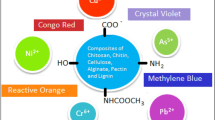
Abstract
Wastewater contaminated by dyes is a major issue brought about by the increase of human and industrial activities. The development of adsorbents based on polysaccharides and functional fillers is a feasible strategy to remove dyes from contaminated wastewater. Literature research over the last two decades indicated the most common dyes and the most frequent polysaccharide-base composites used for the removal of dyes. Methylene blue is the most frequent dye used in adsorption studies. Composites based on chitosan, alginate, and cellulose (or cellulose derivatives) and magnetic nanoparticles or graphene/graphene oxide are the most frequent systems applied as adsorbents. The adsorption in most cases is driven by electrostatic interactions between the composites and the dyes. For this reason, chitosan, alginate, and carboxymethyl cellulose are excellent candidates for the development of composites. Magnetic composites are advantageous because they can be easily recovered from the medium by the magnet approach. Graphene/graphene oxide particles have a large surface area, increasing the adsorption capacity. Along the sections, the functionality of different polysaccharides towards the adsorption of dyes was discussed in light of the reported literature. The last section points to possible paths to develop remediation processes and dyes based on biological or natural sources.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bechtold T, Mussak R (2009) Handbook of natural colorants. Wiley, Chichester. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470744970
Hunger K (ed) (2002) Industrial dyes, 1st edn. Wiley, Frankfurt. http://doi.org/10.1002/3527602011
Sabnis RW (2010) Handbook of biological dyes and stains. Wiley. http://doi.org/10.1002/9780470586242
Nassau K (1998) The fifteen causes of color. In: AZimuth. Elsevier Masson SAS, pp 123–168. http://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-6783(98)80007-X
Spencer J (2021) The sustainable development goals. Des Glob Challenges Goals 12–25. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003099680-3
United Nations Secretary (2017) Water action decade 2018–2028, New York. Available at http://digitallibrary.un.org/record/859143
Berradi M, Hsissou R, Khudhair M et al (2019) Textile finishing dyes and their impact on aquatic environs. Heliyon 5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02711
Crini G, Lichtfouse E (2019) Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 17:145–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0785-9
Voragen ACJ, Rolin C, Marr BU et al (2003) Polysaccharides. In: Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany
McNaught AD, Wilkinson A (eds) (2019) The IUPAC compendium of chemical terminology, 2nd edn. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), Oxford, UK. https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook
Theng BKG (2012c) The clay minerals. In: Developments in clay science, 2nd edn. Elsevier B.V., pp 3–45. http://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53354-8.00001-3
Theng BKG (2012d) Polysaccharides. In: Developments in clay science, pp 351–390. http://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53354-8.00011-6
Banerjee S, Pillai SC, Falaras P et al (2014) New insights into the mechanism of visible light photocatalysis. J Phys Chem Lett 5:2543–2554. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz501030x
Toledo PVO, Marques LR, Petri DFS (2019) Recyclable Xanthan/TiO2 composite cryogels towards the photodegradation of Cr(VI) ions and methylene blue dye. Int J Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8179842
Frizzo MS, Betega K, Poffo CM et al (2021) Highly enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic performance of TiO2 quantum dots synthesized by microwaves for degradation of reactive red azo dye. J Nanoparticle Res 23:113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05237-x
Nguyen TTH, Qureshi D, Lim S et al (2021) Introduction to polysaccharides. In: Food, medical, and environmental applications of polysaccharides. Elsevier, pp 3–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819239-9
Burkinshaw SM (2016) Physico-chemical aspects of textile coloration. Wiley, Chichester. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118725658
Sabnis RW (2015) Handbook of fluorescent dyes and probes, 1st edn. Wiley. http://doi.org/10.1002/9781119007104
Tardivo JP, Del Giglio A, De Oliveira CS et al (2005) Methylene blue in photodynamic therapy: from basic mechanisms to clinical applications. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 2:175–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1572-1000(05)00097-9
Martins BF, de Toledo PVO, Petri DFS (2017) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose based aerogels: synthesis, characterization and application as adsorbents for wastewater pollutants. Carbohydr Polym 155:173–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.082
Toledo PVO, Petri DFS (2019) Hydrophilic, hydrophobic, Janus and multilayer xanthan based cryogels. Int J Biol Macromol 123:1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.193
Hatakeyama T, Hatakeyama H (2017) Heat capacity and nuclear magnetic relaxation times of non-freezing water restrained by polysaccharides, revisited. J Biomat Sci 28:1215–1230. http://doi.org/10.10807/09205063.2017.1291551
Toledo PVO, Bernardinelli OD, Sabadini E, Petri DFS (2020) The states of water in tryptophan grafted hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hydrogels and their effect on the adsorption of methylene blue and rhodamine B. Carbohydr Polym 248:116765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116765
Ougiya H, Hioki N, Watanabe K, Morinaga Y, Yoshinaga F, Samejima M (1998) Relationship between the physical properties and surface area of cellulose derived from adsorbates of various molecular sizes. Biosci Bioechnol Biochem 62:1880–1884. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.62.1880
Mazeau K, Wyszomirski M (2012) Modelling of Congo red adsorption on the hydrophobic surface of cellulose using molecular dynamics. Cellulose 19:1495–1506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9757-6
Silva RA, Carmona-Ribeiro AM, Petri DFS (2013) Enzymatic activity of cholesterol oxidase immobilized onto polymernanoparticles mediated by Congo red. Colloids Surf B 110:347–355. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.03.024
Silva RA, Carmona-Ribeiro AM, Petri DFS (2014) Catalytic behavior of lipase immobilized onto Congo red and PEG-decorated particles. Molecules 19:8610–8628. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19068610
Pereira AGB, Rodrigues FHA, Paulino AT et al (2021) Recent advances on composite hydrogels designed for the remediation of dye-contaminated water and wastewater: a review. J Clean Prod 284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124703
Sabnis RW (2007) Handbook of acid-base indicators. CRC Press, San Francisco. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780849382192
De Araujo RE, Gomes ASL, De Araújo CB (2000) Measurements of pKa of organic molecules using third-order nonlinear optics. Chem Phys Lett 330:347–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(00)01108-8
