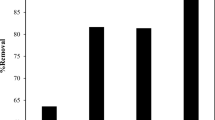Abstract
In the present work, a natural bentonite (B) was first modified with the cationic surfactant hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide to form an organobentonite (OB) material. Alginate/organobentonite beads (A–OB) were then obtained by encapsulating organobentonite (OB) in calcium alginate (A). Different alginate/organobentonite ratios were applied during bead preparation, yielding beads denoted A–OB1 (1/1 w/w), A–OB2 (1/2 w/w), and A–OB3 (1/3 w/w), respectively. These adsorbents were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction and were used to eliminate the dye methylene blue (MB) from aqueous solution. Two adsorption isotherm models—the Freundlich and Langmuir models—were fitted to adsorption data obtained upon varying the initial dye concentration (25–300 mg L−1). The Langmuir isotherm model gave the best fit to the isotherm data. Among the three types of A–OB beads, A–OB1 presented the greatest MB adsorption capacity. The amount of MB adsorbed per gram of adsorbent (qmax) increased from 344.4 mg g−1 for OB to 972.29 mg g−1 for A–OB1. Pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models were investigated, and the latter gave the best fit to the experimental kinetic data. The calculated thermodynamic factors (ΔS°, ΔH°, and ΔG°) for the sorption process revealed that the adsorption was spontaneous, endothermic, and physical in nature. To test adsorbent reusability, desorption studies were performed, and the results showed that MB was desorbed from A–OB1 with a removal percentage of 94.04% after six cycles. These results indicate that the novel adsorbent A–OB1 is recyclable (even after six regenerative cycles), inexpensive, and can be used to remove the dye MB from aqueous solution.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas M, Adil M, Ehtisham-ul-Haque S, Munir B, Yameen M, Ghaffar A, Shar GA, Tahir MA, Iqbal M (2018) Vibrio fischeri bioluminescence inhibition assay for ecotoxicity assessment: a review. Sci Total Environ 626:1295–1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.066
Adeyemo AA, Adeoye IO, Bello OS (2017) Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: a review. Appl Water Sci 7(2):543–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0322-y
Aichour A, Zaghouane-Boudiaf H, Iborra CV, Polo MS (2018) Bioadsorbent beads prepared from activated biomass/alginate for enhanced removal of cationic dye from water medium: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Liq 256:533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.073
Alabarse FG, Conceição RV, Balzaretti NM, Schenato F, Xavier AM (2011) In-situ FTIR analyses of bentonite under high-pressure. Appl Clay Sci 51:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.11.017
Al-a'qarbeh MM, Shammout MW, Awwad AM (2020) Nano platelets kaolinite for the adsorption of toxic metal ions in the environment. Chem Int 6(2):49–55. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3361011
Alasadi AM, Khaili FI, Awwad AM (2019) Adsorption of Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) ions by nano kaolinite: thermodynamics and kinetics studies. Chem Int 5(4):258–268. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2644985
Anirudhan TS, Ramachandran M (2015) Adsorptive removal of basic dyes from aqueous solutions by surfactant modified bentonite clay (organoclay): kinetic and competitive adsorption isotherm. Process Saf Environ Prot 95:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2015.03.003
Awwad AM, Amer MW, Al-aqarbeh MM (2020) TiO2-kaolinite nanocomposite prepared from the Jordanian kaolin clay: adsorption and thermodynamics of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions in aqueous solution. Chem Int 6(4):168–178. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3597558
Bedin KC, Martins AC, Cazetta AL, Pezoti O, Almeida VC (2016) KOH-activated carbon prepared from sucrose spherical carbon: adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for methylene blue removal. Chem Eng J 286:476–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.099
Belhouchat N, Zaghouane-Boudiaf H, Viseras C (2017) Removal of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution with activated organo-bentonite/sodium alginate encapsulated beads. Appl Clay Sci 135:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.08.031
Ben Arfi R, Karoui S, Mougin K, Ghorbal A (2017) Adsorptive removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution by utilizing almond shell as bioadsorbent. Euro Mediterr J Environ Integr 2:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-017-0032-y
Benhouria A, Azharul Islam M, Zaghouane-Boudiaf H, Boutahala M, Hameed BH (2015) Calcium alginate–bentonite–activated carbon composite beads as highly effective adsorbent for methylene blue. Chem Eng J 270:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.030
