Abstract
Background
The Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis (FIHOA) is a simple, reliable, and reproducible specific instrument to evaluate hand OA that can be applied both in clinical practice and research protocols. In order to be used in Brazil, FIHOA has to be translated into Portuguese, culturally adapted and have the reliability of the translated FIHOA version tested, which is the purpose of this study.
Methods
The FIHOA was translated into Brazilian Portuguese and administered to 68 patients with hand OA recruited between May 2019 and February 2020. The test-retest was applied to 32 patients and the reliability was assessed using Spearman’s correlation coefficient and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The internal consistency reliability was evaluated using Cronbach’s alpha. External construction validity was assessed using the Spearman’s correlation test between FIHOA and pain, assessed with a Visual Analogue Scale (VAS), the Cochin Hand Functional Scale (CHFS) and Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ).
Results
The 30 participants that initially answered the translated version of the FiHOA did not report difficulties in understanding or interpreting the translated version. The test-retest reliability for the total score was strong (r = 0.86; ICC = 0.89). Mean differences (1.37 ± 0.68) using Bland Altman’s analysis did not significantly differ from zero and no systematic bias was observed. Cronbach’s alpha was also high (0.89) suggesting a strong internal coherence in the test items. There were also correlations between FIHOA and the CHFS (r = 0.88), HAQ (r = 0.64) and pain in the hands both at rest (r = 0.55) and in motion (r = 0.44).
Conclusion
The translation of the FIHOA into Brazilian Portuguese proved a valid instrument for measuring the functional capacity of patients with hand OA who understand Brazilian Portuguese.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most prevalent chronic arthropathy, involving particularly the hands, knee, cervical and lumbar spine and the hip [1, 2]. This is also true in Brazil, as it was recently reported, indicating a high OA prevalence [3]. Hand OA usually evolves with worsening symptoms with advanced age, being more prevalent in women. It is most commonly bilateral with symmetrical joint involvement [1, 4]. In addition to the pain component there is usually impairment of grip and pinch function particularly in those with a severe form [2, 4]. Initiatives published by the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials (OMERACT) and Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) recommend the application of function measures to evaluate hand OA [5, 6]. The Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis (FIHOA) is a free-of-charge, simple, reliable, and reproducible specific instrument to evaluate hand OA that can be applied both in clinical practice and research protocols [7, 8]. It has been originally published in an English version and various translations into other languages have been provided [9,10,11,12]. In order to be used in another language, a questionnaire has to be translated, culturally adapted and validated [13]. Our aim was to translate, culturally adapt and test the reliability of a Portuguese version of the FIHOA.
Methodology
Translation and cultural adaptation
The translation process was performed according to the guidelines for validation and cross-cultural adaptation, as described previously [13]. The original version of FIHOA was translated into Portuguese by two independent native Portuguese-speaking persons. Minor differences were observed between the versions of the texts of the 02 translators. The discrepancies between the translations were discussed with the translators and a consensus Portuguese translation was made. The consensus Portuguese version was then translated back into English by two bilingual native English speakers that were unaware of the original version. This consensus version was compared with the original questionnaire in order to assess semantic equivalence between the two versions and thus confirm a final translated version of the questionnaire. Following, the final version of the translated text was analyzed by three independent rheumatologists and a physiotherapist, also native Portuguese speakers, reaching a final cross-culturally adapted Portuguese consensus translation (Table 1).
Patients
A total of 68 consecutive patients attending the outpatient clinic of the Rheumatology Service of the Hospital das Clínicas of the Faculdade de Medicina of the Universidade Federal do Ceará were recruited between May 2019 and February 2020. The protocol was approved by the Local Ethics Committee (CAAE:07360819930015045; May 20, 2019) and all participants signed an informed consent prior to inclusion. Patients had to be native Portuguese speakers, within 40 to 75 years-old age range and meet the classification criteria for Hand OA according to the American College of Rheumatology [14]. Exclusion criteria included skin lesions restricting range of motion, crystal-related arthropathies (gout, calcium pyrophosphate disease), other immune-mediated diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthropathies, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus), hemochromatosis, history of upper limb trauma in the past 20 years, previous hand surgery, presence of a neurological disease or other musculoskeletal disease affecting the function of the upper limb.
