrasensitive chemiluminescent detection of DNA hybridization and single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Anal Chem 78:3738–3744
Yu WW, Qu L, Guo W, Peng X (2003) Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem Mater 15:2854–2860
Choi Y, Kim HP, Hong SM, Ryu JY, Han SJ, Song R (2009) In situ visualization of gene expression using polymer-coated quantum-dot–DNA conjugates. Small 5:2085–2091
Tian JN, Liu RJ, Zhao YC, Peng Y, Hong X, Xu Q, Zhao SL (2010) Synthesis of CdTe/CdS/ZnS quantum dots and the application in imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and immunoassay for alpha fetoprotein. Nanotechnology 21(30):305101–305108
Li T, Zhou YY, Sun JY, Tang DB, Guo SX, Ding XP (2011) Ultrasensitive detection of mercury(II) ion using CdTe quantum dots in sol–gel-derived silica spheres coated with calix[6]arene as fluorescent probes. Microchim Acta 175:113–119
Li T, Dong S, Wang E (2009) Label-free colorimetric detection of aqueous mercury zon (Hg2+) using Hg2+ modulated Gquadruplex-based DNAzymes. Anal Chem 81:2144
Liu BY, Zeng F, Wu SZ, Wang JS, Tang FC (2013) Ratiometric sensing of mercury(II) based on a FRET process on silica core-shell nanoparticles acting as vehicles. Microchim Acta 180:845–853
Wang RZ, Zhou DL, Huang H, Zhang M, Feng JJ, Wang AJ (2013) Water-soluble homo-oligonucleotide stabilized fluorescent silver nanoclusters as fluorescent probes for mercury ion. Microchim Acta 180:1287–1293
Shen TF, Yue QL, Jian XX, Wang L, Xu SL, Li HB, Gu XH, Zhang SQ, Liu JF (2013) A reusable and sensitive biosensor for total mercury in canned fish based on fluorescence polarization. Talanta 117:81–86
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21165004, 21163002), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation of China (2010GXNSFF013001, 2012GXNSFBA053022), Innovation Plan in Graduate Education of Guangxi Province (2010106020703 M70) and the project of Key Laboratory for the Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources(Guangxi Normal University), Ministry of Education of China(CMEMR2011-14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 296 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Tian, J., Hu, K. et al. Sensitive aptamer-based fluorescence polarization assay for mercury(II) ions and cysteine using silver nanoparticles as a signal amplifier. Microchim Acta 181, 1423–1430 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1296-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1296-4