Abstract
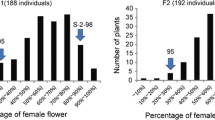
Owing to its diverse sex types, the cucumber plant has been studied widely as a model for sex determination. In addition to environmental factors and plant hormones, three major genes—F/f, M/m, and A/a—regulate the sex types in the cucumber plant. By combining the bulked segregant analysis (BSA) and the sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) technology, we identified eight markers linking to the M/m locus. Among them, the two closely linked SRAP markers flanking the M/m locus were the co-dominant marker ME1EM26 and the dominant marker ME1EM23. Further, the co-dominant marker ME8SA7 co-segregated with the M/m locus. With the chromosome walking method using the cucumber genomic bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library, we successfully developed a co-dominant SCAR marker S_ME1EM23 from the ME1EM23 sequence. Along with the other two co-dominant SCAR markers S_ME1EM26 and S_ME8SA7 (developed from ME1EM26 and ME8SA7, respectively) in a larger segregating population (900 individuals), the M/m locus was mapped between S_ME1EM26 (5.4 cM) and S_ME1EM23 (0.7 cM), and S_ME8SA7 co-segregated with it.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lippman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Atsmon D (1968) The interaction of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors in stem elongation and floral development of cucumber plants. Ann Bot 32:877–882
Atsmon D, Galun E (1960) A morphogenetic study of staminate, pistillate and hermaphrodite flowers in Cucumis sativus L. Phytomorphology 10:110–115
Barret P, Delourme R, Foisset N, Renard M (1998) Development of a SCAR (sequence characterized amplified region) marker for molecular tagging of the dwarf BREIZH (Bzh) gene in Brassica napus L. Theor Appl Genet 97:828–833
Bassam BJ, Caetana-Anolles G, Gresshoff PM (1991) Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196:80–83
Bradeen JM, Simon PW (1998) Conversion of an AFLP fragment linked to the carrot Y2 locus to a simple, co-dominant, PCR based marker form. Theor Appl Genet 97:960–967
Clark MS (1997) Plant molecular biology: a laboratory manual. Springer, Berlin
Dijkhuizen A, Kennard WC, Havey MJ, Staub JE (1996) RFLP variability and genetic relationships in cultivated cucumber. Euphytica 90:79–87
Engelke T, Mibus H, Tatlioglu T (1999) Approaches to isolating the gene M/m for femaleness in Cucumis sativus L. ISHS Acta Hort 492:355–361
Ferriol M, Pico B, Nuez F (2003) Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 107:271–282
Flankel R, Galun E (1977) Pollination mechanisms: reproduction and plant breeding. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Galun E (1961) Study of the inheritance of sex expression in the cucumber: the interaction of major genes with modifying genetic and non-genetic factors. Genetica 32:134–163
Goffinet MC (1990) Comparative ontogeny of male and female flowers of Cucumis sativus. In: Bates EM, Robinson RW, Jeffrey C (eds) Biology and utilization of the Cucurbitaceae. Cormell University Press, New York, pp 288–304
Guan Y, Chen Q, Pan JS, Li Z, He HL, Wu AZ, Song RT, Cai R (2008) Construction of a BAC library from cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) and identification of linkage group specific clones. Prog Nat Sci 18:143–147
Hao YJ, Wang DH, Peng YB, Bai SL, Xu LY, Li YQ, Xu ZH, Bai SN (2003) DNA damage in the early primordial anther is closely correlated with stamen arrest in the female flower of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Planta 217:888–895
Kamachi S, Sekimoto H, Kondo N, Sakai S (1997) Cloning of a cDNA for a 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase that is expressed during development of female flowers at the apices of Cucumis sativus L. Plant Cell Physiol 38:1197–1206
Kamachi S, Mizusawa H, Matsuura S, Sakai S (2000) Expression of two 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase genes, CS-ACS1 and CS-ACS2, correlated with sex phenotypes in cucumis plants (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Biotechnol 17:69–74
Kater MM, Franken J, Carney KJ, Colombo L, Angenent GC (2001) Sex determination in the monoecious species cucumber is confined to specific floral whorls. Plant Cell 13:481–493
Knopf RR, Trebitsh T (2006) The female-specific CS-ACS1G gene of cucumber. A case of gene duplication and recombination between the non-sex-specific 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase gene and a branched-chain amino acid transaminase gene. Plant Cell Physiol 47:1217–1228
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Kubicki B (1969) Investigation of sex determination in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Genet Pol 10:5–143
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMARKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural population. Genomics 1:174–181
