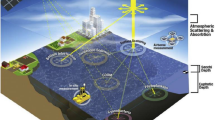
Abstract
Water quality assessment is a critical aspect of maintaining the health of aquatic ecosystem. The escalating issue of water pollution poses a significant threat to human well-being, necessitating the need for water quality evaluation. Geospatial technology, particularly GIS tools, plays a vital role in monitoring and map** water quality over larger spatial and temporal scales. This chapter explores the integration of geospatial technology and in situ observations to enhance the understanding of water quality dynamics in aquatic ecosystems. Geospatial technology, including remote sensing from satellites, offers broad-scale coverage and continuous monitoring, providing data on various optical and thermal properties of water bodies. In situ observations involve direct measurements taken at specific locations, providing ground truth data for calibration and validation. This chapter delves into the potential of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to process and analyze vast and diverse data sets, improving predictive modelling and parameter retrievals. It discusses challenges such as spatial and temporal resolutions, atmospheric interference, and data integration, along with solutions for data assimilation, sensor network optimization, and real-time monitoring. Overall, this chapter provides valuable insights into the integration of geospatial technology and in situ observations, offering practical guidance for researchers and water resource managers seeking to construct accurate and comprehensive water quality dynamics in aquatic ecosystems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, K., Abiye, T., & Adam, E. (2022). Integrating in situ and current generation satellite data for temporal and spatial analysis of harmful algal blooms in the Hartbeespoort Dam, Crocodile River Basin, South Africa. Remote Sensing, 14(17), 4277.
Bailey, S. W., & Werdell, P. J. (2006). A multisensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products. Remote Sensing of Environment, 102(1–2), 12–23.
Becker, R. H., Sayers, M., Dehm, D., Shuchman, R., Quintero, K., Bosse, K., & Sawtell, R. (2019). Unmanned aerial system based spectroradiometer for monitoring harmful algal blooms: A new paradigm in water quality monitoring. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 45(3), 444–453.
Bierman, P., Lewis, M., Ostendorf, B., & Tanner, J. (2011). A review of methods for analysing spatial and temporal patterns in coastal water quality. Ecological Indicators, 11(1), 103–114.
Cabral, J. P. (2010). Water microbiology. Bacterial pathogens and water. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(10), 3657–3703.
Carr, G. M., & Neary, J. P. (2008). Water quality for ecosystem and human health. UNEP/Earthprint.
Chawla, I., Karthikeyan, L., & Mishra, A. K. (2020). A review of remote sensing applications for water security: Quantity, quality, and extremes. Journal of Hydrology, 585, 124826.
Chorus, I., & Welker, M. (2021). Toxic cyanobacteria in water: A guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management (p. 858). Taylor & Francis.
Crain, C. M., Halpern, B. S., Beck, M. W., & Kappel, C. V. (2009). Understanding and managing human threats to the coastal marine environment. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1162(1), 39–62.
Creighton, C., Hobday, A. J., Lockwood, M., & Pecl, G. T. (2016). Adapting management of marine environments to a changing climate: A checklist to guide reform and assess progress. Ecosystems, 19, 187–219.
Dinka, M. O. (2018). Safe drinking water: Concepts, benefits, principles and standards. In Water challenges of an urbanizing world (p. 163). InTech.
Gholizadeh, M. H., Melesse, A. M., & Reddi, L. (2016). A comprehensive review on water quality parameters estimation using remote sensing techniques. Sensors, 16(8), 1298.
Glasgow, H. B., Burkholder, J. M., Reed, R. E., Lewitus, A. J., & Kleinman, J. E. (2004). Real-time remote monitoring of water quality: A review of current applications, and advancements in sensor, telemetry, and computing technologies. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 300(1–2), 409–448.
Griffith, J. A. (2002). Geographic techniques and recent applications of remote sensing to landscape-water quality studies. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 138, 181–197.
Kneese, A. V., & Bower, B. T. (2013). Managing water quality: Economics, technology, institutions. RFF Press.
Liang, J. L., Dziuban, E. J., Craun, G. F., Hill, V., Moore, M. R., Gelting, R. J., et al. (2006). Surveillance for waterborne disease and outbreaks associated with drinking water and water not intended for drinking—United States, 2003–2004. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report: Surveillance Summaries, 55(12), 31–65.
Liu, H., Yu, T., Hu, B., Hou, X., Zhang, Z., Liu, X., Liu, J., Wang, X., Zhong, J., Tan, Z., & **a, S. (2021). Uav-borne hyperspectral imaging remote sensing system based on acousto-optic tunable filter for water quality monitoring. Remote Sensing, 13(20), 4069.
Liversedge, L. (2007). Turbidity map** and prediction in ice marginal lakes at the Bering Glacier System, Alaska (Doctoral dissertation).
Mao, Z., Chen, J., Pan, D., Tao, B., & Zhu, Q. (2012). A regional remote sensing algorithm for total suspended matter in the East China Sea. Remote Sensing of Environment, 124, 819–831.
McKinna, L. I., Furnas, M. J., & Ridd, P. V. (2011). A simple, binary classification algorithm for the detection of Trichodesmium spp. within the Great Barrier Reef using MODIS imagery. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 9(2), 50–66.
Molden, D. (Ed.). (2013). Water for food water for life: A comprehensive assessment of water management in agriculture. Routledge.