Impert O, Katafias A, Kita P et al (2003) Kinetics and mechanism of a fast leuco-methylene blue oxidation by copper(ii)–halide species in acidic aqueous media. J Chem Soc Dalt Trans 3:348–353. https://doi.org/10.1039/b205786g
Stratton SG, Taumoefolau GH, Purnell GE et al (2017) Tuning the pKa of fluorescent rhodamine pH probes through substituent effects. Chem A Eur J 23:14064–14072. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201703176
Perrin DD, Dempsey B, Serjeant EP (1981) pK a prediction for organic acids and bases. Springer, Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-5883-8
Patel H (2019) Fixed-bed column adsorption study: a comprehensive review. Appl Water Sci 9:45–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0927-7
Al-Ghouti MA, Da’ana DA (2020) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: a review. J Hazard Mater 393:122383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383
Tran HN, You SJ, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Chao HP (2017) Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Water Res 120:88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014
Sabra W, Deckwer WD (2004) Alginate—a polysaccharide of industrial interest and diverse biological functions. In: Dumitriu S (ed) Polysacharides. Structural diversity and functional versatility, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton/USA, pp 515–533. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420030822-25
Izydorczyk M, Cui S, Wang Q (2005) Polysaccharide gums. In: Food carbohydrates. CRC Press. http://doi.org/10.1201/9780203485286.ch6
Morris ER, Rees DA, Thom D (1980) Characterisation of alginate composition and block-structure by circular dichroism. Carbohydr Res 81:305–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6215(00)85661-X
Sun L, Fugetsu B (2014) Graphene oxide captured for green use: influence on the structures of calcium alginate and macroporous alginic beads and their application to aqueous removal of acridine orange. Chem Eng J 240:565–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.083
Alver E, Metin AÜ, Brouers F (2020) Methylene blue adsorption on magnetic alginate/rice husk bio-composite. Int J Biol Macromol 154:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.330
Cojocaru C, Humelnicu AC, Samoila P et al (2018) Optimized formulation of NiFe2O4@Ca-alginate composite as a selective and magnetic adsorbent for cationic dyes: experimental and modeling study. React Funct Polym 125:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.02.008
Mahmoodi NM (2013) Magnetic ferrite nanoparticle-alginate composite: synthesis, characterization and binary system dye removal. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 44:322–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2012.11.014
Rocher V, Siaugue JM, Cabuil V, Bee A (2008) Removal of organic dyes by magnetic alginate beads. Water Res 42:1290–1298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.09.024
Jabli M, Hassine BB (2018) Improved removal of dyes by [sodium alginate/4-methyl-2-(naphthalen-2-yl)-N-propylpentanamide-functionalized ethoxy-silica] composite gel beads. Int J Biol Macromol 117:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.194
Pashaei-Fakhri S, Peighambardoust SJ, Foroutan R et al (2021) Crystal violet dye sorption over acrylamide/graphene oxide bonded sodium alginate nanocomposite hydrogel. Chemosphere 270:129419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129419
Qiu H, Qiu Z, Wang J et al (2014) Enhanced swelling and methylene blue adsorption of polyacrylamide-based superabsorbents using alginate modified montmorillonite. J Appl Polym Sci 131:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40013
Rashidzadeh A, Olad A, Salari D (2015) The effective removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions by NaAlg-g-poly(acrylic acid-co-acryl amide)/clinoptilolite hydrogel nanocomposite. Fibers Polym 16:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-015-0354-9
Subhan H, Alam S, Shah LA et al (2021) Sodium alginate grafted poly(N-vinyl formamide-co-acrylic acid)-bentonite clay hybrid hydrogel for sorptive removal of methylene green from wastewater. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 611:125853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125853
Theng BKG (2012) Negatively charged polymers (Polyanions). Dev Clay Sci 4:111–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53354-8.00004-9
Laysandra L, Fabryanty R, Ju YH et al (2019) Renewable rarasaponin-bentonite-alginate composite with sponge-like structure and its application for crystal violet removal from aqueous solution. Desalin Water Treat 160:354–365. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24196
Singh V (2015) Mesoporous titania spheres derived from sodium alginate-gum acacia composite beads: efficient adsorbent for “Reactive blue H5G” dye. J Environ Chem Eng 3:2727–2737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.09.021
Benhouria A, Islam MA, Zaghouane-Boudiaf H et al (2015) Calcium alginate-bentonite-activated carbon composite beads as highly effective adsorbent for methylene blue. Chem Eng J 270:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.030
Boukhalfa N, Boutahala M, Djebri N, Idris A (2019) Kinetics, thermodynamics, equilibrium isotherms, and reusability studies of cationic dye adsorption by magnetic alginate/oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes composites. Int J Biol Macromol 123:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.102
Fabryanty R, Valencia C, Soetaredjo FE et al (2017) Removal of crystal violet dye by adsorption using bentonite—alginate composite. J Environ Chem Eng 5:5677–5687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.10.057
Gomri F, Finqueneisel G, Zimny T et al (2018) Adsorption of Rhodamine 6G and humic acids on composite bentonite–alginate in single and binary systems. Appl Water Sci 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0823-6
Kumar M, Tamilarasan R, Sivakumar V (2013) Adsorption of Victoria Blue by carbon/Ba/alginate beads: kinetics, thermodynamics and isotherm studies. Carbohydr Polym 98:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.05.078
Lai KC, Lee LY, Hiew BYZ et al (2020) Utilisation of eco-friendly and low cost 3D graphene-based composite for treatment of aqueous Reactive Black 5 dye: characterisation, adsorption mechanism and recyclability studies. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 114:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2020.09.024
Oladipo AA, Gazi M (2016) Uptake of Ni2+ and rhodamine B by nano-hydroxyapatite/alginate composite beads: batch and continuous-flow systems. Toxicol Environ Chem 98:189–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2015.1115506
Patanjali P, Mandal A, Chopra I, Singh R (2020) Adsorption of cationic dyes onto biopolymer-bentonite composites: kinetics and isotherm studies. Int J Environ Anal Chem 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1849660
Mallakpour S, Behranvand V, Mallakpour F (2021) Adsorptive performance of alginate/carbon nanotube-carbon dot-magnesium fluorohydroxyapatite hydrogel for methylene blue-contaminated water. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105170
