Abstract
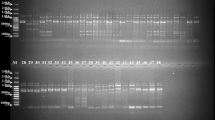
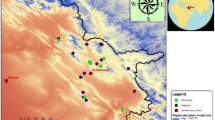
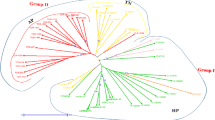
Aeluropus littoralis is a valuable halophyte grass belonging to the same family of wheat and is used as forage. Although A. littoralis has the potential to become an important genetic resource for improving salt and drought tolerance in economically important crops, no SSR markers have been developed for it. The main goal was to rapidly develop a set of genic SSR markers for A. littoralis. Repeat analysis of non-redundant EST sequences of Aeluropus and transferability assessment of 110 SSR-rich loci from rice and wheat were used to identify EST-SSRs. Then selected EST-SSR loci and some physiological traits includings Na+, K+ and Ash content were utilized for marker characterization and assessment of genetic diversity among A. littoralis accessions collected from all around the country. The results showed that 6.7% of EST records of A. littoralis comprising SSR motifs which was used for desiging 18 primer pairs (ALES). In addition 48 SSR loci (GDES) from 110 of the gramineae were shown to be transferable to A. littoralis based on the PCR profiles. Finally, genotypic clustering based on EST-SSR markers divided the accessions into seven groups. The accessions were also categorized into six groups according to the physiological traits. Our finding indicated that there are remarkable variations about 33% in coding regions of Iranian Aeluropus accessions. The results of both genotypic and physiologic clustering were partially consistent and most groups corresponded to geographic regions.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Khodashenas, M., Aeluropus peterganicus (Poaceae), a new species from Iran, Iran. J. Bot., 2008, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 13–15.
Khodashenas, M., Two new records and a new combination of the genus Aeluropus Trin (Poaceae) for the flora of Iran, Iran. J. Bot., 2009, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 61–62.
Watson, L. and Dallwitz, M.J., The Grass Genera of the World, Wallingford: CAB Int., 1992. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859600076668
Zouari, N., Saad, R.B., Legavre, T., Azaza, J., Sabau, X., Jaoua, M., Masmoudi, K., and Hassairi, A., Identification and sequencing of ESTs from the halophyte grass Aeluropus littoralis, Gene, 2007, vol. 404, nos. 1–2, pp. 61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2007.08.021
Barhoumi, Z., Djebali, W., Abdelly, C., Chaïbi, W., and Smaoui, A., Ultrastructure of Aeluropus littoralis leaf salt glands under NaCl stress, Protoplasma, 2008, vol. 233, nos. 3–4, pp. 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-008-0003-x
Nasiri, N., Shokri, E., and Nematzadeh, G.A., Aeluropus littoralis NaCl-induced vacuolar H+-ATPase Subunit c: Molecular cloning and expression analysis, Russ. J. Genet., 2012, vol. 48, no. 12, pp. 1199–1206. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795412080054
Younesi-Melerdi, E., Nematzadeh, G., and Shokri, E., Codon bias patterns in photosynthetic genes of halophytic grass Aeluropus littoralis, J. Plant Mol. Breed., 2014, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 12–20. https://doi.org/10.22058/JPMB.2014.8425
Wang, I.J., Glor, R.E., and Losos, J.B., Quantifying the roles of ecology and geography in spatial genetic divergence, Ecol. Lett., 2013, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 175–182. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12025
Singh, R.K., Jena, S.N., Khan, S., Yadav, S., Banarjee, N., Raghuvanshi, S., Bhardwaj, V., Dattamajumder, S.K., Kapur, R., Solomon, S., and Swapna, M., Development, cross-species/genera transferability of novel EST-SSR markers and their utility in revealing population structure and genetic diversity in sugarcane, Gene, 2013, vol. 524, no. 2, pp. 309–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.03.125
Ebrahimi, S., Seyed, T.B., and Sharif, N.B., Microsatellite isolation and characterization in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.), Iran. J. Biotechnol., 2010, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 156–163.