Mouw, C. B., Greb, S., Aurin, D., DiGiacomo, P. M., Lee, Z., Twardowski, M., et al. (2015). Aquatic color radiometry remote sensing of coastal and inland waters: Challenges and recommendations for future satellite missions. Remote Sensing of Environment, 160, 15–30.
Mushtaq, F., & Nee Lala, M. G. (2017). Remote estimation of water quality parameters of Himalayan lake (Kashmir) using Landsat 8 OLI imagery. Geocarto International, 32(3), 274–285.
Mushtaq, F., Nee Lala, M. G., & Pandey, A. C. (2015). Assessment of pollution level in a Himalayan Lake, Kashmir, using geomatics approach. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 95(11), 1001–1013.
Mushtaq, F., Ahmed, P., & Nee Lala, M. G. (2021). Spatiotemporal change in the surface temperature of Himalayan lake and its interrelation with water quality and growth in aquatic vegetation. Geocarto International, 36(3), 241–261.
Mushtaq, F., Nee Lala, M. G., & Mantoo, A. G. (2022). Trophic state assessment of a freshwater Himalayan Lake using Landsat 8 OLI satellite imagery: A case study of Wular Lake, Jammu and Kashmir (India). Earth and Space Science, 9(3), e2021EA001653.
Naja, G. M., & Volesky, B. (2017). Toxicity and sources of Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr, As, and radionuclides in the environment. In Handbook of advanced industrial and hazardous wastes management (pp. 855–903). CRC Press.
Park, J., Kim, K. T., & Lee, W. H. (2020). Recent advances in information and communications technology (ICT) and sensor technology for monitoring water quality. Water, 12(2), 510.
Peters, E. C., Gassman, N. J., Firman, J. C., Richmond, R. H., & Power, E. A. (1997). Ecotoxicology of tropical marine ecosystems. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 16(1), 12–40.
Ritchie, J. C., Zimba, P. V., & Everitt, J. H. (2003). Remote sensing techniques to assess water quality. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 69(6), 695–704.
Saad, A., & Gamatié, A. (2020). Water management in agriculture: A survey on current challenges and technological solutions. IEEE Access, 8, 38082–38097.
Schmoll, O. (Ed.). (2006). Protecting groundwater for health: Managing the quality of drinking-water sources. World Health Organization.
Sit, M., Demiray, B. Z., **ang, Z., Ewing, G. J., Sermet, Y., & Demir, I. (2020). A comprehensive review of deep learning applications in hydrology and water resources. Water Science and Technology, 82(12), 2635–2670.
Sonone, S. S., Jadhav, S., Sankhla, M. S., & Kumar, R. (2020). Water contamination by heavy metals and their toxic effect on aquaculture and human health through food chain. Letters in Applied NanoBioScience, 10(2), 2148–2166.
Taylor, R. G., Scanlon, B., Döll, P., Rodell, M., Van Beek, R., Wada, Y., et al. (2013). Ground water and climate change. Nature Climate Change, 3(4), 322–329.
Thakur, J. K., Singh, S. K., & Ekanthalu, V. S. (2017). Integrating remote sensing, geographic information systems and global positioning system techniques with hydrological modelling. Applied Water Science, 7(4), 1595–1608.
Topp, S. N., Pavelsky, T. M., Jensen, D., Simard, M., & Ross, M. R. (2020). Research trends in the use of remote sensing for inland water quality science: Moving towards multidisciplinary applications. Water, 12(1), 169.
Usali, N., & Ismail, M. H. (2010). Use of remote sensing and GIS in monitoring water quality. Journal of Sustainable Development, 3(3), 228.
Volk, M., Hirschfeld, J., Dehnhardt, A., Schmidt, G., Bohn, C., Liersch, S., & Gassman, P. W. (2008). Integrated ecological-economic modelling of water pollution abatement management options in the Upper Ems River Basin. Ecological Economics, 66(1), 66–76.
World Health Organization. (2021). Guidelines on recreational water quality. Volume 1: Coastal and fresh waters. World Health Organization.
**ao, Y., Guo, Y., Yin, G., Zhang, X., Shi, Y., Hao, F., & Fu, Y. (2022). UAV multispectral image-based urban river water quality monitoring using stacked ensemble machine learning algorithms—A case study of the Zhanghe river, China. Remote Sensing, 14(14), 3272.
Yang, H., Kong, J., Hu, H., Du, Y., Gao, M., & Chen, F. (2022). A review of remote sensing for water quality retrieval: Progress and challenges. Remote Sensing, 14(8), 1770.
Yuan, X., Wang, S., Fan, F., Dong, Y., Li, Y., Lin, W., & Zhou, C. (2022). Spatiotemporal dynamics and anthropologically dominated drivers of chlorophyll-a, TN and TP concentrations in the Pearl River Estuary based on retrieval algorithm and random forest regression. Environmental Research, 215, 114380.
Zhao, Y., Yu, T., Hu, B., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Liu, X., ... & Song, S. (2022). Retrieval of Water Quality Parameters Based on Near-Surface Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Algorithm. Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5305.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kumari, N., Kadave, K., Marandi, S., Pandey, S., Kumar, G. (2023). Constructing the Dynamics of Water Quality Parameters Using Geospatial Technology and In Situ Observations. In: Mushtaq, F., Farooq, M., Mukherjee, A.B., Ghosh Nee Lala, M. (eds) Geospatial Analytics for Environmental Pollution Modeling. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45300-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-45300-7_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-45299-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-45300-7
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)