Initially, 30 participants with hand OA answered the translated version of the questionnaire in order to assess the complete understanding of all items and whether the questions included the expected concepts without redundancy. Questions that could not be understood by more than 20% of the responders were analyzed, revised and resubmitted to another 30 group of patients. This procedure would be repeated until all questions were understood by over 80% of the patients in order to assure cultural adaptation. None of the participants reported difficulty in understanding and interpreting the questions involved in the final Portuguese version of FIHOA and the expert committee decided that no resubmission of the questionnaire to another group of participants and no further adjustments were necessary.
Subsequently, another group of patients was recruited to answer the questionnaire three times (test-retest phase). At first, participants were interviewed twice by different evaluators to check for inter-observer reliability. The second interview was conducted between 7 and 15 days after the first visit to assess intra-observer reliability. All questionnaires were answered under the supervision of an interviewer.
Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis score and other measures
FIHOA
The FIHOA contains 10 questions with one sex specific question included. The responses are scaled on a four-point Likert scale (0 = possible without difficulty, 1 = possible with slight difficulty, 2 = possible with important difficulty, 3 = impossible), to avoid any centralization of the answers. The range of scores is 0 to 30 [6].
Visual Analogue Scale for Hand Pain
Pain was assessed using a Visual Analogue Scale (VAS, 0–100 mm) for pain at rest and movement considering overall pain in the index hand during the last week.
Cochin Hand Functional Scale (CHFS)
The CHFS is an instrument for assessing functional disability of the hands that was initially developed in France to be used in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. It consists of a questionnaire of 18 questions (range 0–90) about activities of daily living that has been applied in other diseases involving the hand, including OA, and has been translated and validated into Brazilian Portuguese [15].
Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ)
The HAQ is a validated scale to assess functional daily living activities that can be used with arthritis patients and has been translated into Brazilian Portuguese (range 0–60) [16].
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 23 and the R program (version 3). A minimum sample size was defined as 50, based on a 5:1 criterion considering at least 5 respondents for each question, as described previously [17]. In this case, a minimum of 50 respondents for the 10 questions FIHOA questionnaire. Demographic and clinical characteristics were described using the mean and standard deviation for continuous variables and percentages for categorical variables. The main variable analyzed was the total score of the sum of the instrument’s items. The Wilcoxon test was used to compare FIHOA scores between test and retest.
Test-retest reliability
The analysis of the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient and the Bland-Altman graph were used to assess inter-observer and intra-observer reproducibility. A level of ICC ≥ 0.7 was considered strong at the scale level. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) considering a 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were calculated for each isolated item as well as for total scores using a two-way random model. Spearman’s coefficient of 0.1–0.3, 0.31–0.5 and > 0.5 were considered weak, moderate and strong correlation, respectively.
Internal consistency
Cronbach’s alpha test was performed to assess the internal consistency of FIHOA. This instrument was used to measure the global correlation between items within the scale and levels > 0.7 were considered an adequate performance [16]. We calculated the total item correlations adjusted for the specific item. A correlation of at least 0.4 was considered adequate to validate the internal consistency of the scale.
Internal construct and external validity
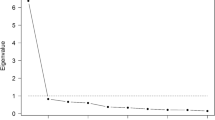
Internal construction validity was assessed with analysis factor according to the standard “eigenvalue > 1” rule (the Kaiser criterion). Spearman’s correlation test was used to verify the validity of external construction. External validity was assessed with the correlation of FIHOA with VAS of pain and the CHFS and HAQ instruments.
Results
Clinical and demographic characteristics
The Portuguese version of FIHOA was applied to 68 patients. The average time to answer the questionnaire was around 3 min. The clinical and demographic characteristics are shown in Table 2. Initially, 30 participants with hand OA answered the translated version of the questionnaire in order to assess the complete understanding of all items and none of the participants reported difficulty in understanding and interpreting the questions involved in the final Portuguese version of FIHOA. Following, the test-retest phase was performed with 38 participants. In this phase, six participants didn’t complete the 1st FIHOA assessment (5 did not answer item 7 and 1 did not answer question 7 and question 4) and were excluded from the analysis (Table 2).
