Abstract
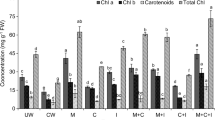
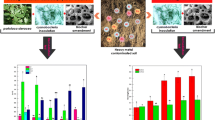
Wastewater generated from industries contains numerous contaminants, among which heavy metals (HMs) are non-degradable. This research work highlights the use of commonly used ornamental plants, Nicotiana alata L. and Petunia hydrida L., with compost (C) and peat moss (M), and rhizospheric bacterial augmentation using Pseudomonas japonica, for the phytostabilization of HMs from synthetic wastewater. After plant–soil acclimatization, plants were exposed for 6 weeks to synthetic wastewater, containing cadmium, chromium, copper, lead, nickel, and zinc concentrations (based on the HMs level of wastewaters collected from textile and pharmaceutical industry). Physiological response, biochemical status, and enzymatic fluctuations of plants and the distribution of HMs in plant parts and soil, were quantified. With the combined use (5% each v/v conditioner/soil) of C and M, in bio-augmented soil, physiological response and enzymatic status of both plants improved, with decreased stress injury due to HMs. Further, the plant HMs uptake was reduced, with better stabilization of HM in soil. For better phytostabilization of HMs in wastewater, the use of compost, peat moss, and bacterial augmentation is recommended with Nicotiana alata L. and Petunia hydrida L.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonkiewicz J, Baran A, Pełka R, Wisła-Świder A, Nowak E, Konieczka P (2019) A mixture of cellulose production waste with municipal sewage as new material for an ecological management of wastes. Ecotox Environ Safe 169:607–614
Antonkiewicz J, Kołodziej B, Bielińska EJ, Witkowicz R, Tabor S (2018) Using Jerusalem artichoke to extract heavy metals from municipal sewage sludge amended soil. Pol J Environ Stud 27:513–527
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Arshad M, Khan AHA, Hussain I, Anees M, Iqbal M, Soja G, Linde C, Yousaf S (2017) The reduction of chromium (VI) phytotoxicity and phytoavailability to wheat (Triticum aestivum L) using biochar and bacteria. Appl soil ecol 114:90–98
Asemoloye MD, Jonathan SG, Ahmad R (2018) Synergistic plant-microbes interactions in the rhizosphere: a potential headway for the remediation of hydrocarbon polluted soils. Int J Phytoremediat 21:71–83
Busi E, Maranghi S, Corsi L, Basosi R (2016) Environmental sustainability evaluation of innovative self-cleaning textiles. J Clean Prod 133:439–450
Chandanshive VV, Kadam SK, Khandare RV, Kurade MB, Jeon B-H, Jadhav JP, Govindwar SP (2018) In situ phytoremediation of dyes from textile wastewater using garden ornamental plants effect on soil quality and plant growth. Chemosphere 210:968–976
Chen G-X, Asada K (1989) Ascorbate peroxidase in tea leaves: occurrence of two isozymes and the differences in their enzymatic and molecular properties. Plant Cell Physiol 30:987–998
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32:93–101
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
Etesami H (2018) Bacterial mediated alleviation of heavy metal stress and decreased accumulation of metals in plant tissues: mechanisms and future prospects. Ecotox Environ Safe 147:175–191
Fellbaum CR, Mensah JA, Cloos AJ, Strahan GE, Pfeffer PE, Kiers ET, Bücking H (2014) Fungal nutrient allocation in common mycorrhizal networks is regulated by the carbon source strength of individual host plants. New Phytol 203:646–656
Feng J, Lin Y, Yang Y, Shen Q, Huang J, Wang S, Zhu X, Li Z (2018) Tolerance and bioaccumulation of Cd and Cu in Sesuvium portulacastrum. Ecotox Environ Safe 147:306–312
Frew A, Powell JR, Hiltpold I, Allsopp PG, Sallam N, Johnson SN (2017) Host plant colonisation by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi stimulates immune function whereas high root silicon concentrations diminish growth in a soil-dwelling herbivore. Soil Biol Biochem 112:117–126
Gadipelly C, Pérez-González A, Yadav GD, Ortiz I, Ibáñez R, Rathod VK, Marathe KV (2014) Pharmaceutical industry wastewater: review of the technologies for water treatment and reuse. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:11571–11592
Ghori NH, Ghori T, Hayat M, Imadi S, Gul A, Altay V, Ozturk M (2019) Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1807–1828
