Abstract
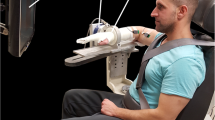
Elbow joint damage requires rehabilitation through continuous passive motion (CPM) devices or additional surgery, underscoring the significance of effective and consistent post-surgical rehabilitation. In this paper, we present an IMU sensor-based XGBoost model specifically designed for patients with elbow joint impairments, aiming to overcome the limitations of existing elbow rehabilitation methods. The proposed XGBoost model employs Softmax as its objective function to facilitate multi-class classification, while utilizing an Error function to minimize the error rate. For model training, we compiled a dataset using subjects, adhering to government guidelines for recommended elbow exercise postures and angles. We evaluated the performance of the implemented model by conducting comparisons with the tree-based ensemble model Random Forest, and the commercial model Teachable Machine. The results of this comparison showed that our proposed model achieved an average classification performance of 93.8%, while the Random Forest model exhibited an average of 91.6%, and Teachable Machine demonstrated an average of 94.9%. In conclusion, the performance of our implemented model was found to be comparable to that of existing commercial models. Moving forward, we plan to broaden our research scope by incorporating electromyography (EMG) signals, with the intention of applying our findings to various applications such as lower limb rehabilitation, prosthetic manipulation, and elbow Continuous Passive Motion (CPM) rehabilitation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, S.Y., et al.: Personalized exercise recommender system for rehabilitation using graph neural networks. J. Korean Inst. Commun. Inf. Sci. 47(4), 644–655 (2022)
Cheon, S.J., Moon, K.P., Seo, H.E., Kang, J.H.: Comparison of clinical outcomes between arthroscopic anterior compartment debridement with posterior compartment mini-open debridement and arthroscopic both compartments debridement of the primary elbow osteoarthritis. J. Korean Orthop. Assoc. 57(1), 44–52 (2022)
Kim, J.H., Park, J.H.: The usefulness of AI-based CPM exercise: a study. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 34(1), 1–10 (2022)
Kim, K.G., Chung, W.Y.: A home-based remote rehabilitation system with motion recognition for joint range of motion improvement. J. Korea Inst. Convergence Signal Process. 20(3), 151–158 (2019)
National Knowledge Portal. Disability Assessment Criteria. Ministry of Health and Welfare, 99 (2020)
Carney, M., et al.: Teachable machine: approachable web-based tool for exploring machine learning classification. In: Extended Abstracts of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 1–8 (2020)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Technology development Program (RS-2023-00223289) funded by the Ministry of SMEs and Startups (MSS, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kim, JJ., Seo, JY., Noh, YH., Jung, SJ., Jeong, DU. (2024). Development of IMU Sensor-Based XGBoost Model for Patients with Elbow Joint Damage. In: Choi, B.J., Singh, D., Tiwary, U.S., Chung, WY. (eds) Intelligent Human Computer Interaction. IHCI 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14531. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53827-8_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-53827-8_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-53826-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-53827-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)