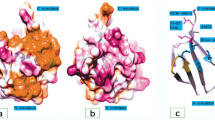
Abstract
NEDDylation, a post-translational modification through three-step enzymatic cascades, plays crucial roles in the regulation of diverse biological processes. NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) as the only activation enzyme in the NEDDylation modification has become an attractive target to develop anticancer drugs. To date, numerous inhibitors or agonists targeting NAE have been developed. Among them, covalent NAE inhibitors such as MLN4924 and TAS4464 currently entered into clinical trials for cancer therapy, particularly for hematological tumors. This review explains the relationships between NEDDylation and cancers, structural characteristics of NAE and multistep mechanisms of NEDD8 activation by NAE. In addition, the potential approaches to discover NAE inhibitors and detailed pharmacological mechanisms of NAE inhibitors in the clinical stage are explored in depth. Importantly, we reasonably investigate the challenges of NAE inhibitors for cancer therapy and possible development directions of NAE-targeting drugs in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Neuronal precursor cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 8 (NEDD8) shares about 60% of the amino acids with ubiquitin, which covalently binds to substrate proteins by generating an isopeptide chain between the lysine residue of substrates and the glycine residue of NEDD8 [1,2,3,4,5]. NEDDylation is a biochemical process of post-translational modification that conjugates NEDD8 to substrate proteins through the successive enzymatic cascades [6,7,8,9,10]. In the initial stage of NEDDylation, the precursor of NEDD8 is hydrolyzed to mature NEDD8 by the precursor processing enzymes [11,12,13,14]. Next, the mature NEDD8 is activated in the presence of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the E1 NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) consisting of amyloid protein-binding protein 1 (APPBP1) and ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 3 (UBA3) [15,16,17]. Then, the activated NEDD8 is transferred to NEDD8-conjugating enzyme E2s (UBC12 and UBE2F) via a trans-thiolation process [18, Not applicable. NEDD8-activating enzyme Neuronal precursor cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 8 Adenosine triphosphate Amyloid protein-binding protein 1 Ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 3 Cullin-RING ligases Active adenylation domain Inactive adenylation domain Catalytic cysteine Ubiquitin fold domain Acute myeloid leukemia Half-life Area under the plasma concentration–time curve Volume of distribution Clearance Peak concentration I-kappa-B-alpha Adenosine 5′-monophosphate TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma Tricarboxylic acid cycle Oxidative phosphorylation system Tumor microenvironment Nuclear factor κB Multiple myeloma Hematologic malignancies Hodgkin lymphoma Myelodysplastic syndromes Acute lymphoblastic leukemia Chronic lymphocytic leukemia Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia Myeloproliferative neoplasm Myelodysplastic syndromes Chromosome ten Protein kinase B Pyruvate kinase isoform M2 Interleukin-17A Zubiete-Franco I, Fernández-Tussy P, Barbier-Torres L, Simon J, Fernández-Ramos D, Lopitz-Otsoa F, et al. Deregulated neddylation in liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 2017;65:694–709. Jiang Y, Li L, Li Y, Liu G, Hoffman RM, Jia L. Neddylation regulates macrophages and implications for cancer therapy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:681186. He X, Zhu A, Feng J, Wang X. Role of neddylation in neurological development and diseases. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2022;69:330–41. Zhou Q, Zheng Y, Sun Y. Neddylation regulation of mitochondrial structure and functions. Cell Biosci. 2021;11:55. Yu Q, Jiang Y, Sun Y. Anticancer drug discovery by targeting cullin neddylation. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020;10:746–65. Stuber K, Schneider T, Werner J, Kovermann M, Marx A, Scheffner M. Structural and functional consequences of NEDD8 phosphorylation. Nat Commun. 2021;12:5939. Castagnoli L, Mandaliti W, Nepravishta R, Valentini E, Mattioni A, Procopio R, et al. Selectivity of the CUBAN domain in the recognition of ubiquitin and NEDD8. FEBS J. 2019;286:653–77. Schwechheimer C. NEDD8-its role in the regulation of Cullin-RING ligases. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2018;45:112–9. Mohanty P, Chatterjee KS, Das R. NEDD8 deamidation inhibits cullin RING ligase dynamics. Front Immunol. 2021;12:695331. Baek K, Krist DT, Prabu JR, Hill S, Klügel M, Neumaier L-M, et al. NEDD8 nucleates a multivalent cullin-RING-UBE2D ubiquitin ligation assembly. Nature. 2020;578:461–6. Ribet D, Cossart P. Ubiquitin, SUMO, and NEDD8: key targets of bacterial pathogens. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28:926–40. Kostrhon S, Prabu JR, Baek K, Horn-Ghetko D, von Gronau S, Klügel M, et al. CUL5-ARIH2 E3–E3 ubiquitin ligase structure reveals cullin-specific NEDD8 activation. Nat Chem Biol. 2021;17:1075–83. Zhao B, Zhang K, Villhauer EB, Bhuripanyo K, Kiyokawa H, Schindelin H, et al. Phage display to identify nedd8-mimicking peptides as inhibitors of the Nedd8 transfer cascade. ChemBioChem. 2013;14:1323–30. Watson IR, Irwin MS, Ohh M. NEDD8 pathways in cancer, sine quibus non. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:168–76. Schmidt MHH, Dikic I. Ubiquitin and NEDD8: brothers in arms. Sci STKE. 2006;2006:pe50. Kamitani T, Kito K, Nguyen HP, Yeh ETH. Characterization of NEDD8, a developmentally down-regulated ubiquitin-like protein. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:28557–62. Assumpção ALFV, Lu Z, Marlowe KW, Shaffer KS, Pan X. Targeting NEDD8-activating enzyme is a new approach to treat canine diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Vet Comp Oncol. 2018;16:606–15. Li L, Kang J, Zhang W, Cai L, Wang S, Liang Y, et al. Validation of NEDD8-conjugating enzyme UBC12 as a new therapeutic target in lung cancer. EBioMedicine. 2019;45:81–91. Wang S, **an J, Li L, Jiang Y, Liu Y, Cai L, et al. NEDD8-conjugating enzyme UBC12 as a novel therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:123. Huang DT, Paydar A, Zhuang M, Waddell MB, Holton JM, Schulman BA. Structural basis for recruitment of Ubc12 by an E2 binding domain in NEDD8’s E1. Mol Cell. 2005;17:341–50. Zhou W, Xu J, Tan M, Li H, Li H, Wei W, et al. UBE2M is a stress-inducible dual E2 for neddylation and ubiquitylation that promotes targeted degradation of UBE2F. Mol Cell. 2018;70:1008–24. Zhou L, Lin X, Zhu J, Zhang L, Chen S, Yang H, et al. NEDD8-conjugating enzyme E2s: critical targets for cancer therapy. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9:23. Zheng Y-C, Guo Y-J, Wang B, Wang C, Mamun MAA, Gao Y, et al. Targeting neddylation E2s: a novel therapeutic strategy in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:57. Chew E-H, Hagen T. Substrate-mediated regulation of cullin neddylation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:17032–40. Zhou H, Lu J, Liu L, Bernard D, Yang C-Y, Fernandez-Salas E, et al. A potent small-molecule inhibitor of the DCN1-UBC12 interaction that selectively blocks cullin 3 neddylation. