Summary
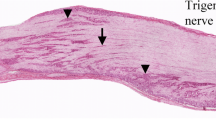
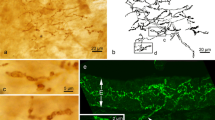
Calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive cells were identified within the epithelium of distal conducting airways in the human fetus and infant. Several peptides and amines, including calcitonin, have been identified previously within a specific population of airway epithelial cells. These cells, referred to as pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, are postulated to be airway chemoreceptors responsible for changes in ventilation and perfusion in response to changes in airway gas composition. Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive cells could be identified throughout the period of development studies (20 weeks gestation to 3 months of age), but were present in only limited numbers in less than 50% of individuals (n=23). In contrast, large numbers of calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive cells were identified in 100% of infants (1–3 months, n=5) with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The differential processing of mRNA transcribed from the calcitonin gene in neural and non-neural tissue suggests that calcitonin, rather than calcitonin gene-related peptide, is the primary product of translation in pulmonary neuroendocrine cells. However, considering the potent vasodilatory and bronchoconstrictive effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide, its presence in pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, even in small amounts, may be important in controlling pulmonary vaso- and/or bronchomotor tone. The presence of large numbers of calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive cells in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia suggests that calcitonin gene-related peptide may be one further agent contributing to the pulmonary pathophysiology seen in this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG, Ong ES, Evans RM (1982) Processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNA's encoding polypeptide products. Nature 298:240–244
Amara SG, Arriza JL, Leff SE, Swanson LW, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG (1985) Expression in brain of a messenger RNA encoding a novel neuropeptide homologous to calcitonin gene-related peptide. Science 229:1094–1097
Barnes PJ (1986) Asthma as an axon reflex. Lancet 8475:242–245
Becker KL (1984) Historical perspective on the pulmonary endocrine cell. In: Becker KL, Gazdar AF (eds) The endocrine lung in health and disease. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 156–161
Becker KL, Silva OL, Snider RH, Moore CF, Geelhoed GW, Nash D, O'Neill WJ, Fink RJ, Murphy TM, Klass EM, Rohatgi PK (1984) The pathophysiology of pulmonary calcitonin. In: Becker KL, Gazdar AF (eds) The endocrine lung in health and disease. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 277–299
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Morris HR, Maclntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313:54–56
Brain SD, Maclntyre I, Williams TJ (1986) A second form of human calcitonin gene-related peptide which is a potent vasodilator. Eur J Pharmacol 124:349–352
Cadieux A, Springhall DR, Mulderry PK, Rodrigo J, Ghatei MA, Terenghi G, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1986) Occurrence, distribution and ontogeny of CGRP immunoreactivity in the rat lower respiratory tract: Effect of capsaicin treatment and surgical denervations. Neuroscience 19(2):605–627
Cutz E, Gillan JE, Track NS (1984) Pulmonary endocrine cells in the develo** human lung and during neonatal adaptation. In: Becker KL, Gazdar AF (eds) The endocrine lung in health and disease. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 210–231
Edbrooke MR, Parker D, McVey JH, Riley JH, Sorenson GD, Pettengil OS, Craig RK (1985) Expression of the human calcitonin/CGRP gene in lung and thyroid carcinoma. EMBO J 4(3):715–724
Fisher LA, Kikkawa DO, River JE, Amara SG, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG, Vale WW, Brown MR (1983) Stimulation of noradrenergic sympathetic outflow by calcitonin gene-related peptide. Nature 305:534–536
Gennari C, Fischer JA (1985) Cardiovascular action of calcitonin gene-related peptide in humans. Calcif Tissue Int 37:581–584
Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M, Maclntyre I, Hillyard CJ, Girgis S (1985) Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous, vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett 57:125–130
Gulbenkian S, Merighi A, Wharton J, Varndell IM, Polak JM (1986) Ultrastructural evidence for the coexistence of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in secretory vesicles of peripheral nerves in the guinea pig. J Neurocytol 15(4):535–542
Holman JJ, Craig RK, Marshall I (1986) Human α and β-CGRP and rat α-CGRP are coronary vasodilators in the rat. Peptides 7:231–235
Hoppener JW, Steenbergh PH, Moonen PJ, Wagenaar SS, Jansz HS, Lips CJ (1986) Detection of mRNA encoding calcitonin, calcitonin gene-related peptide and propiomelanocortin in human tumors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 47(1–2):125–130