Oussalah A, Boukerroui A (2020) Removal of cationic dye using alginate–organobentonite composite beads. Euro-Mediterranean J Environ Integr 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-020-00199-3
Pei Y, Guo D, An Q et al (2018) Hydrogels with diffusion-facilitated porous network for improved adsorption performance. Korean J Chem Eng 35:2384–2393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-018-0181-y
Qian LW, Yang MX, Zhang SF et al (2018) Preparation of a sustainable bioadsorbent by modifying filter paper with sodium alginate, with enhanced mechanical properties and good adsorption of methylene blue from wastewaters. Cellulose 25:2021–2036. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1674-x
Shi J, Zhang H, Yu Y et al (2020) Adsorption properties of calcium alginate-silica dioxide hybrid adsorbent to methylene blue. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 30:2114–2125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01357-z
Wang W, Zhao Y, Bai H et al (2018) Methylene blue removal from water using the hydrogel beads of poly(vinyl alcohol)-sodium alginate-chitosan-montmorillonite. Carbohydr Polym 198:518–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.06.124
Elkady M, Hassan H (2015) Equilibrium and dynamic profiles of azo dye sorption onto innovative nano-zinc oxide biocomposite. Curr Nanosci 11:805–814. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573413711666150415003115
Elkady MF, Shokry Hassan H, El-Sayed EM (2015) Basic violet decolourization using alginate immobilized nanozirconium tungestovanadate matrix as cation exchanger. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/385741
Duraipandian J, Rengasamy T, Vadivelu S (2017) Experimental and modeling studies for the removal of crystal violet dye from aqueous solutions using eco-friendly Gracilaria corticata seaweed activated carbon/Zn/alginate polymeric composite beads. J Polym Environ 25:1062–1071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0879-z
Dinu MV, Lazar MM, Dragan ES (2017) Dual ionic cross-linked alginate/clinoptilolite composite microbeads with improved stability and enhanced sorption properties for methylene blue. React Funct Polym 116:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2017.05.001
Li Y, Du Q, Liu T et al (2013) Methylene blue adsorption on graphene oxide/calcium alginate composites. Carbohydr Polym 95:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.094
Pawar RR, Lalhmunsiama GP et al (2018) Porous synthetic hectorite clay-alginate composite beads for effective adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 114:1315–1324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.008
Wang Y, Li Y, Zhang X, Zheng H (2020) Removal of methylene blue from water by copper alginate/activated carbon aerogel: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. J Polym Environ 28:200–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01577-x
Wang B, Gao B, Wan Y (2019) Comparative study of calcium alginate, ball-milled biochar, and their composites on aqueous methylene blue adsorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:11535–11541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1497-1
Yap PL, Hassan K, Auyoong YL et al (2020) All-in-one bioinspired multifunctional graphene biopolymer foam for simultaneous removal of multiple water pollutants. Adv Mater Interfaces 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202000664
Shan C, Wang L, Li Z et al (2019) Graphene oxide enhanced polyacrylamide-alginate aerogels catalysts. Carbohydr Polym 203:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.024
Sun Q, Fu CW, Aguila B et al (2018) Pore environment control and enhanced performance of enzymes infiltrated in covalent organic frameworks. J Am Chem Soc 140:984–992. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b10642
Yang M, Wang L, Cheng Y et al (2019) Light- and pH-responsive self-healing hydrogel. J Mater Sci 9983–9994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03547-z
Rinaudo M (2006) Chitin and chitosan: properties and applications. Prog Polym Sci 31:603–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2006.06.001
Roberts GAF (1992) Preparation of chitin and chitosan. Chitin Chem 54–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-11545-7_2
Kaczmarek MB, Struszczyk-Swita K, Li X et al (2019) Enzymatic modifications of chitin, chitosan, and chitooligosaccharides. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00243
No HK, Meyers SP (1995) Preparation and characterization of chitin and chitosan—a review. J Aquat Food Prod Technol 4:27–52. https://doi.org/10.1300/J030v04n02_03
Yeul VS, Rayalu SS (2013) Unprecedented chitin and chitosan: a chemical overview. J Polym Environ 21:606–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-012-0458-x
Li B, Ren Z (2020) Superior adsorption of direct dye from aqueous solution by Y(III)-chitosan-doped fly ash composite as low-cost adsorbent. J Polym Environ 28:1811–1821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01728-5
Zhu T, Huang W, Zhang L et al (2017) Adsorption of Cr(VI) on cerium immobilized cross-linked chitosan composite in single system and coexisted with Orange II in binary system. Int J Biol Macromol 103:605–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.051
Hui M, Shengyan P, Yaqi H et al (2018) A highly efficient magnetic chitosan “fluid” adsorbent with a high capacity and fast adsorption kinetics for dyeing wastewater purification. Chem Eng J 345:556–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.115
Blachnio M, Budnyak TM, Derylo-Marczewska A et al (2018) Chitosan-silica hybrid composites for removal of sulfonated azo dyes from aqueous solutions. Langmuir 34:2258–2273. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b04076
Hongduo T, Liu Y, Li B et al (2020) Preparation of chitosan graft polyacrylic acid/graphite oxide composite and the study of its adsorption properties of cationic dyes. Polym Sci Ser A 62:272–283. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965545X20030141
Wang L, Zhang J, Wang A (2011) Fast removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid)/attapulgite composite. Desalination 266:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.065
Khapre MA, Jugade RM (2020) Hierarchical approach towards adsorptive removal of Alizarin Red S dye using native chitosan and its successively modified versions. Water Sci Technol 82:715–731. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.376
Chen B, Zhao H, Chen S et al (2019) A magnetically recyclable chitosan composite adsorbent functionalized with EDTA for simultaneous capture of anionic dye and heavy metals in complex wastewater. Chem Eng J 356:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.222
Elwakeel KZ, El-Bindary AA, Ismail A, Morshidy AM (2016) Sorptive removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R from aqueous solution by diethylenetriamine functionalized magnetic macro-reticular hybrid material. RSC Adv 6:22395–22410. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra26508h
Li K, Li P, Cai J et al (2016) Efficient adsorption of both methyl orange and chromium from their aqueous mixtures using a quaternary ammonium salt modified chitosan magnetic composite adsorbent. Chemosphere 154:310–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.100