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1150. Scott Daniel C, Sviderskiy Vladislav O, Monda Julie K, Lydeard John R, Cho Shein E, Harper JW, et al. Structure of a RING E3 trapped in action reveals ligation mechanism for the ubiquitin-like protein NEDD8. Cell. 2014;157:1671–84. **rodimas DP, Sundqvist A, Nakamura A, Shen L, Botting C, Hay RT. Ribosomal proteins are targets for the NEDD8 pathway. EMBO Rep. 2008;9:280–6. Yan Z-H, Burkhardt A, Loke H-K, Chen J, Xu Q, Brauer P, et al. Quantifiable analysis of cellular pathway inhibition of a Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor, MLN4924, using AlphaScreen. Anal Biochem. 2013;439:109–15. Li X, Yokoyama NN, Zhang S, Ding L, Liu H-M, Lilly MB, et al. Flavokawain A induces deNEDDylation and Skp2 degradation leading to inhibition of tumorigenesis and cancer progression in the TRAMP transgenic mouse model. Oncotarget. 2015;6:41809–24. Hammill JT, Scott DC, Min J, Connelly MC, Holbrook G, Zhu F, et al. Piperidinyl ureas chemically control defective in cullin neddylation 1 (DCN1)-mediated cullin neddylation. J Med Chem. 2018;61:2680–93. Zhao J, Zhang B, Lai G, Xu R, Chu G, Zhao Y. 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid regulates the expression of Nedd4-2 in kidney and liver through a neddylation modification pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16:9671–7. Zhang X, Zhang Y-L, Qiu G, Pian L, Guo L, Cao H, et al. Hepatic neddylation targets and stabilizes electron transfer flavoproteins to facilitate fatty acid β-oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:2473–83. Wu K-J, Zhong H-J, Li G, Liu C, Wang H-MD, Ma D-L, et al. Structure-based identification of a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor via drug repurposing. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;143:1021–7. Olaizola P, Lee-Law PY, Fernandez-Barrena MG, Alvarez L, Cadamuro M, Azkargorta M, et al. Targeting NAE1-mediated protein hyper-NEDDylation halts cholangiocarcinogenesis and impacts on tumor-stroma crosstalk in experimental models. J Hepatol. 2022;77:177–90. Bornstein G, Ganoth D, Hershko A. Regulation of neddylation and deneddylation of cullin1 in SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase by F-box protein and substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:11515–20. Wu J-T, Lin H-C, Hu Y-C, Chien C-T. Neddylation and deneddylation regulate Cul1 and Cul3 protein accumulation. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:1014–20. Zhou L, Zhang W, Sun Y, Jia L. Protein neddylation and its alterations in human cancers for targeted therapy. Cell Signal. 2018;44:92–102. Markmiller S, Fulzele A, Higgins R, Leonard M, Yeo GW, Bennett EJ. Active protein neddylation or ubiquitylation is dispensable for stress granule dynamics. Cell Rep. 2019;27:1356–63. Zou T, Zhang J. Diverse and pivotal roles of neddylation in metabolism and immunity. FEBS J. 2021;288:3884–912. Enchev RI, Schulman BA, Peter M. Protein neddylation: beyond cullin-RING ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16:30–44. Ying J, Zhang M, Qiu X, Lu Y. Targeting the neddylation pathway in cells as a potential therapeutic approach for diseases. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018;81:797–808. Soucy TA, Smith PG, Milhollen MA, Berger AJ, Gavin JM, Adhikari S, et al. An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a new approach to treat cancer. Nature. 2009;458:732–6. Zhou L, Lin X, Zhang L, Chen S, Chen J, Zhou Z, et al. Neddylation pathway promotes myeloid-derived suppressor cell infiltration via NF-κB-mCXCL5 signaling in lung cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;113:109329. Mittler F, Obeïd P, Haguet V, Allier C, Gerbaud S, Rulina AV, et al. Mechanical stress shapes the cancer cell response to neddylation inhibition. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41:115. Jayabalan AK, Sanchez A, Park RY, Yoon SP, Kang G-Y, Baek J-H, et al. NEDDylation promotes stress granule assembly. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12125. Guo Z, Wang S, **e Y, Han Y, Hu S, Guan H, et al. HUWE1-dependent DNA-PKcs neddylation modulates its autophosphorylation in DNA damage response. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:400. Guan J, Zheng X. NEDDylation regulates RAD18 ubiquitination and localization in response to oxidative DNA damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508:1240–4. Brown JS, Jackson SP. Ubiquitylation, neddylation and the DNA damage response. Open Biol. 2015;5:150018. Li Z, Cui Q, Wang X, Li B, Zhao D, **a Q, et al. Functions and substrates of NEDDylation during cell cycle in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;90:101–12. Zhao Y, Morgan MA, Sun Y. Targeting neddylation pathways to inactivate cullin-RING ligases for anticancer therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;21:2383–400. Kittai A, Best SR, Rowland T, Bruss N, Okada C, Danilov AV. Pevonedistat, a small molecule inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE), induces cell cycle deregulation, anaphase catastrophe, and apoptosis in T-cell lymphoma cells. Blood. 2018;132:1667. McMillin DW, Jacobs HM, Delmore JE, Buon L, Hunter ZR, Monrose V, et al. Molecular and cellular effects of NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibition in myeloma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11:942–51. Milhollen MA, Narayanan U, Soucy TA, Veiby PO, Smith PG, Amidon B. Inhibition of NEDD8-activating enzyme induces rereplication and apoptosis in human tumor cells consistent with deregulating CDT1 turnover. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3042–51. Godbersen C, Eastman A, Brown JR, Danilov AV. Targeting microenvironment-mediated NFκb activation with MLN4924, an inhibitor of the Nedd8-activating enzyme, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood. 2013;122:2875. Luo Z, Pan Y, Jeong LS, Liu J, Jia L. Inactivation of the cullin (CUL)-RING E3 ligase by the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 triggers protective autophagy in cancer cells. Autophagy. 2012;8:1677–9. Allan DC, Phillips JC. Evolution of the ubiquitin-activating enzyme Uba1 (E1). Physica A. 2017;483:456–61. Bhogaraju S, Dikic I. Ubiquitination without E1 and E2 enzymes. Nature. 2016;533:43–4. Lv Z, Yuan L, Atkison JH, Williams KM, Vega R, Sessions EH, et al. Molecular mechanism of a covalent allosteric inhibitor of SUMO E1 activating enzyme. Nat Commun. 2018;9:5145. Barghout SH, Schimmer AD. E1 enzymes as therapeutic targets in cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73:1–58. Burroughs AM, Iyer LM, Aravind L. Natural history of the E1-like superfamily: implication for adenylation, sulfur transfer, and ubiquitin conjugation. Proteins. 2009;75:895–910. Lv Z, Yuan L, Atkison JH, Aldana-Masangkay G, Chen Y, Olsen SK. Domain alternation and active site remodeling are conserved structural features of ubiquitin E1. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:12089–99. Walden H, Podgorski MS, Schulman BA. Insights into the ubiquitin transfer cascade from the structure of the activating enzyme for NEDD8. Nature. 