Bhatti HN, Mahmood Z, Kausar A, Yakout SM, Shair OH, Iqbal M (2020) Biocomposites of polypyrrole, polyaniline and sodium alginate with cellulosic biomass: adsorption–desorption, kinetics and thermodynamic studies for the removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Int J Biol Macromol 153:146–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.306
Boukerroui A, Ouali MS (2000) Activation of a bentonite by an ammonium salt evolution of the exchange capacity and of the specific surface area. Ann Chim Sci Mat 25:583–590
Caglar B, Topcu C, Coldur F, Sarp G, Caglar S, Tabak A, Sahin E (2016) Structural, thermal, morphological and surface charge properties of dodecyltrimethylammonium-smectite composites. J Macromol Struct 1105:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.10.017
Dai WJ, Wu P, Liu D, Hu J, Cao Y, Liu TZ, Okoli CP, Wang B, Li L (2020) Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous solution by organic montmorillonite sodium alginate nanocomposites. Chemosphere 251:126074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126074
Djebri N, Boutahala M, Chelali N, Boukhalfa N, Zeroual L (2016) Enhanced removal of cationic dye by calcium alginate/organo-bentonite beads: modeling, kinetics, equilibriums, thermodynamic and reusability studies. Int J Biol Macromol 92:1277–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.08.013
El-Sayed GO (2011) Removal of methylene blue and crystal violet from aqueous solutions by palm kernel fiber. Desalination 272:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.01.025
Fabryanty R, Valencia C, Soetaredjo FE, Putro JN, Santoso SP, Kurniawan A, Jub YH, Ismadji S (2017) Removal of crystal violet dye by adsorption using bentonite–alginate composite. J Environ Chem Eng 5:5677–5687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.10.057
Freundlich H (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem 57:385–471
Hameed BH, Ahmad AL, Latiff KNA (2007) Adsorption of basic dye (methylene blue) onto activated carbon prepared from rattan sawdust. Dyes Pigments 75:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.05.039
Hassan AF, Abdel-Mohsen AM, Fouda MMG (2014) Comparative study of calcium alginate, activated carbon, and their composite beads on methylene blue adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 102:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.104
He Y, Wu Z, Tu L, Han Y, Zhang G, Li C (2015) Encapsulation and characterization of slow-release microbial fertilizer from the composites of bentonite and alginate. Appl Clay Sci 109–110:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.02.001
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Iqbal M (2016) Vicia faba bioassay for environmental toxicity monitoring: a review. Chemosphere 144:785–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.09.048
Iqbal M, Abbas M, Nisar J, Nazir A, Qamar AZ (2019) Bioassays based on higher plants as excellent dosimeters for ecotoxicity monitoring: a review. Chem Int 5(1):1–80. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1475399
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Mesoporous Iraqi red kaolin clay as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue dye: adsorption kinetic, isotherm and mechanism study. Surf Interfac 18:100422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2019.100422
Jung KW, Choi BH, Hwang MJ, Jeong TU, Ahn KH (2016) Fabrication of granular activated carbons derived from spent coffee grounds by entrapment in calcium alginate beads for adsorption of acid orange 7 and methylene blue. Bioresour Technol 219:185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.098
Kausar A, Iqbal M, Javed A, Aftab K, Nazli ZH, Bhatti HN, Nouren S (2018) Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: a review. J Mol Liq 256:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.034
Kausar A, Naeem K, Hussain T, Nazli ZH, Bhatti HN, Jubeen F, Nazir A, Iqbal M (2019) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/clay composite for direct rose FRN dye removal from aqueous media: comparison of linear and non-linear regression methods. J Mater Res Technol 8(1):1161–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.07.020
Kausar A, Shahzad R, Iqbal J, Muhammad N, Ibrahim SM, Iqbal M (2020) Development of new organic–inorganic, hybrid bionanocomposite from cellulose and clay for enhanced removal of drimarine yellow HF-3GL dye. Int J Biol Macromol 149:1059–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.012
Kıransan M, Soltani RDC, Hassani A, Karaca S, Khataee A (2014) Preparation of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide modified montmorillonite nanomaterial for adsorption of a textile dye. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:2565–2577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.06.007