Test – retest reliability
The Portuguese version of FIHOA was applied on two occasions with an interval of 7 or 15 days. No statistically significant difference between the evaluations was observed (Wilcoxon test: p = 0.32). The average score of each item and the total score of the FIHOA test-retest are reported in Table 3 showing no differences between the two evaluations. The average of the total score of the FIHOA was 9.9 ± 7.2 in the first assessment and 8.6 ± 6.5 in the second evaluation. The Spearman value for the total score was 0.86 and there was a variation for each item ranging from 0.4 to 0.8. The ICC of 0.89 for the total score was considered strong and the ICC for each single item was considered good to strong (0.6–0.9) and ICC for interobserver, which was 0.92, was also strong. Mean differences (1.37 ± 0.68) using Bland Altman’s analysis did not significantly differ from zero and no systematic bias was observed, as illustrated in Fig. 1.
Internal consistency
A high (0.89) Cronbach’s alpha was achieved, meaning a strong internal consistency between the test item. These values were also high even after deleting an item, ranging from 0.91 to 0.93, further confirming the internal consistency of the translated version of the test. The individual items of the Brazilian version of FIHOA showed a moderate correlation adjusted to the total of the items. All correlations were statistically significant (p < 0.01), as shown in Table 4.
Validity of internal construction
Factor analysis was performed to assess the internal structural validity of the Brazilian version of FIHOA. The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin was 0.821, which suggests that the sample size was adequate. Bartlett’s sphericity test produced a high χ2 of 185.0 (P < 0.01), which indicates that the factorial model was appropriate. The selection of two components represented 67.8% of the overall variation. The two factors represented 54.3 and 13.4%, of the total variation, respectively.
All 10 FIHOA items were positively correlated with factor 1 (representing 54.3% of the variance). Therefore, factor 1 may reflect the general capacity to perform activities composing the FIHOA. The correlation model became clearer with the varimax rotation, establishing a two-dimensional model for the Brazilian version of FIHOA.
The rotation suggested that the first factor captured items such as activities that require coordination of the fingers and activities related to holding objects for a long period of time by pinching fingers. This factor also captured activities that need to hold objects in the hand applying a higher level of force. The first factor consists of the following six items: item 4 (“Are you able to lift a full bottle with the hand?”); item 6 (“Are you able to tie a knot?”); item 3 (“Are you able to cut cloth or paper with a pair of scissors?”); item 8 (“Are you able to fasten buttons?”); item 9 (“Are you able to write for a long period of time?”) and item 2 (“Are you able to cut meat with a knife?”).
The second factor explains 13.4% of the total variance and is made up of item 5 (“Are you able to clench your fist?”), 1 (Are you able to turn a key in a lock?), 7 (“Are you able to sew?” Or “Are you able to use a screwdriver?”) and 10 (would you accept a handshake without reluctance?”). These activities seem to be particularly related to the ability to perform rotation, flexion and extension of the wrist and hand grip movement. Item 7 had a strong correlation with both factors (factor 1 (519) and factor 2 (698)), meaning that the activity evaluated in item 7 is also related to the ability of coordinated finger movements. Factor 2 was opposed from item 5 to item 8, suggesting that individuals who were able to close their hands more easily had a lot of difficulty in performing the task of fastening buttons.
Validity of external construction
We calculated Spearman’s rho values between the total score of the Brazilian version of FIHOA, VAS of hand pain at rest and in motion, CHFS and HAQ. There was a strong direct correlation between FIHOA and CHFS (Spearman’s rho = 0.89, P < 0.01) and moderate correlation for FIHOA and HAQ (Spearman’s rho = 0.64, P < 0.01). There was also a moderate correlation with VAS values for pain in the hands at rest (Spearman’s rho = 0.55, P < 0.01) and a moderate correlation with VAS values for pain in the hands when in motion (Spearman’s rho = 0.44, P < 0.01).
The Bland and Altman graph concerning the analysis of the FIHOA x HAQ tools showed that the mean differences were distributed close to zero and within 2 SD. Almost all observations were within the upper and lower limits identified by the SD, with only 03 values differing from the mean in more than three SD. The Bland and Altman analysis of the FIHOA x CHFS tools showed that the mean differences were close to 10, between 02 SD. Almost all observations were within the upper and lower limits identified by the SD, and none differed from the mean by more than three SD. No systematic trend of differences was observed in both analyzes.