2003;422:330–4. Shah P, Chaumet A, Royle SJ, Bard FA. The NAE pathway: autobahn to the nucleus for cell surface receptors. Cells. 2019;8:915. Yue Y, Ma Y, Qian P, Guo H. Catalytic mechanism of the ubiquitin-like NEDD8 transfer in RING E3–E2∼NEDD8-target complex from QM/MM free energy simulations. J Chem Inf Model. 2018;58:422–9. Lim M, Newman JA, Williams HL, Masino L, Aitkenhead H, Gravard AE, et al. A ubiquitin-binding domain that binds a structural fold distinct from that of ubiquitin. Structure. 2019;27:1316–25. Akimoto G, Fernandes AP, Bode JW. Site-specific protein ubiquitylation using an engineered, chimeric E1 activating enzyme and E2 SUMO conjugating enzyme Ubc9. ACS Cent Sci. 2022;8:275–81. Miles JA, Frost MG, Carroll E, Rowe ML, Howard MJ, Sidhu A, et al. The Fanconi anemia DNA repair pathway is regulated by an interaction between ubiquitin and the E2-like fold domain of FANCL. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:20995–1006. Wang J, Hu W, Cai S, Lee B, Song J, Chen Y. The intrinsic affinity between e2 and the Cys domain of E1 in ubiquitin-like modifications. Mol Cell. 2007;27:228–37. Hill ZB, Pollock SB, Zhuang M, Wells JA. Direct proximity tagging of small molecule protein targets using an engineered NEDD8 ligase. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138:13123–6. Kurz T, Pintard L, Willis JH, Hamill DR, Gönczy P, Peter M, et al. Cytoskeletal regulation by the Nedd8 ubiquitin-like protein modification pathway. Science. 2002;295:1294–8. Kamitani T, Kito K, Fukuda-Kamitani T, Yeh ETH. Targeting of NEDD8 and its conjugates for proteasomal degradation by NUB1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:46655–60. Wu K, Yamoah K, Dolios G, Gan-Erdene T, Tan P, Chen A, et al. DEN1 is a dual function protease capable of processing the C terminus of Nedd8 and deconjugating hyper-neddylated CUL1. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:28882–91. Walden H, Podgorski MS, Huang DT, Miller DW, Howard RJ, Minor DL, et al. The structure of the APPBP1-UBA3-NEDD8-ATP complex reveals the basis for selective ubiquitin-like protein activation by an E1. Mol Cell. 2003;12:1427–37. Huang DT, Miller DW, Mathew R, Cassell R, Holton JM, Roussel MF, et al. A unique E1–E2 interaction required for optimal conjugation of the ubiquitin-like protein NEDD8. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:927–35. Huang DT, Hunt HW, Zhuang M, Ohi MD, Holton JM, Schulman BA. Basis for a ubiquitin-like protein thioester switch toggling E1–E2 affinity. Nature. 2007;445:394–8. Souphron J, Waddell MB, Paydar A, Tokgöz-Gromley Z, Roussel MF, Schulman BA. Structural dissection of a gating mechanism preventing misactivation of ubiquitin by NEDD8’s E1. Biochemistry. 2008;47:8961–9. Brownell JE, Sintchak MD, Gavin JM, Liao H, Bruzzese FJ, Bump NJ, et al. Substrate-assisted inhibition of ubiquitin-like protein-activating enzymes: the NEDD8 E1 inhibitor MLN4924 forms a NEDD8-AMP mimetic in situ. Mol Cell. 2010;37:102–11. Lin C-M, Jiang Z, Gao Z, Arancillo M, Burgess K. Small molecules targeting the NEDD8·NAE protein–protein interaction. Chem Sci. 2021;12:1535–43. Cappadocia L, Lima CD. Ubiquitin-like protein conjugation: structures, chemistry, and mechanism. Chem Rev. 2018;118:889–918. Kitahara R, Yamaguchi Y, Sakata E, Kasuya T, Tanaka K, Kato K, et al. Evolutionally conserved intermediates between ubiquitin and NEDD8. J Mol Biol. 2006;363:395–404. Huang DT, Zhuang M, Ayrault O, Schulman BA. Identification of conjugation specificity determinants unmasks vestigial preference for ubiquitin within the NEDD8 E2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008;15:280–7. Zhong H-J, Wang W, Kang T-S, Yan H, Yang Y, Xu L, et al. A Rhodium(III) complex as an inhibitor of neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 8-activating enzyme with in vivo activity against inflammatory bowel disease. J Med Chem. 2017;60:497–503. Agius MP, Ko K, Johnson TK, Phadke S, Soellner MB. Conformation-tunable ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors. Chem Commun. 2022;58:3541–4. Tang CP, Clark O, Ferrarone JR, Campos C, Lalani AS, Chodera JD, et al. GCN2 kinase activation by ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors. Nat Chem Biol. 2022;18:207–15. Lu C, Lu P, Gong L, Zhu L-J, An Y, Wang Y. Rational design and development of novel NAE inhibitors for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Med Chem Res. 2023;32:442–74. Kim H-R, Jarhad DB, Sahu PK, Sung K, An D, Hyun YE, et al. Asymmetric synthesis of Fluoro-MLN4924 as a selective NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) inhibitor. Asian J Org Chem. 2019;8:1641–7. Li Y, Plesescu M, Prakash SR. Synthesis of two isotopically labeled versions of NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) inhibitor. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011;52:1807–10. Li Y, Wang C, Xu T, Pan P, Yu Q, Xu L, et al. Discovery of a small molecule inhibitor of cullin neddylation that triggers ER stress to induce autophagy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11:3567–84. Zhong H-J, Yang H, Chan DS-H, Leung C-H, Wang H-M, Ma D-L. A metal-based inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e49574. Xu GW, Toth JI, da Silva SR, Paiva S-L, Lukkarila JL, Hurren R, et al. Mutations in UBA3 confer resistance to the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 in human leukemic cells. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e93530. Li Y, Niu J-H, Wang Y. Machine learning-based neddylation landscape indicates different prognosis and immune microenvironment in endometrial cancer. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1084523. Tong S, Si Y, Yu H, Zhang L, **e P, Jiang W. MLN4924 (Pevonedistat), a protein neddylation inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and migration of human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2017;7:5599. Ho IL, Kuo K-L, Liu S-H, Chang H-C, Hsieh J-T, Wu J-T, et al. MLN4924 synergistically enhances cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity via JNK and Bcl-xL pathways in human urothelial carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16948. Chen P, Hu T, Liang Y, Jiang Y, Pan Y, Li C, et al. Synergistic inhibition of autophagy and neddylation pathways as a novel therapeutic approach for targeting liver cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:9002–17. Sun Y, Baechler SA, Zhang X, Kumar S, Factor VM, Arakawa Y, et al. Targeting neddylation sensitizes colorectal cancer to topoisomerase I inhibitors by inactivating the DCAF13-CRL4 ubiquitin ligase complex. Nat Commun. 2023;14:3762. Hong X, Li S, Li W, **e M, Wei Z, Guo H, et al. Disruption of protein neddylation with MLN4924 attenuates paclitaxel-induced apoptosis and microtubule polymerization in ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508:986–90. Brandt B, Németh M, Berta G, Szünstein M, Heffer M, Rauch TA, et al. A promising way to overcome temozolomide resistance through inhibition of protein neddylation in glioblastoma cell lines. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:7929. Li J-A, Rong Y, Mao W, Zhang L, Kuang T, Lou W. Gene expression profiling reveals the genomic changes caused by MLN4924 and the sensitizing effects of NAPEPLD knockdown in pancreatic cancer. Cell Cycle. 