Johnson DE, Lock JE, Elde RP, Thompson TR (1982) Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells in hyaline membrane disease and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res 16:446–454
Johnson DE, Kulik TJ, Lock JE, Elde RP, Thompson TR (1985) Bombesin-, calcitonin-, and serotonin-immunoreactive pulmonary neuroendocrine cells in acute and chronic neonatal lung disease. Pediatr Pulmonol l[Suppl]:S13-S20
Lauweryns JM, Van Lommel A (1982) Morphometric analysis of hypoxia-induced synaptic activity in intrapulmonary neuroepithelial bodies. Cell Tissue Res 226:201–214
Lauweryns JM, Cokelaere M, Lerut T, Theunynck P (1978) Crosscirculation studies on the influence of hypoxia and hypoxaemia on neuro-epithelial bodies in young rabbits. Cell Tissue Res 193:373–386
Le Greves P, Nyberg F, Terenius L, Hokfelt T (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent inhibitor of substance P degradation. Eur J Pharmacol 115:309–311
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1982) Capsaicin-sensitive vagal neurons involved in control of vascular permeability in rat trachea. Acta Physiol Scand 115:521–523
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1983) Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature 303:251–253
Lundberg JM, Franco-Cereceda A, Hua X, Hökfelt T, Fischer JA (1985) Co-existence of substance P and calcitonin generelated peptide-like immunoreactivities in sensory nerves in relation to cardiovascular and bronchoconstrictor effects of capsaicin. Eur J Pharmacol 108:315–319
Marshall I, Al-Kazwini SJ, Roberts PM, Shepperson NB, Adams M, Craig RK (1986a) Cardiovascular effects of human and rat CGRP compared in the rat and other species. Eur J Pharmacol 123:207–216
Marshall I, Al-Kazwini SJ, Holman JJ, Craig RK (1986b) Human and rat-CGRP but not calcitonin cause mesenteric vasodilatation in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 123:217–222
Mason RT, Peterfruend RA, Sawchenko PE, Corrigan AZ, Rivier JE, Vale WW (1984) Release of the predicted calcitonin gene related peptide from cultured rat trigeminal ganglion cells. Nature 308:653–655
Palmer JBD, Cuss FMC, Mulderry PK, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, Barnes PJ (1985) Calcitonin gene related peptide is a potent constrictor of human airway smooth muscle. Thorax 40(9):713
Piotrowski W, Foreman JC (1986) Some effects of calcitonin generelated peptide in human skin and on histamine release. Br J Dermatol 114:37–46
Regal JF, Johnson DE (1983) Indomethacin alters the effects of substance-P and VIP on isolated airway smooth muscle. Peptides 4:581–584
Riley JH, Edbrooke MR, Craig RK (1986) Ectopic synthesis of high-Mr calcitonin by the BEN lung carcinoma cell line reflects aberrant proteolytic processing. FEBS Lett 198:71–79
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod JJ, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW, Evans RM (1983) Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissuespecific RNA processing. Nature 304:129–135
Sabate MI, Stolarsky LS, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Varndell IM, Ghatei MA, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG (1985) Regulation of neuroendocrine gene expression by alternative RNA processing. J Biol Chem 260(5):2589–2592
Sigrist S, Franco-Cereceda A, Muff R, Henke H, Lundberg JM, Fischer JA (1986) Specific receptor and cardiovascular effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide. Endocrinology 119(1):381–389
Skofitsch G, Jacobowitz DM (1985) Autoradiographic distribution of 125I calcitonin gene-related peptide binding sites in the rat central nervous system. Peptides 4:975–986
Steenbergh PH, Hoppener JWM, Zanberg J, Lips CJM, Jansz HS (1985) A second human calcitonin/CGRP gene. FEBS Lett 183:403–407
Sternberger LA, Hardy PH, Cuculis JJ, Meyer JG (1970) The unlabeled antibody method of immunohistochemistry. Preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem 18:315–333
Struthers AD, Brown MJ, MacDonald DWR, Beacham JL, Ste venson JC, Morris HR, MacIntyre I (1986) Human calcitonin gene related peptide: A potent endogenous vasodilator in man. Clin Sci 70:389–393
Wharton J, Gulbenkian S, Mulderry PK, Ghatei MA, McGregor GP, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1986) Capsaicin induces a depletion of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-immunoreactive nerves in the cardiovascular system of the guinea pig and rat. J Auton Ner Syst 16:289–309
Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Hokfelt T, Lundberg JM, Forssmann WG, Reinecke M, Tschopp FA, Fischer JA (1984) Immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P coexist in sensory neurons to the spinal cord and interact in spinal behavioral responses of the rat. Neurosci Lett 52:199–204
Uddman R, Edvinsson L, Ekblad E, Håkanson R, Sundler F (1986) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP): Perivascular distribution and vasodilatory effects. Regul Pept 15(1):1–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, D.E., Wobken, J.D. Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in airway epithelial cells of the human fetus and infant. Cell Tissue Res. 250, 579–583 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218949
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218949