Marnani NN, Shahbazi A (2019) A novel environmental-friendly nanobiocomposite synthesis by EDTA and chitosan functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for high removal of Rhodamine B: adsorption mechanism and separation property. Chemosphere 218:715–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.109
Pereira FAR, Sousa KS, Cavalcanti GRS et al (2017) Green biosorbents based on chitosan-montmorillonite beads for anionic dye removal. J Environ Chem Eng 5:3309–3318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.06.032
Jabli M (2020) Synthesis, characterization, and assessment of cationic and anionic dye adsorption performance of functionalized silica immobilized chitosan bio-polymer. Int J Biol Macromol 153:305–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.323
Auta M, Hameed BH (2013) Coalesced chitosan activated carbon composite for batch and fixed-bed adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 105:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.12.021
Cao CY, Zhang T, Cong Q (2017) Adsorption of acid fuchsin onto the chitosan–montmorillonite composite. Mar Georesources Geotechnol 35:799–805. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2016.1240277
Sirajudheen P, Meenakshi S (2020) Lanthanum (III) incorporated chitosan-montmorillonite composite as flexible material for adsorptive removal of azo dyes from water. Mater Today Proc 27:318–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.11.040
Budnyak TM, Błachnio M, Slabon A et al (2020) Chitosan deposited onto fumed silica surface as sustainable hybrid biosorbent for acid orange 8 dye capture: effect of temperature in adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J Phys Chem C 124:15312–15323. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04205
Akar ST, San E, Akar T (2016) Chitosan-alunite composite: an effective dye remover with high sorption, regeneration and application potential. Carbohydr Polym 143:318–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.01.066
Feng T, Xu L (2013) Adsorption of acid red onto chitosan/rectorite composites from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 3:21685–21690. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra43384f
Sirajudheen P, Karthikeyan P, Ramkumar K, Meenakshi S (2020) Effective removal of organic pollutants by adsorption onto chitosan supported graphene oxide-hydroxyapatite composite: a novel reusable adsorbent. J Mol Liq 318:114200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114200
Sheshmani S, Mashhadi S (2018) Potential of magnetite reduced graphene oxide/chitosan nanocomposite as biosorbent for the removal of dyes from aqueous solutions. Polym Compos 39:E457–E462. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.24608
Manatunga DC, De Silva RM, De Silva KMN, Ratnaweera R (2016) Natural polysaccharides leading to super adsorbent hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for the removal of heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 6:105618–105630. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra22662k
Dotto GL, Rodrigues FK, Tanabe EH et al (2016) Development of chitosan/bentonite hybrid composite to remove hazardous anionic and cationic dyes from colored effluents. J Environ Chem Eng 4:3230–3239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.07.004
Jiang H, Chen P, Luo S et al (2013) Synthesis of novel biocompatible composite Fe3O4/ZrO2/chitosan and its application for dye removal. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 23:393–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-012-9792-7
Debnath S, Parashar K, Pillay K (2017) Ultrasound assisted adsorptive removal of hazardous dye Safranin O from aqueous solution using crosslinked graphene oxide-chitosan (GO-CH) composite and optimization by response surface methodology (RSM) approach. Carbohydr Polym 175:509–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.07.088
Ragab A, Ahmed I, Bader D (2019) The removal of Brilliant Green dye from aqueous solution using nano hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite as a sorbent. Molecules 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050847
Kloster GA, Mosiewicki MA, Marcovich NE (2019) Chitosan/iron oxide nanocomposite films: effect of the composition and preparation methods on the adsorption of congo red. Carbohydr Polym 221:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.089
Kochkina NE, Skobeleva OA, Khokhlova YV (2017) Investigation of cationic starch/Na-montmorillonite bionanocomposite adsorbent prepared by vibration milling for acid dye removal. Part Sci Technol 35:259–264. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2016.1153546
Wang J, Zhou Q, Song D et al (2015) Chitosan–silica composite aerogels: preparation, characterization and Congo red adsorption. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 76:501–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3800-7
Zheng L, Wang C, Shu Y et al (2015) Utilization of diatomite/chitosan-Fe (III) composite for the removal of anionic azo dyes from wastewater: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 468:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.12.015
Vardikar HS, Bhanvase BA, Rathod AP, Sonawane SH (2018) Sonochemical synthesis, characterization and sorption study of Kaolin-Chitosan-TiO2 ternary nanocomposite: advantage over conventional method. Mater Chem Phys 217:457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.07.014
Yan H, Li H, Yang H et al (2013) Removal of various cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using a kind of fully biodegradable magnetic composite microsphere. Chem Eng J 223:402–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.113
Kausar A, Naeem K, Tariq M et al (2019) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/clay composite for direct Rose FRN dye removal from aqueous media: comparison of linear and non-linear regression methods. J Mater Res Technol 8:1161–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.07.020
Chen Y, Chen L, Bai H, Li L (2013) Graphene oxide-chitosan composite hydrogels as broad-spectrum adsorbents for water purification. J Mater Chem A 1:1992–2001. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ta00406b
Joudi M, Nasserlah H, Hafdi H et al (2020) Synthesis of an efficient hydroxyapatite–chitosan–montmorillonite thin film for the adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes: adsorption isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic study. SN Appl Sci 2:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2848-3
Muinde VM, Onyari JM, Wamalwa B, Wabomba JN (2020) Adsorption of malachite green dye from aqueous solutions using mesoporous chitosan–zinc oxide composite material. Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 2:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2020.07.005
Zhou Q, Gao Q, Luo W et al (2015) One-step synthesis of amino-functionalized attapulgite clay nanoparticles adsorbent by hydrothermal carbonization of chitosan for removal of methylene blue from wastewater. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 470:248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.01.092