2022;21:152–71. Zhang H, He P, Zhou Q, Lu Y, Lu B. The potential oncogenic and MLN4924-resistant effects of CSN5 on cervical cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:369. Jiang Y, Cheng W, Li L, Zhou L, Liang Y, Zhang W, et al. Effective targeting of the ubiquitin-like modifier NEDD8 for lung adenocarcinoma treatment. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2020;36:349–64. Chen Y, Du M, Yusuying S, Liu W, Tan Y, **e P. Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 (Pevonedistat), inhibits miR-1303 to suppress human breast cancer cell proliferation via targeting p27Kip1. Exp Cell Res. 2020;392:112038. Vanderdys V, Allak A, Guessous F, Benamar M, Read PW, Jameson MJ, et al. The neddylation inhibitor pevonedistat (MLN4924) suppresses and radiosensitizes head and neck squamous carcinoma cells and tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17:368–80. **e P, Yang J-P, Cao Y, Peng L-X, Zheng L-S, Sun R, et al. Promoting tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, NEDD8 serves as a potential theranostic target. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e2834. ** Y, Zhang P, Wang Y, ** B, Zhou J, Zhang J, et al. Neddylation blockade diminishes hepatic metastasis by dampening cancer stem-like cells and angiogenesis in uveal melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:3741–54. Lan H, Tang Z, ** H, Sun Y. Neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 suppresses growth and migration of human gastric cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24218. Traore T, Mihollen M, Garnsey J, Berger A, Manfredi M, Cosmopolous K, et al. Antitumor activity of MLN4924, an investigational inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE), in preclinical models of melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:8594. Aubry A, Yu T, Bremner R. Preclinical studies reveal MLN4924 is a promising new retinoblastoma therapy. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6:2. El-Mesery M, Rosenthal T, Rauert-Wunderlich H, Schreder M, Stühmer T, Leich E, et al. The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 sensitizes a TNFR1+ subgroup of multiple myeloma cells for TNF-induced cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:611. Wang X, Li L, Liang Y, Li C, Zhao H, Ye D, et al. Targeting the neddylation pathway to suppress the growth of prostate cancer cells: therapeutic implication for the men’s cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:974309. Zhang S, Zhang J, Deng Z, Liu H, Mao W, Jiang F, et al. Circadian clock components RORα and Bmal1 mediate the anti-proliferative effect of MLN4924 in osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7:66087–99. Calandrini C, van Hooff SR, Paassen I, Ayyildiz D, Derakhshan S, Dolman MEM, et al. Organoid-based drug screening reveals neddylation as therapeutic target for malignant rhabdoid tumors. Cell Rep. 2021;36:109568. Mackintosh C, García-Domínguez DJ, Ordóñez JL, Ginel-Picardo A, Smith PG, Sacristán MP, et al. WEE1 accumulation and deregulation of S-phase proteins mediate MLN4924 potent inhibitory effect on Ewing sarcoma cells. Oncogene. 2013;32:1441–51. Milhollen MA, Traore T, Adams-Duffy J, Thomas MP, Berger AJ, Dang L, et al. MLN4924, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, is active in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma models: rationale for treatment of NF-κB-dependent lymphoma. Blood. 2010;116:1515–23. Yoshimura C, Muraoka H, Ochiiwa H, Tsuji S, Hashimoto A, Kazuno H, et al. TAS4464, a highly potent and selective inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme, suppresses neddylation and shows antitumor activity in diverse cancer models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019;18:1205–16. Muraoka H, Yoshimura C, Kawabata R, Tsuji S, Hashimoto A, Ochiiwa H, et al. Activity of TAS4464, a novel NEDD8 activating enzyme E1 inhibitor, against multiple myeloma via inactivation of nuclear factor κB pathways. Cancer Sci. 2019;110:3802–10. Ochiiwa H, Ailiken G, Yokoyama M, Yamagata K, Nagano H, Yoshimura C, et al. TAS4464, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, activates both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways via c-Myc-mediated regulation in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene. 2021;40:1217–30. Yamamoto N, Shimizu T, Yonemori K, Kitano S, Kondo S, Iwasa S, et al. A first-in-human, phase 1 study of the NEDD8 activating enzyme E1 inhibitor TAS4464 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig New Drugs. 2021;39:1036–46. Chen JJ, Tsu CA, Gavin JM, Milhollen MA, Bruzzese FJ, Mallender WD, et al. Mechanistic studies of substrate-assisted inhibition of ubiquitin-activating enzyme by adenosine sulfamate analogues. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:40867–77. Lukkarila JL, da Silva SR, Ali M, Shahani VM, Xu GW, Berman J, et al. Identification of NAE inhibitors exhibiting potent activity in leukemia cells: exploring the structural determinants of NAE specificity. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2011;2:577–82. An H, Statsyuk AV. Development of activity-based probes for ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like protein signaling pathways. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:16948–62. Zhang S, Tan J, Lai Z, Li Y, Pang J, **ao J, et al. Effective virtual screening strategy toward covalent ligands: identification of novel NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitors. J Chem Inf Model. 2014;54:1785–97. An H, Statsyuk AV. An inhibitor of ubiquitin conjugation and aggresome formation. Chem Sci. 2015;6:5235–45. **ong C, Zhou L, Tan J, Song S, Bao X, Zhang N, et al. Development of potent NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitors bearing a pyrimidotriazole scaffold. J Med Chem. 2021;64:6161–78. Zhou L-N, **ong C, Cheng Y-J, Song S-S, Bao X-B, Huan X-J, et al. SOMCL-19-133, a novel, selective, and orally available inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme (NAE) for cancer therapy. Neoplasia. 2022;32:100823. Khalife J, Radomska HS, Santhanam R, Huang X, Neviani P, Saultz J, et al. Pharmacological targeting of miR-155 via the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 (Pevonedistat) in FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2015;29:1981–92. Swords RT, Kelly KR, Smith PG, Gansey JJ, Mahalingam D, Padmanabhan S, et al. MLN4924, a novel first in class small molecule inhibitor of the Nedd8 activating enzyme (NAE), has potent activity in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2009;114:1021. Visconte V, Nawrocki ST, Espitia CM, Kelly KR, Possemato A, Beausoleil SA, et al. Comprehensive quantitative proteomic profiling of the pharmacodynamic changes induced by MLN4924 in acute myeloid leukemia cells establishes rationale for its combination with azacitidine. Leukemia. 