Ma, J.Q., Ma, C.L., Yao, M.Z., **, J.Q., Wang, Z.L., Wang, X.C., and Chen, L., Microsatellite markers from tea plant expressed sequence tags (ESTs) and their applicability for cross-species/genera amplification and genetic map**, Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam, Neth.), 2012, vol. 134, no. 1, pp. 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2011.10.029
Parthiban, S., Govindaraj, P., and Senthilkumar, S., Comparison of relative efficiency of genomic SSR and EST-SSR markers in estimating genetic diversity in sugarcane, 3 Biotech, 2018, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 144–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1172-8
Mohammadzadeh, F., Monirifar, H., Saba, J., Valizadeh, M., Haghighi, A.R., Zanjani, B.M., Barghi, M., and Tarhriz, V., Genetic variation among Iranian alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) populations based on RAPD markers, Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon., 2011, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 93–104. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjpt.v18i2.9296
Zhou, Q., Luo, D., Ma, L., **e, W., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., and Liu, Z., Development and cross-species transferability of EST-SSR markers in Siberian wildrye (Elymus sibiricus L.) using Illumina sequencing, Sci. Rep., 2016, vol. 6, p. 20549. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20549
Liu, C., Fan, B., Cao, Z., Su, Q., Wang, Y.A., Zhang, Z., Wu, J., and Tian, J., A deep sequencing analysis of transcriptomes and the development of EST-SSR markers in mungbean (Vigna radiata), J. Genet., 2016, vol. 95, no. 3, pp. 527–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-016-0663-9
Salimi, H., Bahar, M., Mirlohi, A., and Talebi, M., Assessment of the genetic diversity among potato cultivars from different geographical areas using the genomic and EST microsatellites, Iran. J. Biotechnol., 2016, vol. 14, no 4, p. 270. https://doi.org/10.15171/ijb.1280
Kantety, R.V., LaRota, M., Matthews, D.E., and Sorrells, M.E., Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat, Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 2002, vol. 48, no. 5, pp. 501–510. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014875206165
Yang, Z.J., Peng, Z.S., and Yang, H., Identification of novel and useful EST-SSR markers from de novo transcriptome sequence of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), Genet. Mol. Res., 2016, vol. 15, no. 1, p. 15017509. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15017509
Jo, W.S., Kim, H.Y., and Kim, K.M., Development and characterization of polymorphic EST based SSR markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare), 3 Biotech, 2017, vol. 7, no. 4, p. 265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0899-y
Yu, J.K., LaRota, M., Kantety, R.V., and Sorrells, M.E., EST derived SSR markers for comparative map** in wheat and rice, Mol. Genet. Genomics, 2004, vol. 271, no. 6, pp. 742–751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1027-3
Ukoskit, K., Posudsavang, G., Pongsiripat, N., Chatwachirawong, P., Klomsa-ard, P., Poomipant, P., and Tragoonrung, S., Detection and validation of EST-SSR markers associated with sugar-related traits in sugarcane using linkage and association map**, Genomics, 2019, vol. 111, no. 1, pp. 1–9. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0888754318300272.
Ashraf, J., Malik, W., Iqbal, M.Z., Ali, K.A., Qayyum, A., Noor, E., Abid, M.A., Naseer, C.H., and Ahmad, M.Q., Comparative analysis of genetic diversity among Bt cotton genotypes using EST-SSR, ISSR and morphological markers, J. Agric. Sci. Technol., 2016, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 517–531.