Chen X, He L (2017) Microwave irradiation assisted preparation of chitosan composite microsphere for dye adsorption. Int J Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2672597
Haldorai Y, Kharismadewi D, Tuma D, Shim JJ (2015) Properties of chitosan/magnetite nanoparticles composites for efficient dye adsorption and antibacterial agent. Korean J Chem Eng 32:1688–1693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0368-9
Haldorai Y, Shim JJ (2014) An efficient removal of methyl orange dye from aqueous solution by adsorption onto chitosan/MgO composite: a novel reusable adsorbent. Appl Surf Sci 292:447–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.11.158
Jiang R, Fu Y-Q, Zhu H-Y et al (2012) Removal of methyl orange from aqueous solutions by magnetic maghemite/chitosan nanocomposite films: adsorption kinetics and equilibrium. J Appl Polym Sci 125:E540–E549. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.37003
Mahmoodian H, Moradi O, Shariatzadeha B et al (2015) Enhanced removal of methyl orange from aqueous solutions by poly HEMA-chitosan-MWCNT nano-composite. J Mol Liq 202:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.10.040
Liu L, Ge J, Yang LT et al (2016) Facile preparation of chitosan enwrap** Fe3O4 nanoparticles and MIL-101(Cr) magnetic composites for enhanced methyl orange adsorption. J Porous Mater 23:1363–1372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-016-0195-y
Ouyang A, Wang C, Wu S et al (2015) Highly porous core-shell structured graphene-chitosan beads. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:14439–14445. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03369
Yuvaraja G, Chen DY, Pathak JL et al (2020) Preparation of novel aminated chitosan Schiff’s base derivative for the removal of methyl orange dye from aqueous environment and its biological applications. Int J Biol Macromol 146:1100–1110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.236
Zhang J, Zhou Q, Ou L (2012) Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution by chitosan/alumina composite. J Chem Eng Data 57:412–419. https://doi.org/10.1021/je2009945
Zhao P, Zhang R, Wang J (2017) Adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution using chitosan/diatomite composite. Water Sci Technol 75:1633–1642. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.034
Auta M, Hameed BH (2014) Chitosan-clay composite as highly effective and low-cost adsorbent for batch and fixed-bed adsorption of methylene blue. Chem Eng J 237:352–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.09.066
Fan L, Luo C, Sun M et al (2012) Preparation of novel magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composite as effective adsorbents toward methylene blue. Bioresour Technol 114:703–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.02.067
Fan L, Luo C, Sun M et al (2013) Synthesis of magnetic β-cyclodextrin-chitosan/graphene oxide as nanoadsorbent and its application in dye adsorption and removal. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 103:601–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.11.023
Hassan H, Salama A, El-ziaty AK, El-Sakhawy M (2019) New chitosan/silica/zinc oxide nanocomposite as adsorbent for dye removal. Int J Biol Macromol 131:520–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.087
Idohou EA, Fatombi JK, Osseni SA et al (2020) Preparation of activated carbon/chitosan/Carica papaya seeds composite for efficient adsorption of cationic dye from aqueous solution. Surf Interfaces 21:100741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100741
Karaer H, Kaya I (2016) Synthesis, characterization of magnetic chitosan/active charcoal composite and using at the adsorption of methylene blue and reactive blue4. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 232:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.06.006
Li Q, Zhao Y, Wang L, Aiqin W (2011) Adsorption characteristics of methylene blue onto the N-succinyl-chitosan-g-polyacrylamide/attapulgite composite. Korean J Chem Eng 28:1658–1664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0037-1
Liu Y, Zheng Y, Wang A (2010) Enhanced adsorption of Methylene Blue from aqueous solution by chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid)/vermiculite hydrogel composites. J Environ Sci 22:486–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60134-0
Mokhtar A, Abdelkrim S, Djelad A et al (2020) Adsorption behavior of cationic and anionic dyes on magadiite-chitosan composite beads. Carbohydr Polym 229:115399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115399
Sabzevari M, Cree DE, Wilson LD (2018) Graphene oxide-chitosan composite material for treatment of a model dye effluent. ACS Omega 3:13045–13054. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01871
Vieira T, Artifon SES, Cesco CT et al (2021) Chitosan-based hydrogels for the sorption of metals and dyes in water: isothermal, kinetic, and thermodynamic evaluations. Colloid Polym Sci 299:649–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04786-2
Zhou Y, Gao B, Zimmerman AR et al (2014) Biochar-supported zerovalent iron for removal of various contaminants from aqueous solutions. Bioresour Technol 152:538–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.11.021
El-Zawahry MM, Abdelghaffar F, Abdelghaffar RA, Hassabo AG (2016) Equilibrium and kinetic models on the adsorption of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solution using Eichhornia crassipes/chitosan composite. Carbohydr Polym 136:507–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.071
Li J, Cai J, Zhong L et al (2018) Adsorption of reactive dyes onto chitosan/montmorillonite intercalated composite: multi-response optimization, kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic study. Water Sci Technol 77:2598–2612. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.221
Li L, Iqbal J, Zhu Y et al (2018) Chitosan/Ag-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite beads as a potential adsorbent for the efficient removal of toxic aquatic pollutants. Int J Biol Macromol 120:1752–1759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.190
Parsaeian MR, Dadfarnia S, Haji Shabani AM, Hafezi Moghaddam R (2020) Green synthesis of a high capacity magnetic polymer nanocomposite sorbent based on the natural products for removal of Reactive Black 5. Int J Environ Anal Chem 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1748612
Travlou NA, Kyzas GZ, Lazaridis NK, Deliyanni EA (2013) Graphite oxide/chitosan composite for reactive dye removal. Chem Eng J 217:256–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.008
Travlou NA, Kyzas GZ, Lazaridis NK, Deliyanni EA (2013) Functionalization of graphite oxide with magnetic chitosan for the preparation of a nanocomposite dye adsorbent. Langmuir 29:1657–1668. https://doi.org/10.1021/la304696y
Elwakeel KZ, El-Bindary AA, Ismail A, Morshidy AM (2017) Magnetic chitosan grafted with polymerized thiourea for remazol brilliant blue R recovery: effects of uptake conditions. J Dispers Sci Technol 38:943–952. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2016.1216436
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Malek NNA, ALOthman ZA (2020) Statistical optimization and modeling for color removal and COD reduction of reactive blue 19 dye by mesoporous chitosan-epichlorohydrin/kaolin clay composite. Int J Biol Macromol 164:4218–4230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.201