2016;30:1190–4. Zhang W, Liang Y, Li L, Wang X, Yan Z, Dong C, et al. The Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 (TAK-924/Pevonedistat) induces apoptosis via c-Myc-Noxa axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 2019;52:e12536. Wu M-H, Lee C-Y, Huang T-J, Huang K-Y, Tang C-H, Liu S-H, et al. MLN4924, a protein neddylation inhibitor, suppresses the growth of human chondrosarcoma through inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress-related apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;20:72. Ai T-J, Sun J-Y, Du L-J, Shi C, Li C, Sun X-N, et al. Inhibition of neddylation by MLN4924 improves neointimal hyperplasia and promotes apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells through p53 and p62. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:319–29. Liu X, Jiang Y, Wu J, Zhang W, Liang Y, Jia L, et al. NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, MLN4924 (Pevonedistat) induces NOXA-dependent apoptosis through up-regulation of ATF-4. Biophys Res Commun. 2017;488:1–5. Godbersen JC, Humphries LA, Danilova OV, Kebbekus PE, Brown JR, Eastman A, et al. The Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 Thwarts microenvironment-driven NF-κB activation and induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:1576–89. Bahjat M, de Wilde G, van Dam T, Maas C, Bloedjes T, Bende RJ, et al. The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induces DNA damage in Ph+ leukemia and sensitizes for ABL kinase inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 2019;18:2307–22. Chen Y, Sun L. Inhibition of NEDD8 NEDDylation induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells via p53 signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2022;42:BSR20220994. Milhollen M, Narayanan U, Duffy J, Amidon B, Soucy TA, Berger AJ, et al. MLN4924, a potent and novel small molecule inhibitor of Nedd8 activating enzyme, induces DNA re-replication and apoptosis in cultured human tumor cells. Blood. 2008;112:3621. Lv Y, Li B, Han K, **ao Y, Yu X, Ma Y, et al. The Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 suppresses colon cancer cell growth via triggering autophagy. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;22:617–25. Rellinger EJ, Padmanabhan C, Qiao J, Appert A, Waterson AG, Lindsley CW, et al. ML327 induces apoptosis and sensitizes Ewing sarcoma cells to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;491:463–8. Kuo K-L, Ho IL, Shi C-S, Wu J-T, Lin W-C, Tsai Y-C, et al. MLN4924, a novel protein neddylation inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and migration of human urothelial carcinoma: In vitro and in vivo studies. Cancer Lett. 2015;363:127–36. Gao Q, Yu G-Y, Shi J-Y, Li L-H, Zhang W-J, Wang Z-C, et al. Neddylation pathway is up-regulated in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and serves as a potential therapeutic target. Oncotarget. 2014;5:7820–32. Lin JJ, Milhollen MA, Smith PG, Narayanan U, Dutta A. NEDD8-targeting drug MLN4924 Elicits DNA rereplication by stabilizing Cdt1 in S phase, triggering checkpoint activation, apoptosis, and senescence in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010;70:10310–20. Read MA, Brownell JE, Gladysheva TB, Hottelet M, Parent LA, Coggins MB, et al. Nedd8 modification of Cul-1 activates SCFβTrCP-dependent ubiquitination of IκBα. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:2326–33. Zhou W, Xu J, Li H, Xu M, Chen ZJ, Wei W, et al. Neddylation E2 UBE2F promotes the survival of lung cancer cells by activating CRL5 to degrade NOXA via the K11 linkage. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:1104–16. Zhao L, Yue P, Lonial S, Khuri FR, Sun S-Y. The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, MLN4924, cooperates with TRAIL to augment apoptosis through facilitating c-FLIP degradation in head and neck cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:2415–25. Zhou Q, Li H, Li Y, Tan M, Fan S, Cao C, et al. Inhibiting neddylation modification alters mitochondrial morphology and reprograms energy metabolism in cancer cells. JCI Insight. 2019;4:e121582. Yu R, Liu T, ** S-B, Ning C, Lendahl U, Nistér M, et al. MIEF1/2 function as adaptors to recruit Drp1 to mitochondria and regulate the association of Drp1 with Mff. Sci Rep. 2017;7:880. Fonseca TB, Sánchez-Guerrero Á, Milosevic I, Raimundo N. Mitochondrial fission requires DRP1 but not dynamins. Nature. 2019;570:E34-42. Yu R, Liu T, Ning C, Tan F, ** S-B, Lendahl U, et al. The phosphorylation status of Ser-637 in dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) does not determine Drp1 recruitment to mitochondria. J Bio Chem. 2019;294:17262–77. Wan J, Zhu J, Li G, Zhang Z. Radiosensitization of human colorectal cancer cells by MLN4924: an inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2015;15:527–34. Wei D, Li H, Yu J, Sebolt JT, Zhao L, Lawrence TS, et al. Radiosensitization of human pancreatic cancer cells by MLN4924, an investigational NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2012;72:282–93. Wang X, Zhang W, Yan Z, Liang Y, Li L, Yu X, et al. Radiosensitization by the investigational NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 (pevonedistat) in hormone-resistant prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7:38380–91. Ding Z, Knipp GT, van Rijn RM, Chester JA, Watts VJ. The CUL3/neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 reduces ethanol-induced locomotor sensitization and inflammatory pain allodynia in mice. Behav Brain Res. 2021;399:113051. Yang D, Tan M, Wang G, Sun Y. The p21-dependent radiosensitization of human breast cancer cells by MLN4924, an investigational inhibitor of NEDD8 activating enzyme. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e34079. Wei D, Morgan MA, Sun Y. Radiosensitization of cancer cells by inactivation of cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases. Transl Oncol. 2012;5:305–12. Begg AC, Stewart FA, Vens C. Strategies to improve radiotherapy with targeted drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:239–53. Godbersen C, Paiva C, Berger AJ, Brown JR, Danilov AV. Targeting Nedd8 activating enzyme induces DNA damage and cell cycle arrest and sensitizes chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B-cells to alkylating agents. Blood. 2014;124:4690. Zhang Q, Hou D, Luo Z, Chen P, Lv B, Wu L, et al. The novel protective role of P27 in MLN4924-treated gastric cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1867. Blank JL, Liu XJ, Cosmopoulos K, Bouck DC, Garcia K, Bernard H, et al. Novel DNA damage checkpoints mediating cell death induced by the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924. Cancer Res. 2013;73:225–34. Wollert T. Autophagy. Curr Biol. 2019;29:R671–7. Yim WW-Y, Mizushima N. Lysosome biology in autophagy. Cell Discov. 2020;6:6. Towers CG, Thorburn A. Therapeutic targeting of autophagy. EBioMedicine. 2016;14:15–23. Levy JMM, Towers CG, Thorburn A. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:528–42. Morel E, Mehrpour M, Botti J, Dupont N, Hamaï A, Nascimbeni AC, et al. Autophagy: a druggable process. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017;57:375–98. Santana-Codina N, Mancias JD, Kimmelman AC. The role of autophagy in cancer. Annu Rev Cancer Biol. 2017;1:19–39. Serrano-Maciá M, Simón J, González-Rellan MJ, Azkargorta M, Goikoetxea-Usandizaga N, Lopitz-Otsoa F, et al. Neddylation inhibition ameliorates steatosis in NAFLD by boosting hepatic fatty acid oxidation via the DEPTOR-mTOR axis. Mol Metab. 