Discussion
This study provides the Portuguese version of the FIHOA questionnaire with cultural adaptation to Brazilian patients, demonstrating a good reliability, validity, and internal consistency in patients with hand OA. Cultural adaptation was not a major issue given the similarity of the meaning of each FIHOA items which can be considered very similar in any culture. Although we did not aim to compare total scores among our patients, our mean of 7.4, which could be considered revealing a moderate functional impairment, are lower than values reported in similar studies carried out in Belgium (10.9), Iran (9.9) and Norway (9.3) [10, 18, 19]. On the other hand, one may consider that our patients presented greater impairment when comparing to scores obtained in studies performing translation of FIHOA in Italy (6.5), Japan (5.5), Morocco (5.0) and Korea (4.4) [11, 12, 20, 21].
We performed an assessment of the level of hand pain at rest and movement, which had not been done in previous FIHOA validation studies. The average level of pain at rest by VAS of the patients in this study was 38.7 mm, similar to the average pain in the population assessed in other studies such as in Belgium (42.9), Italy (35), Norway (41.7) and Korea (35.2) [9, 11, 12, 19]. The average level of global pain in moving hands (67.8) showed an important increase when compared to the level of pain at rest in our study and the other validation studies [9,10,11,12, 19, 21]. Although we initially thought that the level of pain in moving hands could be better correlated with the total score of a functional assessment instrument such as FIHOA, the results showed that there was a better correlation with the mean VAS score of pain in the hands at rest (0.55) compared to the VAS score of pain in the hands in motion (0.44) although the latter still has a moderate level of correlation. Actually, patients report that type of movement and intensity of the force applied influence the level of pain. Studies with a larger number of patients using VAS assessment at rest and movement can be carried out in the future to clarify the correlation of these two characteristics with the FIHOA score.
A good reliability was obtained given the good consistency of answers in the test-retest analysis which may be due to the clarity and simplicity of the questions in the original FIHOA questionnaire, making it possible to be easily translated. This aspect reinforces the validity of applying FIHOA in our patients.
The strong internal consistency of this Portuguese version of FIHOA is illustrated by a high Cronbach’s alpha result. Cronbach’s alpha showed a slight increase if any of the items were deleted and remained at a high value, indicating that the items are suitable for use. The correlation for adjusted item-total is> 0.4 for all items, confirming that there is a strong of association between individual items and the remainder of the scale.
Similar to most studies, the Factor of Analysis of this Portuguese version of FIHOA shows that it is not a one-dimensional tool, as reported by Dreiser et al. [7]. Indeed, similar to results obtained when translating into Persian, we found 2 factors, whereas similar studies performed in Italy and Korea found a greater number of factors [10,11,12]. Remarkably, the Norwegian version of FIHOA was the only one reporting only one dimension [19]. Our results were also able to discriminate the two components, functions of the hands such as: 1) coordination of the fingers and clam** objects at length and 2) rotation, flexion and extension of the wrist and hand grip movement. Other aspects, such as the level of pain in the hands, may have influenced the response pattern of component 2, as most patients with a higher level of disability in item 10 had a higher level of pain measured with the VAS.
The validity of external consistency was also considered good when compared to other instruments that assess functionality such as HAQ and CHFS. Even in comparison with instruments that assess pain level (VAS of pain in hands at rest and in movement), the analysis showed a good level of external correlation.
This study has some limitations, including the relatively low number of patients. We also had only 3 male patients (5%), which preclude a reliable analysis of item 7b, judged to be specific to that gender. It is worth mentioning that hand OA is very predominant in females and most previous similar FIHOA translational studies also had a similar low prevalence of male participants [9, 11, 12, 19, 22, 23]. There was a mean 10-year difference between the groups that participated in the pre-test and test-retest phases. The selection was at random and we believe this difference was irrelevant since the understanding of the phrasing was similar between both groups.
