Abstract
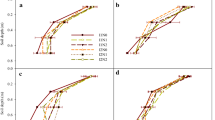
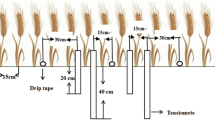
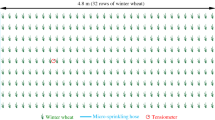
The 2-year field experiments were carried out to research the effect of different irrigation methods, namely border irrigation, sprinkler irrigation, and surface drip irrigation, on root development and profile water uptake in winter wheat. Results showed that the main root distribution zone moved upward under sprinkler and surface drip irrigation when compared to the traditional border irrigation. Profile root distribution pattern changed with irrigation methods. Soil profile water uptake was correlated to the root system and soil water dynamics. Due to the appropriate soil water and higher root density in the surface soil layer under sprinkler and surface drip irrigation, the main water uptake zone was concentrated in the upper layer. Because of the water deficit in the surface layer under border irrigation, water uptake in 50–100 cm depth was stimulated, which caused the main uptake zone downward. The amount and pattern of root water uptake varied with irrigation methods. This may provide valuable information on the aspect of agricultural management.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai WM, Li LH (2003) Effect of irrigation methods and quota on root water uptake and biomass of alfalfa in the Wulanbuhe sandy region of China. Agric Water Manage 62:139–148
Belmans C, Wesseling JG, Feddes RA (1983) Simulation model of the water balance of a cropped soil: SWATRE. J Hydrol 63:271–286
Benjamin JG, Nielsen DC (2006) Water deficit effects on root distribution of soybean, field pea and chickpea. Field Crops Res 97:248–253
Clothier BE, Green SE (1994) Rootzone processes and the efficient use of irrigation water. Agric Water Manage 25:1–12
Feddes RA, Kowalik PJ, Zaradny H (1978) Simulation of field water use and crop yield. Simulation monograph. Pudoc, Wageningen
Hodgson AS, Constable GA, Duddy GR, Daniells IG (1990) A comparison of drip and furrow irrigated cotton on a cracking clay soil. Irrig Sci 11:143–148
Home PG, Panda RK, Kar S (2002) Effect of method and scheduling of irrigation on water and nitrogen use efficiencies of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Agric Water Manage 55:159–170
KÄtterer T, Hansson A, Andrén O (1993) Wheat root biomass and nitrogen dynamics–effects of daily irrigation and fertilization. Plant Soil 151:21–30
Liu HJ, Kang YH (2004) Sprinkler irrigation scheduling using 20 cm standard pan. ASAE/CSAE meeting Paper No. 042093
Liu HJ, Kang YH (2006) Effect of sprinkler irrigation on microclimate in the winter wheat field in the North China Plain. Agric Water Manage 84:3–19
Liu HJ, Kang YH (2007) Sprinkler irrigation scheduling of winter wheat in the North China Plain using a 20 cm standard pan. Irrig Sci 25:149–159
Luo Y, Yu Q, Ou YZ, Tang DY, **e XQ (2000) The evaluation of water uptake models by using precise field observation data. J Hydra Eng 4:73–80 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Merrill SD, Rawlins SL (1979) Distribution and growth of sorghum roots in response to irrigation frequency. Agron J 71:738–745
Phene CJ, Davis KR, Hutmacher RB, Bar-Yosef B, Meek DW, Misaki J (1991) Effect of high frequency surface and subsurface drip irrigation on root distribution of sweet corn. Irrig Sci 12:135–140
Proffitt APB, Berliner PR, Oosterhuis DM (1985) A comparative study of root distribution and water extraction efficiency by wheat grown under high- and low-frequency irrigation. Agron J 77:655–662
Rawlins SL, Roats PAC (1975) Prospects for high-frequency irrigation. Science 188:604–610
Rowse HR (1974) The effect of irrigation on the length, weight, and diameter of lettuce roots. Plant Soil 40:381–391
Salgado E, Cautin R (2008) Avocado root distribution in fine and coarse-textured soils under drip and microsprinkler irrigation. Agric Water Manage 95:817–824
Simunek J, Sejna M, Saito H, Sakai M, van Genuchten MTh (2008) The HYDRUS-1D software package for simulating the one-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media, Version 4.0x, Hydrus Series 3. Department of Environmental Sciences, University of California Riverside, Riverside
Sun ZQ (2006) Research on the effect of sprinkler irrigation on soil structure and the characteristic of water and nitrogen distribution. Ph. D thesis of Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Bei**g, China (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tolk JA, Howell TA, Steiner JL, Krieg DR (1995) Role of transpiration suppression by evaporation of intercepted water in improving irrigation efficiency. Irrig Sci 16:89–95
Torreano SJ, Morris LA (1998) Loblolly pine root growth and distribution under water stress. Soil Sci Soc Am J 62:818–827
Unger PW, Kaspar TC (1994) Soil compaction and root growth: a review. Agron J 86:759–766
van Genuchten MTh (1985) Convective–dispersive transport of solutes involved in sequential first order decay reactions. Comput Geosci 11(2):129–147
Wang D, Yates SR, Simunek J, van Genuchten MTh (1997) Solute transport in simulated conductivity fields under different irrigations. Trans ASAE 123(5):336–343
Xu ZX, Zhang L, Ruan BQ (2006) Analysis on the spatiotemporal distribution of precipitation in the Bei**g region. Arid Land Geogr 29(2):186–192 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yao SM (2005) Effect of sprinkler irrigation on water physiology, photosynthesis, crop growth and water use efficiency of winter wheat. Ph. D thesis of Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Bei**g, China (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu ZW (2007) Science of crop cultivation. China Agric Press, Bei**g (in Chinese)
Zheng CH, Kang YH, Yao SM, Yan CZ, Sun ZQ (2004) Method of root analysis using GIS technology. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 20(1):181–183 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zuo Q, Jie F, Zhang RD, Meng L (2004) A generalized function of wheat’s root length density distribution. Vadose Zone 3:271–277
Acknowledgments
This study is part of the work of Knowledge Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCX2-YW-N-003), and Project 50679077 supported by the National Science Foundation and No. D0706007040191-06 supported by the Bei**g Science and Technology Plan and Project for 100 outstanding Young Scientists (Yaohu Kang) supported by Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Azam-Ali.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, G., Kang, Y., Li, L. et al. Effect of irrigation methods on root development and profile soil water uptake in winter wheat. Irrig Sci 28, 387–398 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-009-0200-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-009-0200-1