Abstract
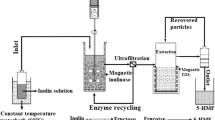
Magnetic nanobiocatalysts (MNBCs) are a promising immobilization approach to ease enzyme recovery during bioprocessing. However, industrial adoption of MNBCs is unfeasible because MNBC-synthesis involves complex and potentially expensive processing steps including synthesis of silica-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Si-SPIONs). We developed a single-step process for Si-SPION synthesis using a tubular electrochemical system (TES) and investigated the effect of concentration of the Na2SiO3 coating agent on Si-SPION properties. The Si-SPIONs were used as a support for attachment of polymer-cellulase conjugate to make MNBCs. The spherical Si-SPIONs were 8–12 nm in diameter including a 2-nm silica coating. Na2SiO3 concentration in the reactor did not affect Si-SPION morphology, but increasing Na2SiO3 concentration reduced SPION productivity in the reactor. Protective properties of the SPION silica coatings were demonstrated by showing that they prevented dissolution of SPIONs in an acid solution for 48 h. Enzyme attachment was quantified as protein adsorption on Si-SPIONs which reached 55 μg/mg Si-SPION. The MNBCs were recovered and reused four times. The use of TES for Si-SPION synthesis is promising to reduce MNBC production complexity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari SA, Husain Q (2012) Potential applications of enzymes immobilized on/in nano materials: A review. Biotechnol Adv 30:512–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.09.005
Han J, Rong J, Wang Y et al (2018) Immobilization of cellulase on thermo-sensitive magnetic microspheres: improved stability and reproducibility. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 41:1051–1060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-018-1934-z
Roth H-C, Schwaminger SP, Peng F, Berensmeier S (2016) Immobilization of cellulase on magnetic nanocarriers. ChemistryOpen 5:183–187. https://doi.org/10.1002/open.201600028
Lien Y-H, Wu T-M (2008) Preparation and characterization of thermosensitive polymers grafted onto silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 326:517–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.06.020
Bohara RA, Thorat ND, Pawar SH (2016) Role of functionalization: strategies to explore potential nano-bio applications of magnetic nanoparticles. RSC Adv 6:43989–44012. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA02129H
Abhari N, Madadlou A, Dini A (2017) Structure of starch aerogel as affected by crosslinking and feasibility assessment of the aerogel for an anti-fungal volatile release. Food Chem 221:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.072
Sodipo BK, Aziz AA (2016) Recent advances in synthesis and surface modification of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with silica. J Magn Magn Mater 416:275–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.05.019
Haddad PS, Duarte EL, Baptista MS et al (2004) Synthesis and characterization of silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Surface and Colloid Science. Springer, Berlin, pp 232–238
Wang P, Zhu Y, Yang X, Li C (2007) Electrochemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles within mesoporous silica microspheres. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 294:287–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.08.015
Abbas M, Abdel-Hamed MO, Chen J (2017) Efficient one-pot sonochemical synthesis of thickness-controlled silica-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4/SiO2) nanospheres. Appl Phys Mater Sci Process 123:775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1397-0
Ahankar H, Ramazani A, Fattahi N et al (2018) Tetramethylguanidine-functionalized silica-coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles catalyzed one-pot three-component synthesis of furanone derivatives. J Chem Sci 130:166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-018-1572-7
Cendrowski K, Sikora P, Zielinska B et al (2017) Chemical and thermal stability of core-shelled magnetite nanoparticles and solid silica. Appl Surf Sci 407:391–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.118
Setyawan H, Fajaroh F, Widiyastuti W et al (2012) One-step synthesis of silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles by electrooxidation of iron in sodium silicate solution. J Nanoparticle Res 14:807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0807-7
Karimzadeh I, Aghazadeh M, Ganjali MR et al (2017) Saccharide-coated superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles (SPIONs) for biomedical applications: An efficient and scalable route for preparation and in situ surface coating through cathodic electrochemical deposition (CED). Mater Lett 189:290–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.12.010
Fajaroh F, Setyawan H, Nur A, Lenggoro IW (2013) Thermal stability of silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles prepared by an electrochemical method. Adv Powder Technol 24:507–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2012.09.008
Xue D-S, Chen G-J, Su B-X et al (2020) On-line spectrophotometric determination of ferrous and total iron in monominerals by flow injection combined with a Schlenk line-based digestion apparatus to exclude oxygen. Microchem J 155:104743
Zholobko O, Hammed A, Zakharchenko A, Borodinov N, Luzinov I, Urbanowicz B, Patsahan T, Ilnytskyi J, Minko S, Pryor SW, Voronov A (2021) Biomimetic cellulosomes assembled on molecular brush scaffolds: random complexes vs enzyme mixtures. ACS Appl Polym Mater 3(4):1840–1853
Samaratunga A, Kudina O, Nahar N et al (2015) Impact of enzyme loading on the efficacy and recovery of cellulolytic enzymes immobilized on enzymogel nanoparticles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:2872–2882
Samaratunga A, Kudina O, Nahar N et al (2015) Modeling the effect of pH and temperature for cellulases immobilized on enzymogel nanoparticles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176:1114–1130
Cabrera L, Gutierrez S, Menendez N et al (2008) Magnetite nanoparticles: Electrochemical synthesis and characterization. Electrochim Acta 53:3436–3441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.12.006
Aghazadeh M (2018) One-step cathodic electrosynthesis of surface capped Fe3O4 ultra-fine nanoparticles from ethanol medium without using coating agent. Mater Lett 211:225–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.09.086
Kalska-Szostko B, Wykowska U, Piekut K, Satuła D (2014) Stability of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in various model solutions. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 450:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.03.002
Kudina O, Zakharchenko A, Trotsenko O et al (2014) Highly efficient phase boundary biocatalysis with enzymogel nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:483–487. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201306831
Arora R, Behera S, Sharma NK, Kumar S (2015) Bioprospecting thermostable cellulosomes for efficient biofuel production from lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Bioprocess 2:1–12
Kohut A, Pryor SW, Voronov A, Minko S (2017) enzymogel nanoparticles chemistry for highly efficient phase boundary biocatalysis. In: Biocatalysis and nanotechnology. Jenny Stanford Publishing, pp 369–399
Ishihara M, Uemura S, Hayashi N, Shimizu K (1991) Semicontinuous enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocelluloses. Biotechnol Bioeng 37:948–954
Grunwald P (2017) Biocatalysis and Nanotechnology. Pan Standord Publishing, Singapore
Funding
This study was funded by the National Science Foundation (Grant number CBET 1604422).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hammed, A., Polunin, Y., Voronov, A. et al. Tubular electrosynthesis of silica-coated magnetite and evaluation of magnetic nanobiocatalyst efficacy during biomass hydrolysis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 45, 1311–1318 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-022-02746-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-022-02746-4