The evaluation of hand functionality through gender-specific questions can have its added value quite questionable in societies where a high and growing number of individuals of both genders have been performing similar tasks in their daily lives. It is assumed that there is a greater influence of a socio-cultural aspect than a functional difference between the two specific questions for each gender. Further studies are needed to investigate whether this gender-specific issue can be eliminated or replaced. Neither did we assess the number and location of the affected joints, nor the presence of Heberden and Bouchard nodes and deformities caused by OA, which may influence dexterity and functional capacity of the fingers. Indeed, the number of nodes in the hands and involvement of the base of the thumb and wrists may be associated with a higher level of pain and functional limitation [19, 24,25,26]. Six patients didn’t complete the 1st FIHOA assessment, leaving some blank items in the questionnaire and were excluded from the analysis. The answers were similar and they justified that they hadn’t performed that task in many years or had never done it (06 patients didn’t know how to sew) and one patient also didn’t know how to answer question 4 and justified that this item didn’t specify the weight of the bottle that he would try to lift.
Conclusion
The Brazilian Portuguese version of the FIHOA questionnaire proved to be a fast, easy-to-handle, reliable valid instrument for measuring the functional capacity of patients with hand OA in native Portuguese speaking patients.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Change history
22 June 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-021-00196-2
Abbreviations
- CHFS:
-
Cochin Hand Functional Scale
- FIHOA:
-
Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis
- HAQ:
-
Health Assessment Questionnaire
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- OA:
-
Osteoarthritis
- OARSI:
-
Osteoarthritis Research Society International
- OMERACT:
-
Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials
- VAS:
-
Visual Analogue Scale
References
Zhang Y, Jordan JM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Clin Geriatr Med. 2010;26(3):355–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2010.03.001.
Bijsterbosch J, Watt I, Meulenbelt I, Rosendaal FR, Huizinga TWJ, Kloppenburg M. Clinical and radiographic disease course of hand osteoarthritis and determinants of outcome after 6 years. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(1):68–73. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2010.133017.
Coimbra IB, Plapler PG, Campos GC. Generating evidence and understanding the treatment of osteoarthritis in Brazil: a study through Delphi methodology. Clinics. 2019;74:e722. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2019/e722.
Zhang W, Doherty M, Leeb BF, Alekseeva L, Arden NK, Bijlsma JW, et al. EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis of hand osteoarthritis: report of a task force of ESCISIT. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(1):8–17. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.084772.
Maheu E, Altman RD, Bloch DA, Doherty M, Hochberg M, Mannoni A, et al. Design and conduct of clinical trials in patients with osteoarthritis of the hand: recommendations from a task force of the Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2006;14(4):303–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2006.02.010.
Pham T, van der Heijde D, Altman RD, Anderson JJ, Bellamy N, Hochberg M, et al. OMERACT-OARSI initiative: Osteoarthritis Research Society International set of responder criteria for osteoarthritis clinical trials revisited. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2004;12(5):389–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2004.02.001.
Dreiser RL, Maheu E, Guillou GB, et al. Validation of an algofunctional index for osteoarthritis of the hand. Rev Rhum Engl. 1995;62(6 suppl 1):43s–53s.
Kloppenburg M, Maheu E, Kraus VB, Cicuttini F, Doherty M, Dreiser RL, et al. Clinical trials recommendations: design and conduct of clinical trials for hand osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2015;23(5):772–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2015.03.007.
Wittoek R, Cruyssen BV, Maheu E, et al. Cross-cultural adaptation of the Dutch version of the Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis (FIHOA) and a study on its construct validity. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2009;17(5):607–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2008.10.006.
Yoosefinejad AK, Motealleh A, Babakhani M. Evaluation of validity and reliability of the Persian version of the functional index of hand osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37(5):719–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-016-3645-6.
Gandini F, Giannitti C, Fattore G, Giordano N, Galeazzi M, Fioravanti A. Validation of an Italian version of the Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis (FIHOA). Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22(5):758–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-011-0579-4.
Ahn GY, Cho S-K, Cha SJ, Nam E, Lee JE, Dreiser RL, et al. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Korean version of the Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis (FIHOA). Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;00(12):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.13412.
Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guillemin F, Ferraz MB. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine. 2000;25(24):3186–91. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-200012150-00014.
Altman R, Alarcón G, Appelrouth D, et al. The American College of Rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hand. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33(11):1601–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780331101.
Chiari A, Sardim CCS, Natour J. Translation, cultural adaptation and reproducibility of the Cochin Hand Functional Scale questionnaire for Brazil. Clin Sci. 2011;66(5):731–6. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1807-59322011000500004.