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Facile synthesis of crosslinked chitosan-tripolyphosphate/kaolin clay composite for decolourization and COD reduction of remazol brilliant blue R dye: optimization by using response surface methodology. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 605:125329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125329
Mohamadi MB, Ejazi H, Azadbakht F (2019) Using composite chitosan-graphene oxide to eliminate reactive blue 19 from water solutions: the study of adsorption kinetics and reaction thermodynamics. Desalin Water Treat 155:341–349. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23816
Jawad AH, Malek NNA, Abdulhameed AS, Razuan R (2020) Synthesis of magnetic chitosan-fly ash/Fe3O4 composite for adsorption of reactive orange 16 dye: optimization by Box-Behnken design. J Polym Environ 28:1068–1082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01669-z
Abdulhameed AS, Jawad AH, Mohammad AKT (2019) Synthesis of chitosan-ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether/TiO2 nanoparticles for adsorption of reactive orange 16 dye using a response surface methodology approach. Bioresour Technol 293:122071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122071
Li J, Cai J, Zhong L et al (2019) Adsorption of reactive red 136 onto chitosan/montmorillonite intercalated composite from aqueous solution. Appl Clay Sci 167:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.10.003
Theng BKG (2012) Positively charged polymers (Polycations). Dev Clay Sci 4:129–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53354-8.00005-0
Rathinam K, Singh SP, Arnusch CJ, Kasher R (2018) An environmentally-friendly chitosan-lysozyme biocomposite for the effective removal of dyes and heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr Polym 199:506–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.055
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24:4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1450-3
Krässig H, Schurz J, Steadman RG et al (2004) Cellulose. In: Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Wiley. http://doi.org/10.1002/14356007.a05_375.pub2
Medronho B, Romano A, Miguel MG et al (2012) Rationalizing cellulose (in)solubility: reviewing basic physicochemical aspects and role of hydrophobic interactions. Cellulose 19:581–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9644-6
Thielking H, Schmidt M (2006) Cellulose ethers. Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, pp 1–2
Tundisi LL, Mostaço GB, Carricondo PC, Petri DFS (2021) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose: physicochemical properties and ocular drug delivery formulations. Eur J Pharm Sci 159:105736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2021.105736
Huang T, Shao YW, Zhang Q et al (2019) Chitosan-cross-linked graphene oxide/carboxymethyl cellulose aerogel globules with high structure stability in liquid and extremely high adsorption ability. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:8775–8788. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b00691
Liu Y, Wang W, ** Y, Wang A (2011) Adsorption behavior of methylene blue from aqueous solution by the hydrogel composites based on attapulgite. Sep Sci Technol 46:858–868. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2010.528502
Malatji N, Makhado E, Ramohlola KE et al (2020) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic clay-based carboxymethyl cellulose-acrylic acid hydrogel nanocomposite for methylene blue dye removal from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:44089–44105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10166-8
Peng N, Hu D, Zeng J et al (2016) Superabsorbent cellulose-clay nanocomposite hydrogels for highly efficient removal of dye in water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:7217–7224. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02178
Biswas S, Mohapatra SS, Kumari U et al (2020) Batch and continuous closed circuit semi-fluidized bed operation: removal of MB dye using sugarcane bagasse biochar and alginate composite adsorbents. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103637
Chen X, Song X, Sun Y (2016) Attapulgite nanofiber-cellulose nanocomposite with core-shell structure for dye adsorption. Int J Polym Sci 2016:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2081734
Liu C, Omer AM, Ouyang XK (2018) Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue dye using carboxymethyl cellulose/k-carrageenan/activated montmorillonite composite beads: isotherm and kinetic studies. Int J Biol Macromol 106:823–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.084
Nayl AA, Abd-Elhamid AI, Abu-Saied MA et al (2020) A novel method for highly effective removal and determination of binary cationic dyes in aqueous media using a cotton-graphene oxide composite. RSC Adv 10:7791–7802. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra09872k
Ren F, Li Z, Tan WZ et al (2018) Facile preparation of 3D regenerated cellulose/graphene oxide composite aerogel with high-efficiency adsorption towards methylene blue. J Colloid Interface Sci 532:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.07.101
Somsesta N, Sricharoenchaikul V, Aht-Ong D (2020) Adsorption removal of methylene blue onto activated carbon/cellulose biocomposite films: equilibrium and kinetic studies. Mater Chem Phys 240:122221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122221
Ghiorghita C-A, Bucatariu F, Dragan ES (2018) Novel silica/polyelectrolyte multilayer core-shell composite microparticles with. Cellul Chem Technol 52:663–672. Available at https://www.cellulosechemtechnol.ro/pdf/CCT7-8(2018)/p.663-672.pdf
Dai H, Huang Y, Huang H (2018) Eco-friendly polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels reinforced with graphene oxide and bentonite for enhanced adsorption of methylene blue. Carbohydr Polym 185:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.073
Eltaweil AS, Elgarhy GS, El-Subruiti GM, Omer AM (2020) Carboxymethyl cellulose/carboxylated graphene oxide composite microbeads for efficient adsorption of cationic methylene blue dye. Int J Biol Macromol 154:307–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.122
Liu J, Chu H, Wei H et al (2016) Facile fabrication of carboxymethyl cellulose sodium/graphene oxide hydrogel microparticles for water purification. RSC Adv 6:50061–50069. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra06438h
Peng S, Liu Y, Xue Z et al (2017) Modified nanoporous magnetic cellulose–chitosan microspheres for efficient removal of Pb(II) and methylene blue from aqueous solution. Cellulose 24:4793–4806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1463-y
Chen L, Li Y, Hu S et al (2016) Removal of methylene blue from water by cellulose/graphene oxide fibres. J Exp Nanosci 11:1156–1170. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2016.1198499
Hu Y, Chen C, Yang L et al (2019) Handy purifier based on bacterial cellulose and Ca-montmorillonite composites for efficient removal of dyes and antibiotics. Carbohydr Polym 222:115017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115017