2021;53:101275. Zhao Y, **ong X, Jia L, Sun Y. Targeting Cullin-RING ligases by MLN4924 induces autophagy via modulating the HIF1-REDD1-TSC1-mTORC1-DEPTOR axis. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e386. Yang D, Zhao Y, Liu J, Sun Y, Jia L. Protective autophagy induced by RBX1/ROC1 knockdown or CRL inactivation via modulating the DEPTOR-MTOR axis. Autophagy. 2012;8:1856–8. Zhao Y, Sun Y. Targeting the mTOR-DEPTOR pathway by CRL E3 ubiquitin ligases: therapeutic application. Neoplasia. 2012;14:360–7. Walton CC, Begelman D, Nguyen W, Andersen JK. Senescence as an amyloid cascade: the amyloid senescence hypothesis. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:129. Lozano-Torres B, Estepa-Fernández A, Rovira M, Orzáez M, Serrano M, Martínez-Máñez R, et al. The chemistry of senescence. Nat Rev Chem. 2019;3:426–41. Varela-Eirín M, Demaria M. Cellular senescence. Curr Biol. 2022;32:R448–52. Hernandez-Segura A, Nehme J, Demaria M. Hallmarks of cellular senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28:436–53. Ruiz de Galarreta M, Lujambio A. DNA sensing in senescence. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19:1008–9. Jia L, Li H, Sun Y. Induction of p21-dependent senescence by an NAE inhibitor, MLN4924, as a mechanism of growth suppression. Neoplasia. 2011;13:561–9. Wang Y, Luo Z, Pan Y, Wang W, Zhou X, Jeong LS, et al. Targeting protein neddylation with an NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induced apoptosis or senescence in human lymphoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16:420–9. Martínez-Zamudio RI, Robinson L, Roux P-F, Bischof O. SnapShot: cellular senescence in pathophysiology. Cell. 2017;170:1044. Zhang Y, Shi C-C, Zhang H-P, Li G-Q, Li S-S. MLN4924 suppresses neddylation and induces cell cycle arrest, senescence, and apoptosis in human osteosarcoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7:45263–74. Wood EA, Lu Z, Jia S, Assumpção ALFV, Van Hesteren MA, Huelsmeyer MK, et al. Pevonedistat targeted therapy inhibits canine melanoma cell growth through induction of DNA re-replication and senescence. Vet Comp Oncol. 2020;18:269–80. Harjes U. Controlling nerves. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:708. Morse MA, Sun W, Kim R, He AR, Abada PB, Mynderse M, et al. The role of angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:912–20. Griffioen AW, Dudley AC. The rising impact of angiogenesis research. Angiogenesis. 2022;25:435–7. Strzyz P. Migrasomes promote angiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24:84. Elfiky AA, Rosenberg JE. Targeting angiogenesis in bladder cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2009;11:244–9. Yetkin-Arik B, Kastelein AW, Klaassen I, Jansen CHJR, Latul YP, Vittori M, et al. Angiogenesis in gynecological cancers and the options for anti-angiogenesis therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1875:188446. Rajabi M, Mousa SA. The role of angiogenesis in cancer treatment. Biomedicines. 2017;5:34. Mao W, Zhang L, Rong Y, Kuang T, Wang D, Xu X, et al. NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 inhibits both the tumor stroma and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer via Gli1 and REDD1. Dig Dis Sci. 2023;68:1351–63. Yao WT, Wu JF, Yu GY, Wang R, Wang K, Li LH, et al. Suppression of tumor angiogenesis by targeting the protein neddylation pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1059. Watson EC, Grant ZL, Coultas L. Endothelial cell apoptosis in angiogenesis and vessel regression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74:4387–403. Folkman J. Angiogenesis and apoptosis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2003;13:159–67. Kollmann K, Heller G, Schneckenleithner C, Warsch W, Scheicher R, Ott RG, et al. A kinase-independent function of CDK6 links the cell cycle to tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:359–60. Bejarano L, Jordāo MJC, Joyce JA. Therapeutic targeting of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:933–59. Wu T, Dai Y. Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 2017;387:61–8. Junttila MR, de Sauvage FJ. Influence of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response. Nature. 2013;501:346–54. Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 2013;19:1423–37. Anderson NM, Simon MC. The tumor microenvironment. Curr Biol. 2020;30:R921–5. Zhou L, Jiang Y, Luo Q, Li L, Jia L. Neddylation: a novel modulator of the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:77. Chang F-M, Reyna SM, Granados JC, Wei S-J, Innis-Whitehouse W, Maffi SK, et al. Inhibition of neddylation represses lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine production in macrophage cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:35756–67. ** H, Liao L, Park Y, Liu Y-C. Neddylation pathway regulates T-cell function by targeting an adaptor protein Shc and a protein kinase Erk signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:624–9. Cheng Q, Liu J, Pei Y, Zhang Y, Zhou D, Pan W, et al. Neddylation contributes to CD4+ T cell-mediated protective immunity against blood-stage Plasmodium infection. PLOS Pathog. 2018;14: e1007440. Cheng M, Hu S, Wang Z, Pei Y, Fan R, Liu X, et al. Inhibition of neddylation regulates dendritic cell functions via Deptor accumulation driven mTOR inactivation. Oncotarget. 2016;7:35643–54. Mathewson N, Toubai T, Kapeles S, Sun Y, Oravecz-Wilson K, Tamaki H, et al. Neddylation plays an important role in the regulation of murine and human dendritic cell function. Blood. 2013;122:2062–73. Handa H, Cheong J-W, Onishi Y, Iida H, Kobayashi Y, Kim H-J, et al. Pevonedistat in East Asian patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes: a phase 1/1b study to evaluate safety, pharmacokinetics and activity as a single agent and in combination with azacitidine. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:56. Ades L, Watts JM, Radinoff A, Arnan M, Cerrano M, Font Lopez P, et al. Phase II study of pevonedistat (P) + azacitidine (A) versus A in patients (pts) with higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)/chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), or low-blast acute myelogenous leukemia (LB AML) (NCT02610777). J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:7506. Zhou X, Mould DR, Zhao D, Sekeres MA, Adès L, Swords RT, et al. Model-based analysis to support dose selection of pevonedistat (PEV) combined with azacitidine (AZA) in patients (pts) with higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)/chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:7042. Watts J, Adès L, Radinoff A, Sangerman MA, Cerrano M, Lopez PF, et al. MDS-336: phase 2 study of pevonedistat + azacitidine versus azacitidine in patients with higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)/chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) or low-blast acute myelogenous leukemia (LB-AML) (NCT02610777): subset analysis in higher-risk MDS. Cl Lymph Myelom Leuk. 2020;20:S323–4. Zeidner JF, Mazerolle F, Bell JA, Cain LE, Faller DV, Dalal M, et al. Randomized phase 2 trial of pevonedistat plus azacitidine versus azacitidine in higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes/chronic myelomonocytic leukemia or low-blast acute myeloid leukemia: exploratory analysis of patient-reported outcomes. Blood. 