Abstract
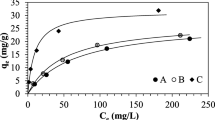
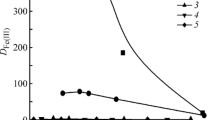
Simultaneous removal of heavy metal and cyanide ions in an ion exchange column is studied on the basis of formation of metal-cyanide complexes at high pH range. Strong base anion exchange resin beads were contacted with water containing heavy metal (Cu, Cd, Zn) and cyanide ions in semi-fluidized and fluidized beds. Compositions of the heavy metal-cyanide complexes formed for different heavy metal and cyanide concentrations are used to explain the ion exchange behavior. Ion exchange equilibrium data of this study were fitted well with the Langmuir isotherm. The ion exchange capacity of CNas metal complexes increased to about three times that of free cyanide due to higher selectivity of metal complexes on the anion exchange resin. The ion exchange efficiency of the three heavy metalcyanide systems decreases as the concentration ratio of cyanide and heavy metal increases. The regeneration rates of the regenerants used was in the order of NaSCN>NaCN>NaOH, and the regeneration rate of NaOH was substantially lower than other two.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akretche, D. E. and Kerdjouj, H., “Donna Dialysis of Copper, Gold, and Silver Cyanides with Various Anion Exchange Membranes,”Talanta,51, 281 (2000).
Avery, N. L. and Fries, W., “Selective Removal of Cyanide from Industrial Waste Effluent with Ion-Exchange Resins,”Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev.,14, 102 (1975).
Bhakta, D., Shukkla, S. S. and Margrave, L. J., “A Novel Photocatan lytic Method for Detoxification of Cyanide Wastes,”Environ. Sci., Technol.,26, 625 (1992).
Chi, G., Fuerstenau, M. C. and Marsden, J.O., “Study of Merrill-Crowe Processing. Part I: Solubility of Zinc in Alkaline Cyanide Solution,”Int. J. Miner. Process,49, 171 (1997).
Cho, S.H. and Jeong, W. J., “Treatment of Electroplating Wastewater Containing Heavy Metal-Cyanide Complex,”J. KSEE,21, 1095 (1999).
Eckenfelder, W.W. Jr., “Industrial Water Pollution Control,” 3rd. Ed., McGraw-Hill Co. (2000).
Fan, L. T., Yang, Y. C. and Wen, C.Y., “Semi-fluidization: Mass Transfer in Semi-fluidized Beds,”AIChE J.,5, 407 (1959).
Fan, L. T., Yang, Y. C. and Wen, C.Y., “Mass Transfer in Semi-fluidized Beds for Solid-Liquid System,”AIChE J.,6, 482 (1960).
Geol, M., Agrawal, V., Kulkarni, A. K., Cramer, S.M. and Gill, W.N., “Stability and Transport Characteristics of Reverse Osmosis Membranes Using Cyanide Rinse Waters,”J. Membranes Sci.,141, 245 (1998).
Goldblatt, E., “Recovery of Cyanide from Waste Cyanide Solutions by Ion Exchange,”Ind. Eng. Chem.,48, 2107 (1956).
Goncalves, M. M.M., Pinto, A. F. and Granato, M., “Biodegradation of Free Cyanide, Thiocynide and Metal Complexed Cyanides in Solutions with Different Compositions,”Environmental Technology,19, 133 (1998).
Goto, M. and Goto, S., “Removal and Recovery of Heavy Metal by Ion Exchange Fiber,”J. Chem. Eng. Japan,20, 467 (1987).
Gupta, A., “Recovery of Metal-Cyanide Complexes from Electroplating Wastewaters by Ion Exchange,” Ph. D. Thesis, The Faculty of Princeton University, U.S.A. (1985).
Hassan, S.O., Vitello, M. P. and Kupferle, M. J., “Treatment Technology Evaluation for Aqueous Metal and Cyanide,”J. Air Waste Manage Assoc. 47, 710 (1991).
Herzorg, A. D., “Cyanide leach Technology and Its Applicability to Alaskan Conditions,” Open File Report, U. S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines, 89 (1996).
Hsu, T. L., Tran, T. and Young, D., “Modeling of the Chemical Speciation of Cyanide Species Application to Effluent Treatment,” Ausimm Extractive Metal Con., 133 (1991).