Wang S, Ma X, Zheng P (2019c) Sulfo-functional 3D porous cellulose/graphene oxide composites for highly efficient removal of methylene blue and tetracycline from water. Int J Biol Macromol 140:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.111
Li B, Zhang Q, Pan Y et al (2020) Functionalized porous magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4 beads prepared from ionic liquid for removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 163:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.280
Sirajudheen P, Nikitha MR, Karthikeyan P, Meenakshi S (2020) Perceptive removal of toxic azo dyes from water using magnetic Fe3O4 reinforced graphene oxide–carboxymethyl cellulose recyclable composite: adsorption investigation of parametric studies and their mechanisms. Surf Interfaces 21:100648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100648
Leshaf A, Ziani Cherif H, Benmansour K (2019) Adsorption of acidol red 2BE-NW dye from aqueous solutions on carboxymethyl cellulose/organo-bentonite composite: characterization, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Polym Environ 27:1054–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01395-1
Zhou C-H, Zhang D, Tong D-S et al (2012) Paper-like composites of cellulose acetate–organo-montmorillonite for removal of hazardous anionic dye in water. Chem Eng J 209:223–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.107
Rahimi K, Mirzaei R, Akbari A, Mirghaffari N (2018) Preparation of nanoparticle-modified polymeric adsorbent using wastage fuzzes of mechanized carpet and its application in dye removal from aqueous solution. J Clean Prod 178:373–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.213
Chen X, Cui J, Xu X et al (2020) Bacterial cellulose/attapulgite magnetic composites as an efficient adsorbent for heavy metal ions and dye treatment. Carbohydr Polym 229:115512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115512
Sankararamakrishnan N, Singh N, Srivastava I (2020) Hierarchical nano Fe(0)@FeS doped cellulose nanofibres derived from agrowaste—potential bionanocomposite for treatment of organic dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 151:713–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.155
Santoso SP, Kurniawan A, Soetaredjo FE et al (2019) Eco-friendly cellulose–bentonite porous composite hydrogels for adsorptive removal of azo dye and soilless culture. Cellulose 26:3339–3358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02314-2
Tanzifi M, Tavakkoli Yaraki M, Karami M et al (2018) Modelling of dye adsorption from aqueous solution on polyaniline/carboxymethyl cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposites. J Colloid Interface Sci 519:154–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.02.059
Wang M, Wang L, Wang A (2013) Characterization and Congo Red uptake capacity of a new lignocellulose/organic montmorillonite composite. Desalin Water Treat 51:7120–7129. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.791782
ZabihiSahebi A, Koushkbaghi S, Pishnamazi M et al (2019) Synthesis of cellulose acetate/chitosan/SWCNT/Fe3O4/TiO2 composite nanofibers for the removal of Cr(VI), As(V), methylene blue and Congo red from aqueous solutions. Int J Biol Macromol 140:1296–1304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.214
Zhu HY, Fu YQ, Jiang R et al (2011) Adsorption removal of congo red onto magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4/activated carbon composite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 173:494–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.020
Kausar A, Shahzad R, Iqbal J et al (2020) Development of new organic-inorganic, hybrid bionanocomposite from cellulose and clay for enhanced removal of Drimarine Yellow HF-3GL dye. Int J Biol Macromol 149:1059–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.012
Peighambardoust SJ, Aghamohammadi-Bavil O, Foroutan R, Arsalani N (2020) Removal of malachite green using carboxymethyl cellulose-g-polyacrylamide/montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogel. Int J Biol Macromol 159:1122–1131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.093
Radoor S, Karayil J, Jayakumar A et al (2021) An efficient removal of malachite green dye from aqueous environment using ZSM-5 zeolite/polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl cellulose/sodium alginate bio composite. J Polym Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-02024-y
Ali SM (2018) Fabrication of a nanocomposite from an agricultural waste and its application as a biosorbent for organic pollutants. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:1169–1178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1477-x
Bai Q, **ong Q, Li C et al (2017) Hierarchical porous cellulose/activated carbon composite monolith for efficient adsorption of dyes. Cellulose 24:4275–4289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1410-y
Liu Z, Li D, Dai H, Huang H (2017) Enhanced properties of tea residue cellulose hydrogels by addition of graphene oxide. J Mol Liq 244:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.106
Luo J, Ma X, Zhou X, Xu Y (2021) Construction of physically crosslinked cellulose nanofibrils/alkali lignin/montmorillonoite/polyvinyl alcohol network hydrogel and its application in methylene blue removal. Cellulose 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03847-1
Samadder R, Akter N, Roy AC et al (2020) Magnetic nanocomposite based on polyacrylic acid and carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal for the removal of cationic dye. RSC Adv 10:11945–11956. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra00604a
Shi H, Li W, Zhong L, Xu C (2014) Methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution by magnetic cellulose/graphene oxide composite: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:1108–1118. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4027154
Wang S, Ma X, Zheng P (2019) Sulfo-functional 3D porous cellulose/graphene oxide composites for highly efficient removal of methylene blue and tetracycline from water. Int J Biol Macromol 140:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.111
Wang Z, Song L, Wang Y et al (2021) Construction of a hybrid graphene oxide/nanofibrillated cellulose aerogel used for the efficient removal of methylene blue and tetracycline. J Phys Chem Solids 150:109839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109839
Huang X, Zhan X, Wen C et al (2018) Amino-functionalized magnetic bacterial cellulose/activated carbon composite for Pb2+ and methyl orange sorption from aqueous solution. J Mater Sci Technol 34:855–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2017.03.013
Li W, Zuo P, Xu D et al (2017) Tunable adsorption properties of bentonite/carboxymethyl cellulose-g-poly(2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate) composites toward anionic dyes. Chem Eng Res Des 124:260–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.06.034
Karadağ E, Yel B, Kundakcı S, Üzüm ÖB (2017) Synthesis and application of acrylamide/sodium vinylsulfonate/carboxymethyl cellulose/zeolite hybrid hydrogels as highly swollen effective adsorbents for model cationic dye removal. Desalin Water Treat 74:402–414. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20613