Ferraz MB, Oliveira LM, Araujo PMP, Atra E, Tugwell P. Cross cultural reability of the physical ability dimension of the health assessment questionnaire. J Rheumatol. 1990;17(6):813–7.
Tsang S, Royse CF, Terkawi AS. Guidelines for develo**, translating, and validating a questionnaire in perioperative and pain medicine. Saudi J Anaesth. 2017;11(Suppl 1):S80–9. https://doi.org/10.4103/sja.SJA_203_17.
Gliem JA, Gliem RR. Calculating, interpreting, and reporting cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient for likert-type scales. Midwest research to practice conference in adult, continuing, and community education; 2004. p. 82–8. http://hdl.handle.net/1805/344. Acessed 20 Apr 2020
Moe RH, Garratt A, Slatkowsky-Christensen B, Maheu E, Mowinckel P, Kvien TK, et al. Concurrent evaluation of data quality, reliability and validity of the Australian/Canadian osteoarthritis hand index and the Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49(12):2327–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keq219.
Nakagawa Y, Kurimoto S, Maheu E, Matsui Y, Kanno Y, Menuki K, et al. Cross-cultural translation, adaptation and validation of a Japanese version of the Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis (JFIHOA). BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):173. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-020-03193-6.
Taik FZ, Tahiri L, Rkain H, Aachari I, Maheu E, Allali F. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Arabic version of the Functional Index for Hand Osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):390. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-020-03418-8.
Chaisson CE, Zhang Y, McAlindon TE, Hannan MT, Aliabadi P, Naimark A, et al. Radiographic hand osteoarthritis: incidence, patterns, and influence of pre-existing disease in a population-based sample. J Rheumatol. 1997;24(7):1337–43.
Srikanth VK, Fryer JL, Zhai G, Winzenberg TM, Hosmer D, Jones G. A meta-analysis of sex differences prevalence, incidence and severity of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2005;13(9):769–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2005.04.014.
Marshall M, Van der Windt D, Nicholls E, et al. Radiographic hand osteoarthritis: patterns and associations with hand pain and function in a community dwelling sample. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2009;17(11):1440–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2009.05.009.
Bijsterbosch J, Visser W, Kroon HM, Stamm T, Meulenbelt I, Huizinga TWJ, et al. Thumb base involvement in symptomatic hand osteoarthritis is associated with more pain and funcional disability. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(3):585–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.104562.
Kitisomprayoonkul W, Promsopa K. Chaiwanichsiri D (2010) do Heberden and Bouchard nodes affect finger dexterity in elderly? Rheumatol Int. 2010;30(4):543–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-1196-9.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support we received from Dr. Emmanuel Maheu (Saint Antoine Hospital, Department of Rheumatology, Paris, France) that provided authorization for the translation and advice on the methods for our validation study. We acknowledge partial support of this work from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPQ), Brasil – Grant 308429/2018-4.
Funding
This study received partial support of this work from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPQ), Brasil – Grant 308429/2018–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FVAA, JN, and FACR conceived the article. Data acquisition, analysis and/or interpretation: FVAA, AJ, HALR, JN, FACR. Draft and revision of the work: FVAA, AJ, HALR, JN, FACR. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors are accountable for all aspects of the work particularly regarding integrity of the data and collection of material.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This work was fully compliant with Ethical Standards and receive approval from an Ethics Review Board accredited by the Conselho Nacional de Ética em Pesquisa – Brasil (Ethics Approval: CAAE:07360819930015045; May 20, 2019).
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The author and co-authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose concerning the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
An error was identified in the Acknowledgements section. The authors want to add the below statement: We acknowledge the support we received from Dr. Emmanuel Maheu (Saint Antoine Hospital, Department of Rheumatology, Paris, France) that provided authorization for the translation and advice on the methods for our validation study. The original article has been updated.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
de Azevedo, F.V.A., Rocha, H.A.L., Jones, A. et al. Translation, cultural adaptation and reproducibility of a Portuguese version of the Functional Index for Hand OsteoArthritis (FIHOA). Adv Rheumatol 61, 30 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-021-00189-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-021-00189-1