Jang, J.G., Kim, W. H. and Kim M. R., “Prediction of Gaseous Pollutants and Heavy metals during Fiuidized Bed Incineration of Dye Sludge,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 506 (2001)
Jeon, C., Park, J.Y. and Yoo, Y. J., “Removal of Heavy Metals in Plating Wastewater Using Carboxylated Alginic Acid,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 955 (2001).
Karabulut, S., Karabakan, A., Denizli, A. and Yurum, Y., “Batch Removal of Copper(II) and Zinc(II) from Aqueous Solutions with Lowrank Turkish Coals,”Separation and Purification Technol,18, 177 (2000).
Kim, J. B., Sohn, J. E., Lee, S. S. and Lee, N.W., “Adsorption Characteristics of Cyanide Complex Anion of Heavy Metal on Activated Carbon,”HWAHAK KONGHAK,24, 1 (1986).
Kim, J. S., Chah, S. and Yi, H., “Preperation of Modified Silica for Heavy Metal Removal,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,17, 118 (2000).
Kim, S. J., Lim, K.H., Park, Y.G., Kim, J.H. and Cho, S.Y., “Simultaneous Removal and Recovery of Cadmium and Cyanide Ions in Synthetic Wastewater by Ion Exchange,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 686 (2001).
Kim, S. J., Hwang, K. R. and Cho, S. Y., “Study on Ion-Exchange Behavior of Cu-CN Complexes,”J. Chem. Eng. Japan,34, 193 (2001).
Kim, S. J., Hwang, K. R., Cho, S.Y. and Moon, H., “Simultaneous Removal of Cyanide and Copper Ions in a Semi-Fluidized Ion Exchanger Bed,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,16, 664 (1999).
Kunii, D. and Levenspiel, O., “Fluidization Engineering,” Willy, U.S.A. (1986).
Kuruyama, H. and Catalsarik, T., “Removal of Zinc Cyanide from a Leach Solution by an Anionic Ion-Exchange Resin,”Desalination,129, 1 (2000).
Lee, D.H. and Moon, H., “Adsorption Equillibrium of Heavy Metals on Natural Zeolites,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 247 (2001).
Lee, H. S. and Suh, J.H., “Interference of Aluminium in Heavy metal Biosorption by a Seaweed Biosorbent,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 692 (2001).
Lee, H. S. and Suh, J.H., “Continuous Biosorption of Heavy Metal Ions by Ca-loaded laminaria japonica in Fixed Bed Column,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,17, 477 (2000).
Lee, M. G., Yi, G. and Ahn, B. J., “Conversion of Coal Fly Ash into Zeolite and Heavy Metal Removal Charateristics of the Products,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,17, 325 (2000).
Lin, S.H. and Juang, R. S., “Heavy Metal Removal from Water by Sorption Using Surfactant-Modified Montmorillonite,”J. of Hazardous Materials,92, 315 (2002).
Lucky, G. C., Van Deventer, J. and Shallcross, D.C., “Equilibrium Model for the Sorption of Gold Cyanide and Copper Cyanide on Trimethylamine Ion Exchange Resin in Saline Solution,”Hydrometallurgy,59, 101 (2001).
Mydlarz, J., “Prediction of Packed Bed Height in Liquid-Solid Semifluidization of Homogeneous Mixtures,”Chem. Eng. J.,34, 155 (1987).
Short, A. E., Haselmann, S. F. and Semmend, M. J., “The GM-IX Process-A Pilot Study for Recovering Zinc Cyanide,”J. Environmental Science & Health, Part A,32, 216 (1997).
Weltrowski, M., Martel, B. and Morcellet, M., “Chitosan N-benzyl Sulfonate Derivatives as Sorbents for Removal of Metal Ions in an Acidic Medium,”J. Appl. Polym. Sci.,59, 647 (1996).
Yang, H. C., Yun, J. S. and Kang, M.G., “Mechanisms and Kinetics of Cadmium and Lead Capture by Calcined Kaolin at High Temperatures,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 499 (2001).
Zhou, C. and Chin, D. T., “Copper Recovery and Cyanide Destruction with a Plating B13arrel Cathode and a Packed-Bed Anode,”Plat. Surf. Finish,80, 69 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Professor Dong Sup Doh on the occasion of his retirement from Korea University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SJ., Lim, KH., Joo, KH. et al. Removal of heavy metal-cyanide complexes by ion exchange. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 19, 1078–1084 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02707236
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02707236