Arbeiter, A.B., Hladnik, M., Jakše, J., and Bandelj, D., Identification and validation of novel EST-SSR markers in olives, Sci. Agric., 2017, vol. 74, no. 3, pp. 215–225. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-992x-2016-0111
Jiang, Y., Li, H., Zhang, J., **ang, J., Cheng, R., and Liu, G., Whole Genomic EST-SSR development based on high-throughput transcript sequencing in Proso millet (Panicum miliaceum), Int. J. Agric. Biol., 2018, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 617–620. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/15.0531
Wu, B.D., Fan, R., Hu, L.S., Wu, H.S., and Hao, C.Y., Genetic diversity in the germplasm of black pepper determined by EST-SSR markers, Genet. Mol. Res., 2016, vol. 15, no. 1, p. 8099. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15018099
García-Gómez, B., Razi, M., Salazar, J.A., Prudencio, A.S., Ruiz, D., Dondini, L., and Martínez-Gómez, P., Comparative analysis of SSR markers developed in exon, intron, and intergenic regions and distributed in regions controlling fruit quality traits in Prunus species: genetic diversity and association studies, Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 2018, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 23–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-017-1058-7
Wang, M.L., Dzievit, M., Chen, Z., Morris, J.B., Norris, J.E., Barkley, N.A., Tonnis, B., and GA, Yu, J., Genetic diversity and population structure of castor (Ricinus communis L.) germplasm within the US collection assessed with EST-SSR markers, Genome, 2016, vol. 60, no. 3, pp. 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2016-0116
Chai, L., Biswas, M.K., Yi, H., Guo, W., and Deng, X., Transferability, polymorphism and effectiveness for genetic map** of the Pummelo (Citrus grandis Osbeck) EST-SSR markers, Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam, Neth.), 2013, vol. 155, pp. 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.02.024
Yu, J.K., Dake, T.M., Singh, S., Benscher, D., Li, W., Gill, B., and Sorrells, M.E., Development and map** of EST-derived simple sequence repeat markers for hexaploid wheat, Genome, 2004, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 805–818. https://doi.org/10.1139/g04-057
Dellaporta, S.L., Wood, J., and Hicks, J.B., A plant DNA minipreparation: Version II, Plant Mol. Biol. Rep., 1983, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 19–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02712670
Rohlf, F.J., Numeric taxonomy and multivariate analysis system NTSys-PC Version 1.80 Exeter Software, 1993.
Nei, M. and Li, W.H., Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1979, vol. 76, no. 10, pp. 5269–5273. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269
Excoffier, L., Smouse, P.E., and Quattro, J.M., Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data, Genetics, 1992, vol. 131, no. 2, pp. 479–491.
Rahemi, A., Fatahi, R., Ebadi, A., Taghavi, T., Hassani, D., Gradziel, T., Folta, K., and Chaparro, J., Genetic diversity of some wild almonds and related Prunus species revealed by SSR and EST-SSR molecular markers, Plant Syst. Evol., 2012, vol. 298, no. 1, pp. 173–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-011-0536-x
Ahmadi, J. and Fotokian, M.H., Identification and map** of quantitative trait loci associated with salinity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) using SSR markers, Iran. J. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 21–30.
Wang, J., Chen, Z., **, S., Hu, Z., Huang, Y., and Diao, Y., Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers based on a full-length cDNA library of Napier Grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum), Gene Genomics, 2017, vol. 39, no. 12, pp. 1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-017-0536-5
**, J.Q., Li, S.F., Gong, X.C., Lu, M.Z., Yao, Y.L., **n, Y., and Cui, H.R., Analysis of SSR information in EST resource of tea plants (Camellia sinensis), Bull. Sci. Technol., 2006, vol. 4, pp. 471–476.
Zhu, Y., Hao, Y., Wang, K., Wu, C., Wang, W., Qi, J., and Zhou, J., Analysis of SSRs information and development of SSR markers from walnut ESTs, Int. J. Fruit Sci., 2009, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 394–398.
Shamasbi, F.V., Nasiri, N., and Shokri, E., Genetic diversity of Persian ecotypes of Indian walnut (Aeluropus littoralis (Gouan) Pari.) by AFLP and ISSR markers, Cytol. Genet., 2018, vol. 52, no. 3, pp. 222–230. https://doi.org/10.3103/S009545271803012X
Cortese, L.M., Honig, J., Miller, C., and Bonos, S.A., Genetic diversity of twelve switchgrass populations using molecular and morphological markers, BioEnergy Res., 2010, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 262–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-010-9078-2
Funding
This work was funded by the Genetics and Agricultural Biotechnology, Institute of Tabarestan (GABIT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Authors have contributed equally to this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Meidansary, M., Nasiri, N., Shokri, E. et al. Genic SSR Development and Diversity Assessment of Persian Halophytic Grass, Aeluropus littoralis. Cytol. Genet. 57, 320–334 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452723040096
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452723040096