Kausar A, Shahzad R, Asim S et al (2021) Experimental and theoretical studies of Rhodamine B direct dye sorption onto clay-cellulose composite. J Mol Liq 328:115165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115165
Tian S-Y, Guo J-H, Zhao C et al (2018) Preparation of cellulose/graphene oxide composite membranes and their application in removing organic contaminants in wastewater. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 19:2147–2153. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2019.15808
**ang C, Wang C, Guo R et al (2019) Synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose-reduced graphene oxide aerogel for efficient removal of organic liquids and dyes. J Mater Sci 54:1872–1883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2900-5
Toledo PVO, Martins BF, Pirich CL, Sierakowski MR, Teixeira Neto E, Petri DFS (2019) Cellulose based cryogels as adsorbents for organic pollutants. Macromol Symp 383:1800013. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201800013
Pérez S, Bertoft E (2010) The molecular structures of starch components and their contribution to the architecture of starch granules: a comprehensive review. Starch Stärke 62:389–420. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201000013
Bhattacharyya A, Banerjee B, Ghorai S et al (2018) Development of an auto-phase separable and reusable graphene oxide-potato starch based cross-linked bio-composite adsorbent for removal of methylene blue dye. Int J Biol Macromol 116:1037–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.069
Hosseinzadeh H, Ramin S (2018) Fabrication of starch-graft-poly(acrylamide)/graphene oxide/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite hydrogel adsorbent for removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 106:101–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.182
Bakhshi H, Darvishi A (2016) Preparation and evaluation of hydrogel composites based on starch-g-PNaMA/eggshell particles as dye biosorbent. Desalin Water Treat 57:18144–18156. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1087344
Mittal H, Ray SS (2016) A study on the adsorption of methylene blue onto gum ghatti/TiO2 nanoparticles-based hydrogel nanocomposite. Int J Biol Macromol 88:66–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.032
Karadağ E, Hasgül B, Kundakci S, Üzüm ÖB (2014) A study of polymer/clay hybrid composite sorbent-based AAm/SMA hydrogels and semi-IPNs composed of ɩ-carrageenan and montmorillonite for water and dye sorption. Adv Polym Technol 33. http://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21432
Mahdavinia GR, Rahmani Z, Mosallanezhad A et al (2016) Effect of magnetic laponite RD on swelling and dye adsorption behaviors of κ-carrageenan-based nanocomposite hydrogels. Desalin Water Treat 57:20582–20596. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1111808
Mittal H, Al Alili A, Alhassan SM (2020) High efficiency removal of methylene blue dye using κ-carrageenan-poly(acrylamide-co-methacrylic acid)/AQSOA-Z05 zeolite hydrogel composites. Cellulose 27:8269–8285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03365-6
Pourjavadi A, Bassampour Z, Ghasemzadeh H et al (2016) Porous Carrageenan-g-polyacrylamide/bentonite superabsorbent composites: swelling and dye adsorption behavior. J Polym Res 23:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-0955-z
Li K, Lei Y, Liao J, Zhang Y (2021) A facile synthesis of graphene oxide/locust bean gum hybrid aerogel for water purification. Carbohydr Polym 254:117318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117318
Nesic AR, Velickovic SJ, Antonovic DG (2014) Novel composite films based on amidated pectin for cationic dye adsorption. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 116:620–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.10.031
Qi X, Zeng Q, Tong X et al (2021) Polydopamine/montmorillonite-embedded pullulan hydrogels as efficient adsorbents for removing crystal violet. J Hazard Mater 402:123359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123359
Saberi A, Alipour E, Sadeghi M (2019) Superabsorbent magnetic Fe3O4-based starch-poly (acrylic acid) nanocomposite hydrogel for efficient removal of dyes and heavy metal ions from water. J Polym Res 26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1917-z
**ng G, Liu S, Xu Q, Liu Q (2012) Preparation and adsorption behavior for brilliant blue X-BR of the cost-effective cationic starch intercalated clay composite matrix. Carbohydr Polym 87:1447–1452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.09.038
Karadağ E, Hasgül B, Kundakci S, Üzüm ÖB (2014) Novel composite sorbent AAm/MA hydrogels containing starch and kaolin for water sorption and dye uptake. Bull Mater Sci 37:1637–1646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-014-0723-9
Ansari Mojarad A, Tamjidi S, Esmaeili H (2020) Clay/starch/Fe3O4 nanocomposite as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of methyl violet dye from aqueous media. Int J Environ Anal Chem 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1845665
Karadağ E, Ödemiş H, Kundakçi S, Üzüm ÖB (2016) Swelling characterization of acrylamide/zinc acrylate/xanthan gum/sepiolite hybrid hydrogels and its application in sorption of Janus Green B from aqueous solutions. Adv Polym Technol 35:248–259. https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21547
Makhado E, Pandey S, Ramontja J (2018) Microwave assisted synthesis of xanthan gum-cl-poly (acrylic acid) based-reduced graphene oxide hydrogel composite for adsorption of methylene blue and methyl violet from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 119:255–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.104
Thakur S, Pandey S, Arotiba OA (2017) Sol-gel derived xanthan gum/silica nanocomposite—a highly efficient cationic dyes adsorbent in aqueous system. Int J Biol Macromol 103:596–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.087
Jamee R, Siddique R (2019) Biodegradation of synthetic dyes of textile effluent by microorganisms: an environmentally and economically sustainable approach. Eur J Microbiol Immunol 9:114–118. https://doi.org/10.1556/1886.2019.00018
Jadhav I, Vasniwal R, Shrivastava D, Jadhav K (2016) Microorganism-based treatment of azo dyes. J Environ Sci Technol 9:188–197. https://doi.org/10.3923/jest.2016.188.197
Yusuf M, Shabbir M, Mohammad F (2017) Natural colorants: historical, processing and sustainable prospects. Nat Products Bioprospect 7:123–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13659-017-0119-9
Freitas-Dörr BC, Machado CO, Pinheiro AC et al (2020) A metal-free blue chromophore derived from plant pigments. Sci Adv 6:eaaz0421. http://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz0421
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Toledo, P.V.O., Petri, D.F.S. (2022). Polysaccharide-Composites Materials as Adsorbents for Organic Dyes. In: Muthu, S.S., Khadir, A. (eds) Textile Wastewater Treatment. Sustainable Textiles: Production, Processing, Manufacturing & Chemistry. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2832-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2832-1_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-2831-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-2832-1
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)