Abstract
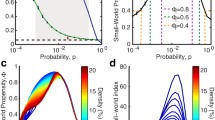
A number of studies have reported small-world properties in human brain networks. Recently Barmpoutis et al. [2] have shown that there exist networks with optimal small-world structure, in the sense that they optimize all small-world attributes compared to other networks of given order and size. We wished to evaluate how close human brain network properties are compared to the properties of optimal small-world networks. We have constructed weighted functional human brain networks based on functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data and MNI anatomical parcellation of brain. These weighted networks were further thresholded in order to obtain a set of simple undirected graphs. In the obtained graphs we computed small-world characteristics and compared them to the characteristics of comparable optimal small-world networks.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard, S., Salvador, R., Whitcher, B., Suckling, J., Bullmore, E.: A resilient, low-frequency, small-world human brain functional network with highly connected association cortical hubs. J. Neurosci. 26(1), 63 (2006)
Barmpoutis, D., Murray, R.: Networks with the smallest average distance and the largest average clustering. Arxiv preprint ar**v:1007.4031 (2010) http://arxiv.org/abs/1007.4031
Barmpoutis, D., Murray, R.: Extremal properties of complex networks. Arxiv preprint ar**v:1104.5532 (2011) http://arxiv.org/abs/1104.5532
Eguiluz, V., Chialvo, D., Cecchi, G., Baliki, M., Apkarian, A.: Scale-free brain functional networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(1), 18, 102 (2005)
Hilgetag, C., Burns, G., O’Neill, M., Scannell, J., Young, M.: Anatomical connectivity defines the organization of clusters of cortical areas in the macaque and the cat. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biol. Sci. 355(1393), 91–110 (2000)
Hong, H., Choi, M., Kim, B.: Synchronization on small-world networks. Phys. Rev. E 65(2), 026,139 (2002)
Latora, V., Marchiori, M.: Economic small-world behavior in weighted networks. The Eur. Phys. J. B 32(2), 249–263 (2003)
Laughlin, S., Sejnowski, T.: Communication in neuronal networks. Science 301(5641), 1870 (2003)
Percival, D., Walden, A.: Wavelet Methods for Time Series Analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2006)
Pinker, S.: The Better Angels of Our Nature: Why Violence Has Declined. Viking Adult, New York (2011)
Salvador, R., Suckling, J., Coleman, M., Pickard, J., Menon, D., Bullmore, E.: Neurophysiological architecture of functional magnetic resonance images of human brain. Cereb. Cortex 15(9), 1332–1342 (2005)
Skidmore, F., Korenkevych, D., Liu, Y., He, G., Bullmore, E., Pardalos, P.: Connectivity brain networks based on wavelet correlation analysis in parkinson fmri data. Neurosci. Lett. 499(1), 47–51 (2011)
Stam, C.: Functional connectivity patterns of human magnetoencephalographic recordings: a ‘small-world’ network? Neurosci. Lett. 355(1–2), 25–28 (2004)
Stephan, K., Hilgetag, C., Burns, G., O’Neill, M., Young, M., Kotter, R.: Computational analysis of functional connectivity between areas of primate cerebral cortex. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences 355(1393), 111 (2000)
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., Mazoyer, B., Joliot, M.: Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15(1), 273–289 (2002)
Watts, D., Strogatz, S.: Collective dynamics of small-world networks. Nature 393(6684), 440–442 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this paper
Cite this paper
Korenkevych, D., Skidmore, F., Goldengorin, B., Pardalos, P.M. (2013). How Close to Optimal Are Small World Properties of Human Brain Networks?. In: Goldengorin, B., Kalyagin, V., Pardalos, P. (eds) Models, Algorithms, and Technologies for Network Analysis. Springer Proceedings in Mathematics & Statistics, vol 32. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5574-5_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5574-5_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-5573-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-5574-5
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)