2020;136:39–40. Smith BN, Cojocari D, Purkal JJ, Arrate M, Ramsey HE, Leverson JD, et al. Pevonedistat, a Nedd-8 activating enzyme inhibitor, upregulates NOXA to increase effectiveness of azacitidine and venetoclax in preclinical models of acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 2019;134:1380. Cojocari D, Smith BN, Purkal JJ, Arrate MP, Huska JD, **ao Y, et al. Pevonedistat and azacitidine upregulate NOXA (PMAIP1) to increase sensitivity to venetoclax in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2021;107:825–35. Swords RT, Savona MR, Maris MB, Erba HP, Berdeja JG, Foran JM, et al. Pevonedistat (MLN4924), an investigational, first-in-class NAE inhibitor, in combination with azacitidine in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) considered unfit for conventional chemotherapy: updated results from the phase 1 C15009 trial. Blood. 2014;124:2313. Bauer TM, Harvey RD, Lee CB, Aggarwal C, Cohen RB, Sedarati F, et al. Investigational NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor pevonedistat (Pev) plus chemotherapy in patients (Pts) with solid tumors (Phase 1b study): Antitumor activity of pev plus carboplatin (Carbo)/paclitaxel (Pac). J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:2580. Lockhart AC, Bauer TM, Aggarwal C, Lee CB, Harvey RD, Cohen RB, et al. Phase Ib study of pevonedistat, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, in combination with docetaxel, carboplatin and paclitaxel, or gemcitabine, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig New Drugs. 2019;37:87–97. Zhou X, Richardson DL, Dowlati A, Goel S, Sahebjam S, Strauss J, et al. Effect of pevonedistat, an investigational NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, on the QTc interval in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2023;12:257–66. Zhou X, Vaishampayan U, Mahalingam D, Harvey RD, Chung KY, Sedarati F, et al. Phase 1 study to evaluate the effects of rifampin on pharmacokinetics of pevonedistat, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig New Drugs. 2022;40:1042–50. Foster J, Reid JM, Minard CG, Isikwei E, Liu X, Berg SL, et al. Phase 1 study of pevonedistat (MLN4924) a NEDD8 activating enzyme inhibitor, in combination with temozolomide (TMZ) and irinotecan (IRN) in pediatric patients with recurrent or refractory solid tumors (ADVL1615). J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:10019. Sekeres MA, Fram RJ, Hua Z, Ades L. Phase 3 study of first line pevonedistat (PEV) + azacitidine (AZA) versus single-agent AZA in patients with higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (HR MDS), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) or low-blast acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:TPS7077. Swords RT, Erba HP, DeAngelo DJ, Bixby DL, Altman JK, Maris M, et al. Pevonedistat (MLN4924), a first-in-class NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndromes: a phase 1 study. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:534–43. Paraiso KHT, **ang Y, Rebecca VW, Abel EV, Chen YA, Munko AC et al. PTEN loss confers BRAF inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells through the suppression of BIM expression. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2750–60. Du M, Peng Z, Gai W, Liu F, Liu W, Chen Y, et al. The absence of PTEN in breast cancer is a driver of MLN4924 resistance. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:667435. Zhou X, Tan M, Nyati MK, Zhao Y, Wang G, Sun Y. Blockage of neddylation modification stimulates tumor sphere formation in vitro and stem cell differentiation and wound healing in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E2935–44. Mao H, Tang Z, Li H, Sun B, Tan M, Fan S, et al. Neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 suppresses cilia formation by modulating AKT1. Protein Cell. 2019;10:726–44. Keller KE, Tan IS, Lee YS. SAICAR stimulates pyruvate kinase isoform M2 and promotes cancer cell survival in glucose-limited conditions. Science. 2012;338:1069–72. Zhou Q, Sun Y. MLN4924: additional activities beyond neddylation inhibition. Mol Cell Oncol. 2019;6:e1618174. Hollebecque A, Argiles G, Andre T, Cervantes A, Leger C, Valette A, et al. A phase I dose-escalation of trifluridine/tipiracil in combination with oxaliplatin in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3626. Kostine M, Mauric E, Tison A, Barnetche T, Barre A, Nikolski M, et al. Baseline co-medications may alter the anti-tumoural effect of checkpoint inhibitors as well as the risk of immune-related adverse events. Eur J Cancer. 2021;157:474–84. He S, Dong G, Wu S, Fang K, Miao Z, Wang W, et al. Small molecules simultaneously inhibiting p53-murine double minute 2 (MDM2) interaction and histone deacetylases (HDACs): discovery of novel multitargeting antitumor agents. J Med Chem. 2018;61:7245–60. Da C, Zhang D, Stashko M, Vasileiadi E, Parker RE, Minson KA, et al. Data-driven construction of antitumor agents with controlled polypharmacology. J Am Chem Soc. 2019;141:15700–9. Siu L, Brody J, Gupta S, Marabelle A, Jimeno A, Munster P, et al. Safety and clinical activity of intratumoral MEDI9197 alone and in combination with durvalumab and/or palliative radiation therapy in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e001095. Dogan I, Iribas A, Ekenel M, Basaran M. Efficacy of vincristine, irinotecan, and temozolomide (VIT) combination in adult patients with metastatic Ewing sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:e23510. Nikanjam M, Liu S, Kurzrock R. Dosing de novo two-drug combinations based on 32,894 patients in phase I–III clinical trials. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:2563. Li K, Liu W, Zhao Q, Wu C, Fan C, Lai H, et al. Combination of tanshinone IIA and doxorubicin possesses synergism and attenuation effects on doxorubicin in the treatment of breast cancer. Phytother Res. 2019;33:1658–69. Salaroglio IC, Belisario DC, Bironzo P, Ananthanarayanan P, Ricci L, Digiovanni S, et al. SKP2 drives the sensitivity to neddylation inhibitors and cisplatin in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41:75. Megger DA, Abou-Eid S, Zülch B, Sitek B. Systematic analysis of synergistic proteome modulations in a drug combination of cisplatin and MLN4924. Mol Omics. 2018;14:450–7. Nawrocki ST, Kelly KR, Smith PG, Keaton M, Carraway H, Sekeres MA, et al. The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 disrupts nucleotide metabolism and augments the efficacy of cytarabine. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:439–47. Czuczman NM, Barth MJ, Dwar R, Mavis C, Klener P, Czuczman MS, et al. Evaluation of the anti-tumor activity of MLN4924, a novel NEDD8 activating enzyme inhibitor, in pre-clinical models of rituximab chemotherapy-sensitive or -resistant B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2012;120:2761. Zhou L, Chen S, Zhang Y, Kmieciak M, Leng Y, Li L, et al. The NAE inhibitor pevonedistat interacts with the HDAC inhibitor belinostat to target AML cells by disrupting the DDR. Blood. 