Hussain F, Hussain I, Khan AHA, Muhammad YS, Iqbal M, Soja G, Reichenauer TG, Yousaf S (2018) Combined application of biochar compost and bacterial consortia with Italian ryegrass enhanced phytoremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Environ Exp Bot 153:80–88
Iqbal A, Mushtaq MU, Khan AH, Nawaz I, Yousaf S, Iqbal M (2019) Influence of Pseudomonas japonica and organic amendments on the growth and metal tolerance of Celosia argentea L. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2019:1–5
Kaewtubtim P, Meeinkuirt W, Seepom S, Pichtel J (2016) Heavy metal phytoremediation potential of plant species in a mangrove ecosystem in Pattani Bay Thailand. Appl Ecol Env Res 14:367–382
Kanwal U, Ali S, Shakoor MB, Farid M, Hussain S, Yasmeen T, Adrees M, Bharwana SA, Abbas F (2014) EDTA ameliorates phytoextraction of lead and plant growth by reducing morphological and biochemical injuries in Brassica napus L. under lead stress. Environ Sci Pollut R 21:9899–9910
Khan AHA, Anees M, Arshad M, Muhammad YS, Iqbal M, Yousaf S (2016) Effects of illuminance and nutrients on bacterial photo-physiology of hydrocarbon degradation. Sci Total Envrion 557:705–711
Khan AHA, Ayaz M, Arshad M, Yousaf S, Khan MA, Anees M, Sultan A, Nawaz I, Iqbal M (2019a) Biogeochemical Cycle Occurrence and Biological Treatments of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). Iran J Sci Technol A 43:1393–1410
Khan AHA, Butt TA, Mirza CR, Yousaf S, Nawaz I, Iqbal M (2019b) Combined application of selected heavy metals and EDTA reduced the growth of Petunia hybrida L. Sci Rep 9:4138
Khan AHA, Nawaz I, Qu Z, Butt TA, Yousaf S, Iqbal M (2020) Reduced growth response of ornamental plant Nicotiana alata L. upon selected heavy metals uptake, with co-application of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Chemosphere 28:125006
Khan AHA, Nawaz I, Yousaf S, Cheema AS, Iqbal M (2019c) Soil amendments enhanced the growth of Nicotiana alata L. and Petunia hydrida L. by stabilizing heavy metals from wastewater. J Envion Manage 242:46–55
Li Z, Wu L, Luo Y, Christie P (2018) Changes in metal mobility assessed by EDTA kinetic extraction in three polluted soils after repeated phytoremediation using a cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator. Chemosphere 194:432–440
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes Methods in enzymology. Elsevier, New York, pp 350–382
Liu K, Lin B (2019) Research on influencing factors of environmental pollution in China: a spatial econometric analysis. J Clean Prod 206:356–364
Ma Y, Oliveira RS, Nai F, Rajkumar M, Luo Y, Rocha I, Freitas H (2015) The hyperaccumulator Sedum plumbizincicola harbors metal-resistant endophytic bacteria that improve its phytoextraction capacity in multi-metal contaminated soil. J Envion Manage 156:62–69
Macci C, Peruzzi E, Doni S, Iannelli R, Masciandaro G (2015) Ornamental plants for micropollutant removal in wetland systems. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:2406–2415
Maehly A, Chance B (1954) The assay of catalases and peroxidase. In: Glick D (ed) Methods of biochemical analysis. Interscience, New York, p 454
Majed N, Real M, Isreq H, Akter M, Azam HM (2016) Food adulteration and bio-magnification of environmental contaminants: a comprehensive risk framework for Bangladesh. Front Environ Sci 4:34
Manzoor M, Khan AHA, Ullah R, Khan MZ, Ahmad I (2016) Environmental epidemiology of cancer in South Asian population: risk assessment against exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and volatile organic compounds. Arab J Sci Eng 41:2031–2043
Marques AP, Oliveira RS, Samardjieva KA, Pissarra J, Rangel AO, Castro PM (2007) Solanum nigrum grown in contaminated soil: effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on zinc accumulation and histolocalisation. Environ Pollut 145:691–699
Midhat L, Ouazzani N, Hejjaj A, Ouhammou A, Mandi L (2019) Accumulation of heavy metals in metallophytes from three mining sites (Southern Centre Morocco) and evaluation of their phytoremediation potential. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 169:150–160