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K Sven Vetenskapsakad Handl 24:1–39
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Li Q, Li Y, Ma X, Du Q, Sui K, Wang D, Wang C, Li H, **a Y (2017) Filtration and adsorption properties of porous calcium alginate membrane for methylene blue removal from water. Chem Eng J 316:623–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.01.098
Lima EC, Bandegharaei AH, Moreno-Piraján JC, Anastopoulos I (2019) A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van't Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J Mol Liq 273:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.10.048
Liu Y (2009) Is the free energy change of adsorption correctly calculated? J Chem Eng Data 54:1981–1985. https://doi.org/10.1021/je800661q
Liu Y, Liu YJ (2008) Biosorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Sep Purif Technol 61:229–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2007.10.002
Liu L, Wan Y, **e Y, Zhai R, Zhang B, Liu J (2012) The removal of dye from aqueous solution using alginate-halloysite nanotube beads. Chem Eng J 187:210–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.136
Makhoukhi B, Djab M, Didi MA (2015) Adsorption of Telon dyes onto bis-imidazolium modified bentonite in aqueous solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 3:1384–1392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.12.012
Marrakchi F, Bouaziz M, Hameed BH (2017) Adsorption of acid blue 29 and methylene blue on mesoporous K2CO3-activated olive pomace boiler ash. Colloids Surf A 535:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.09.014
Momina M, Shahadat M, Ismail S (2020a) Study of the adsorption/desorption of MB dye solution using bentonite adsorbent coating. J Water Process Eng 34:101155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101155
Momina M, Shahadat M, Ismail S (2020b) Regeneration potential of bentonite-based paintosorpTM for removal of industrial dye. Arab J Sci Eng 45:551–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04275-x
Nasrullah A, Bhat AH, Naeem A, Isa MH, Danish M (2018) High surface area mesoporous activated carbon-alginate beads for efficient removal of methylene blue. Int J Biol Macromol 107:1792–1799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.045
Oladipo AA, Gazi M (2014) Enhanced removal of crystal violet by low cost alginate/acid activated bentonite composite beads: optimization and modelling using non-linear regression technique. J Water Process Eng 2:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.04.007
Oussalah A (2020) Caractérisation et modification d’une argile de Maghnia: applications. Doctorate thesis. University of Bejaia, Bejaia
Oussalah A, Boukerroui A, Aichour A, Djellouli B (2019) Cationic and anionic dyes removal by low-cost hybrid alginate/natural bentonite composite beads: adsorption and reusability studies. Int J Biol Macromol 124:854–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.197
Ozcan A, Omeroglu C, Erdogan Y, Ozcan AS (2007) Modification of bentonite with a cationic surfactant: an adsorption study of textile dye reactive blue 19. J Hazard Mater 140:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.06.138
Pandey S (2017) A comprehensive review on recent developments in bentonite-based materials used as adsorbents for wastewater treatment. J Mol Liq 241:1091–1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.06.115
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.047
Rahmani S, Zeynizadeh B, Karami S (2020) Removal of cationic methylene blue dye using magnetic and anionic–cationic modified montmorillonite: kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Appl Clay Sci 184:105391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105391
Santoso E, Ediati R, Kusumawati Y, Bahruji H, Sulistiono DO, Prasetyoko D (2020) Review on recent advances of carbon based adsorbent for methylene blue removal from waste water. Mater Today Chem 16:100233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2019.100233
Uyar G, Kaygusuz H, Erim FB (2016) Methylene blue removal by alginate-clay quasi-cryogel beads. React Funct Polym 106:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2016.07.001
Yu Y, Zhuang YY, Wangy ZH (2001) Adsorption of water-soluble dye onto functionalized resin. J Colloid Interf Sci 242:288–293. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2001.7780
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Mohamed Ksibi, Co-Editor in Chief.
This paper was selected from the 2nd Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI), Tunisia 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oussalah, A., Boukerroui, A. Removal of cationic dye using alginate–organobentonite composite beads. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 5, 55 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-020-00199-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-020-00199-3