2016;127:2219–30. Bhalla KN, Fiskus W. NEDD8 and HDACs: promising cotargets in AML. Blood. 2016;127:2168–70. **ong S, Huang W, Liu X, Chen Q, Ding Y, Huang H, et al. Celecoxib synergistically enhances MLN4924-induced cytotoxicity and EMT inhibition Via AKT and ERK pathways in human urothelial carcinoma. Cell Transplant. 2022;31:09636897221077921. Li J, Song C, Rong Y, Kuang T, Wang D, Xu X, et al. Chk1 inhibitor SCH 900776 enhances the antitumor activity of MLN4924 on pancreatic cancer. Cell Cycle. 2018;17:191–9. Knorr KLB, Schneider PA, Meng XW, Dai H, Smith BD, Hess AD, et al. MLN4924 induces Noxa upregulation in acute myelogenous leukemia and synergizes with Bcl-2 inhibitors. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22:2133–42. Sumi H, Inazuka M, Morimoto M, Hibino R, Hashimoto K, Ishikawa T, et al. An inhibitor of apoptosis protein antagonist T-3256336 potentiates the antitumor efficacy of the Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor pevonedistat (TAK-924/MLN4924). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;480:380–6. Cooper J, Xu Q, Zhou L, Pavlovic M, Ojeda V, Moulick K, et al. Combined inhibition of NEDD8-activating enzyme and mTOR suppresses NF2 loss-driven tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16:1693–704. Ishikawa Y, Nakayama K, Morimoto M, Mizutani A, Nakayama A, Toyoshima K, et al. Synergistic anti-AML effects of the LSD1 inhibitor T-3775440 and the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor pevonedistat via transdifferentiation and DNA rereplication. Oncogenesis. 2017;6:e377. Zhang S, You X, Xu T, Chen Q, Li H, Dou L, et al. PD-L1 induction via the MEK-JNK-AP1 axis by a neddylation inhibitor promotes cancer-associated immunosuppression. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:844. Liang T, Lu L, Song X, Qi J, Wang J. Combination of microtubule targeting agents with other antineoplastics for cancer treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022;1877:188777. Liu T, Wan Y, **ao Y, **a C, Duan G. Dual-target inhibitors based on HDACs: novel antitumor agents for cancer therapy. J Med Chem. 2020;63:8977–9002. Arnst KE, Banerjee S, Chen H, Deng S, Hwang D-J, Li W, et al. Current advances of tubulin inhibitors as dual acting small molecules for cancer therapy. Med Res Rev. 2019;39:1398–426. Fu D-J, Song J, Zhu T, Pang X-J, Wang S-H, Zhang Y-B, et al. Discovery of novel tertiary amide derivatives as NEDDylation pathway activators to inhibit the tumor progression in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;192:112153. Song J, Liu Y, Yuan X-Y, Liu W-B, Li Y-R, Yu G-X, et al. Discovery of 1,2,4-triazine dithiocarbamate derivatives as NEDDylation agonists to inhibit gastric cancers. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;225:113801. Liang Q, Liu M, Li J, Tong R, Hu Y, Bai L, et al. NAE modulators: a potential therapy for gastric carcinoma. Eur J Med Chem. 2022;231:114156. Li X, Pham V, Tippin M, Fu D, Rendon R, Song L, et al. Flavokawain B targets protein neddylation for enhancing the anti-prostate cancer effect of Bortezomib via Skp2 degradation. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17:25. Pham V, Rendon R, Le VX, Tippin M, Fu D-J, Le TH, et al. Gartanin is a novel NEDDylation inhibitor for induction of Skp2 degradation, FBXW2 expression, and autophagy. Mol Carcinog. 2020;59:193–201. Leung C-H, Chan DS-H, Yang H, Abagyan R, Lee SM-Y, Zhu G-Y, et al. A natural product-like inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme. Chem Commun. 2011;47:2511–3. Zhong H-J, Pui-Yan Ma V, Cheng Z, Shiu-Hin Chan D, He H-Z, Leung K-H, et al. Discovery of a natural product inhibitor targeting protein neddylation by structure-based virtual screening. Biochimie. 2012;94:2457–60. Ni S, Chen X, Yu Q, Xu Y, Hu Z, Zhang J, et al. Discovery of candesartan cilexetic as a novel neddylation inhibitor for suppressing tumor growth. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;185:111848. Zhong H-J, Liu L-J, Chan DS-H, Wang H-M, Chan PWH, Ma D-L, et al. Structure-based repurposing of FDA-approved drugs as inhibitors of NEDD8-activating enzyme. Biochimie. 2014;102:211–5. Ma H, Zhuang C, Xu X, Li J, Wang J, Min X, et al. Discovery of benzothiazole derivatives as novel non-sulfamide NEDD8 activating enzyme inhibitors by target-based virtual screening. Eur J Med Chem. 2017;133:174–83. Lu P, Liu X, Yuan X, He M, Wang Y, Zhang Q, et al. Discovery of a novel NEDD8 activating enzyme inhibitor with piperidin-4-amine scaffold by structure-based virtual screening. ACS Chem Biol. 2016;11:1901–7. Lu P, Guo Y, Zhu L, **a Y, Zhong Y, Wang Y. A novel NAE/UAE dual inhibitor LP0040 blocks neddylation and ubiquitination leading to growth inhibition and apoptosis of cancer cells. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;154:294–304. Fu D-J, Cui X-X, Zhu T, Zhang Y-B, Hu Y-Y, Zhang L-R, et al. Discovery of novel indole derivatives that inhibit NEDDylation and MAPK pathways against gastric cancer MGC803 cells. Bioorg Chem. 2021;107:104634. Hao R, Song Y, Li R, Wu Y, Yang X, Li X, et al. MLN4924 protects against interleukin-17A-induced pulmonary inflammation by disrupting ACT1-mediated signaling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019;316:L1070–80. Yu H, Luo H, Chang L, Wang S, Geng X, Kang L, et al. The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 reduces ischemic brain injury in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022;119:e2111896119. Zhang J, Cui J, Zhao F, Yang L, Xu X, Shi Y, et al. Cardioprotective effect of MLN4924 on ameliorating autophagic flux impairment in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by Sirt1. Redox Biol. 2021;46:102114. Andérica-Romero AC, Hernández-Damián J, Vázquez-Cervantes GI, Torres I, Pedraza-Chaverri J. The MLN4924 inhibitor exerts a neuroprotective effect against oxidative stress injury via Nrf2 protein accumulation. Redox Biol. 2016;8:341–7. **e L, Ji X, Tu Y, Wang K, Zhu L, Zeng X, et al. MLN4924 inhibits hedgehog signaling pathway and activates autophagy to alleviate mouse laser-induced choroidal neovascularization lesion. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110654. Not applicable. This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [Grant No. 2022-JYB-XJSJJ025 to Dong-Jun Fu]. This work was also funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation [Grant No. 2020M670239 to Dong-Jun Fu]. D-JF collected the references, designed the outline, prepared all figures and wrote the manuscript. TW offered important guidance of manuscript reviewing and editing. D-JF and TW approved the final manuscript. Not applicable. Not applicable. The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data. Fu, DJ., Wang, T. Targeting NEDD8-activating enzyme for cancer therapy: developments, clinical trials, challenges and future research directions.
J Hematol Oncol 16, 87 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-023-01485-7 Received: Accepted: Published: DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-023-01485-7Availability of data and materials
Abbreviations
References
Acknowledgements
Funding
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Competing interests
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keywords