Nawab J, Ghani J, Khan S, ** W (2018) Minimizing the risk to human health due to the ingestion of arsenic and toxic metals in vegetables by the application of biochar farmyard manure and peat moss. J Envion Manage 214:172–183
Oyetibo GO, Miyauchi K, Huang Y, Chien MF, Ilori MO, Amund OO, Endo G (2017) Biotechnological remedies for the estuarine environment polluted with heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 119:614–625
Raza A, Khan AH, Nawaz I, Qu Z, Yousaf S, Ali MA, Sayal AU, Iqbal M (2019) Evaluation of arsenic-induced stress in Dahlia pinnata Cav.: morphological and physiological response. Soil Sediment Contam 28:716–728
Serrano HC, Cotrim H, Pinto MJ, Martins-Loução MA, Branquinho C (2017) Metal hyperaccumulation patterns within Plantago phylogeny (Plantaginaceae). Plant Soil 411:227–241
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ, Mimura T (2016) Vacuolar compartmentalization as indispensable component of heavy metal detoxification in plants. Plant Cell Environ 39:1112–1126
Tauqeer HM, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Saeed R, Iftikhar U, Ahmad R, Farid M, Abbasi GH (2016) Phytoremediation of heavy metals by Alternanthera bettzickiana: growth and physiological response. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:138–146
Thakur S, Sharma SS (2016) Characterization of seed germination seedling growth and associated metabolic responses of Brassica juncea L cultivars to elevated nickel concentrations. Protoplasma 253:571–580
Üstün Ş, Müller P, Palmisano R, Hensel M, Börnke F (2012) SseF a type III effector protein from the mammalian pathogen Salmonella enterica requires resistance-gene-mediated signalling to activate cell death in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana. New Phytol 194:1046–1060
Wang M, Liu H, Cheng X, Zhang B, Cai C, Wang J (2019a) Hydrothermal treatment of lincomycin mycelial residues: Antibiotic resistance genes reduction and heavy metals immobilization. Bioresource Technol 271:143–149
Wang Y, Zhong B, Shafi M, Ma J, Guo J, Wu J, Ye Z, Liu D, ** H (2019b) Effects of biochar on growth and heavy metals accumulation of moso bamboo (Phyllostachy pubescens) soil physical properties and heavy metals solubility in soil. Chemosphere 219:510–516
**a Y, Liu J, Wang Y, Zhang X, Shen Z, Hu Z (2018) Ectopic expression of Vicia sativa Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (VsCCoAOMT) increases the uptake and tolerance of cadmium in Arabidopsis. Environ Exp Bot 145:47–53
Xu P, Han N, Kang T, Zhan S, Lee KS, ** BR, Li J, Wan H (2016) SeGSTo a novel glutathione S-transferase from the beet armyworm (Spodoptera exigua) involved in detoxification and oxidative stress. Cell Stress Chaperone 21:805–816
Yahmed JB, de Oliveira TM, Novillo P et al (2016) A simple fast and inexpensive method to assess salt stress tolerance of aerial plant part: Investigations in the mandarin group. J Plant Physiol 190:36–43
Yang Y, Song Y, Scheller HV, Ghosh A, Ban Y, Chen H, Tang M (2015) Community structure of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with Robinia pseudoacacia in uncontaminated and heavy metal contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 86:146–158
Zhang X, Zhong B, Shafi M, Guo J, Liu C, Guo H, Peng D, Wang Y, Liu D (2018) Effect of EDTA and citric acid on absorption of heavy metals and growth of Moso bamboo. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:18846–18852
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out due to the funding by Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan to first author, Mr. Khan, under Indigenous 5000 PhDs scheme (Funding number 2AV1-084, 2012). The Authors also want to acknowledge the support by Dr. Hassaan Javed, from Department of Plant Sciences, QAU, Pakistan, for providing the spectrophotometry facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A.H.A., Kiyani, A., Cheema, A.S. et al. Integrative Application of Soil Conditioners and Bio-augmentation for Enhanced Heavy Metal Stabilization from Wastewater and Improved Growth of Nicotiana alata L. and Petunia hydrida L.. J Plant Growth Regul 40, 240–253 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10094-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10094-4