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system base on a simple PCR reaction: its application to map** and gene tagging in Brassiac. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461
Li G, Gao M, Yang B, Quiros CF (2003) Gene for gene alignment between the Brassica and Arabidopsis genomes by direct transcriptome map**. Theor Appl Genet 107:168–180
Liu Z, Fu T, Wang Y, Tu J, Chen B, Zhou Y, Ma C, Shan L (2006) Development of SCAR and CAPS markers for a partially dominant yellow seed coat gene in Brassica Napus L. Euphytica 149:381–385
Malepszy S, Niemirowicz-Szczytt K (1991) Sex determination in cucumber (Cucumis sativus) as a model system for molecular biology. Plant Sci 80:39–47
Mibus H, Tatlioglu T (2004) Molecular characterization and isolation of the F/f gene of femaleness in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1669–1676
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Negi MS, Devic M, Delseny M, Lakshmikumaran M (2000) Identification of AFLP fragments linked to seed coat colour in Brassica juncea and conversion to a SCAR marker for rapid selection. Theor Appl Genet 101:146–152
Noguera FJ, Capel J, Alvarez JI, Lozano R (2005) Development and map** of a codominant SCAR marker linked to the andromonoecious gene of melon. Theor Appl Genet 110:714–720
Perl-Treves R (1999) Male to female conversion along the cucumber shoot: approaches to studying sex genes and floral development in Cucumis sativus. In: Ainsworth CC (ed) Sex determination in plants. BIOS, Oxford, pp 189–286
Przybecki Z, Kowalczyk ME, Siedlecka E, Urabanczyk-Wochniak E, Malepszy S (2003) The isolation of cDNA clones from cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) floral buds coming from plants differing in sex. Cell Mol Biol Lett 8:421–438
Rahman M, McVetty PBE, Li G (2007) Develpoment of SRAP, SNP and multiplexed SCAR molecular markers for the major seed coat color gene in Brassica rapa L. Theor Appl Genet 115:1101–1107
Robinson RW, Munger HM, Whitaker TW, Bohn GM (1976) Genes of Cucubitaceae. HortSci 11:554–568
Saito S, Fujii N, Miyazawa Y, Yamasaki S, Matsuura S, Mizusawa H, Fujita Y, Takahashi H (2007) Correlation between development of female flower buds and expression of the CS-ACS2 gene in cucumber plants. J Exp Bot 58:2897–2907
Shifriss O (1961) Sex control in cucumber. J Hered 52:5–12
Takaheshi H, Saito T, Suge H (1983) Separation of effects of photoperiod and hormones on sex expression in cucumber. Plant Cell Physiol 24:142–154
Tanurdzic M, Banks JA (2004) Sex-determining mechanisms in land plants. Plant Cell 16:S61–S71
Terefe D, Tatlioglu T (2005) Isolation of a partial sequence of a putative nucleotide sugar epimerase, which may involve in stamen development in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor Appl Genet 111:1300–1307
Trebitsh T, Staub JE, O’Neill SD (1997) Identification of a 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase gene linked to the female (F) locus that enhance female sex expression in cucumber. Plant Physiol 113:987–995
Tsao TH (1988) Sex expression in flowering. Acta Phytophysiol Sin 14:203–207
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Lee T, Hornes M, Friters A, Pot J, Paleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang G, Pan JS, Li XZ, He HL, Wu AZ, Cai R (2005) Construction of a cucumber genetic linkage map with SRAP markers and location of the genes for lateral branch traits. Sci China (Ser. C) 48:213–220
Xu M, Li X, Korban SS (2000) AFLP-based detection of DNA methylation. Plant Mol Biol Rep 18:361–368
Yamasaki S, Fujii N, Matsuura S, Mizusawa H, Takahashi H (2001) The M locus and ethylene-controlled sex determination in andromonoecious cucumber plants. Plant Cell Physiol 42:608–619
Yamasaki S, Fujii N, Takahashi H (2003) Photoperiodic regulation of CS-ACS2, CS-ACS4 and CS-ERS gene expression contributes to the femaleness of cucumber flowers through diurnal ethylene production under short-day conditions. Plant Cell Environ 26:537–546
Yamasaki S, Fujii N, Takahashi H (2005) Hormonal regulation of sex expression in plants. Vitam Horm 72:79–110
Yin T, Quinn JA (1995) Tests of a mechanistic model of one hormone regulating both sexes in Cucumis sativus (Cucurbitaceae). Am J Bot 82:1537–1546
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Rentao Song (Shanghai University) for his technical assistance in BAC library. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30500289), National “863” Project (No. 2008AA10Z150), and Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (No. B209).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Hagemann.
Z. Li and J. Pan contribute equally to this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Pan, J., Guan, Y. et al. Development and fine map** of three co-dominant SCAR markers linked to the M/m gene in the cucumber plant (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor Appl Genet 117, 1253–1260 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0859-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0859-3