Abstract
Background
Research shows that nano-bioceramics can modulate the differentiation of dental stem cells. The novel ready-to-use calcium-silicate-based root-canal sealer iRoot SP is widely used in root filling. Accordingly, the aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of iRoot SP on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in human stem cells from the apical papilla (hSCAPs).
Methods
hSCAPs were isolated and characterized in vitro, then cultured with various concentrations of iRoot SP extract. Cell proliferation was assessed by CCK-8 assay, and scratch-wound-healing assays were performed to evaluate cell-migration capacity. hSCAPs were then cultured in osteogenic medium supplemented with iRoot SP extracts. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity assay was used to evaluate ALP enzyme levels. Alizarin red staining and cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) assays were performed to assess calcified-nodule formation and matrix-calcium accumulation of hSCAPs. The mRNA and protein expression levels of the osteogenic markers OCN, OSX, Runx2, and DSPP were determined by qRT-PCR and Western blotting. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and LSD-t tests.
Results
iRoot SP at low concentrations (2, 0.2, and 0.02 mg/mL) is nontoxic to hSCAPs. iRoot SP at concentrations of 0.02 and 0.2 mg/mL significantly increases cell-migration capacity. In terms of osteogenic differentiation, 0.2 mg/mL iRoot SP promotes intracellular ALP activity and the formation of mineralized nodules. Moreover, the expression of osteogenic markers at the mRNA and protein levels are upregulated by iRoot SP.
Conclusion
iRoot SP is an effective filling material for periapical bone regeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Pulpal and periapical diseases are common endodontic conditions, and root canal therapy (RCT) is currently the most effective treatment for such conditions [1]. However, previous studies have revealed treatment-failure rates of 4–15%, even after refined RCT treatment, with such failures evolving into refractory apical periodontitis characterized by persistent inflammatory response and progressive destruction of periapical bone, eventually resulting in tooth loss [2, 3]. Accordingly, increasing numbers of studies are being focused on develo** new clinical strategies for the repair and/or regeneration of damaged endodontic tissue.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are often used to repair inflammatory tissue damage owing to their multi-differentiation ability and anti-inflammatory properties [4,
Western blot
Cells cultured under the same osteogenic-induction conditions were lysed in RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime) after 3 and 7 days. Protein concentrations were measured with BCA protein assay reagent. Equal amounts of protein for each sample were separated using 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and then transferred onto poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes. The membranes were then blocked with 5% nonfat milk and incubated with primary antibodies for OCN, OSX Runx2 (Affinity Biosciences, Cincinnati, OH, USA), and DSPP (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) at 4 °C overnight and then incubated with horseradish-peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (Proteintech, Wuhan, Hubei, China) for 1 h at room temperature. Immunoreactive bands were visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence kit (Thermo Scientific) and the grayscale values were determined with ImageJ software.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 21.0 software. All experiments were conducted in triplicate, and the data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Group comparisons were performed via one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by least significant difference testing. Differences were considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
Results
Characterization of hSCAPs
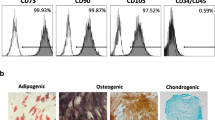
Primary hSCAPs were isolated from the apical papilla tissues by enzyme digestion and presented typical cell colonies at approximately 7 days. The 3rd passage hSCAPs were observed to be spindle-shaped (Fig. 1A). Upon culturing in osteogenic-differentiation medium for 3 weeks, hSCAPs form mineral nodules, which are positively stained with Alizarin Red S (Fig. 1B). Flow cytometry indicated that the cells express MSC surface markers, including CD146 and CD24, but not the hematopoietic marker CD45 (Fig. 1C). Immunofluorescence staining of the hSCAPs revealed that the cells positively express CD24, STRO-1, and vimentin, but not keratin (Fig. 1D). Thus, our obtained cells were confirmed to be MSCs.
Isolation, culture, and characterization of human stem cells of the apical papilla (hSCAPs). A Primary cultured hSCAPs at 7 days (P0). The 3rd passage hSCAPs exhibit spindle-like morphology (P3). B Osteogenic differentiation of hSCAPs: hSCAPs were cultured with or without osteogenic-induction factors for 3 weeks, the mineralized nodules formed are positive to Alizarin red staining. C Flow cytometry analysis of hSCAP surface markers. hSCAPs test positive the for mesenchymal stem cell markers CD24 and CD146 and the negative expression hematopoietic stem cell marker CD45. D Characterization of hSCAPs by immunofluorescence staining: positive for vimentin, STRO-1, and CD24, but not for keratin
Effects of iRoot SP on the cell viability of hSCAPs
CCK-8 assays were used to measure the viability of hSCAPs cultured in media with different concentrations of iRoot SP. The variation in cell viability between all the groups at 1 day is not significantly different (P > 0.05). However, the proliferation of hSCAPs measured at 3 and 5 days is significantly higher for the group exposed to iRoot SP at 0.2 mg/mL as compared with those for the other groups (P < 0.05). Furthermore, there is no significant difference between the 2 mg/mL, 0.02 mg/mL, and control groups in terms of cell viability. However, higher concentrations of iRoot SP (5 and 10 mg/mL) clearly inhibit cell proliferation over the period studied (P < 0.05) (Fig. 2A).
Cell proliferation and migration capacity of hSCAPs cultured with iRoot SP extract at various concentrations. A hSCAP proliferation was measured by CCK-8 assay. The results show that 0.2 mg/mL extract improves the proliferation level at 3 and 5 days compared with the control, and that there is no significant difference between the 0.02 mg/mL, 2 mg/mL, and control groups. B Cell migration processes as observed under a microscope. C Wound-closure percentages of hSCAPs cultured in iRoot SP at 12 h. Scratch-wound-healing assays show that the migration capacity of hSCAPs cultured in 0.02 and 0.2 mg/mL iRoot SP extract were significantly increased compared with the control group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.005. Error bars: mean ± standard deviation
hSCAPs migration
The effect of iRoot SP on the migration of hSCAPs was evaluated by wound-healing assays. The wound closures for hSCAPs cultured with 0.02 and 0.2 mg/mL iRoot SP extract are significantly increased at 12 h as compared with that of the control group (P < 0.05). However, hSCAPs incubated in 2 mg/mL iRoot SP extract exhibit no significant difference in cell migration compared with the control group (P > 0.05) (Fig. 2B, C). Thus, the results show that iRoot SP is biocompatible and has beneficial effects on hSCAPs at appropriate concentrations.
Effects of iRoot SP on the osteogenic differentiation in hSCAPs
As indicated by the results of ALP activity, at 0.2 mg/mL, iRoot SP extract clearly upregulates ALP activity as compared with that in the control group (P < 0.05, Fig. 3A) at different time points. Additionally, there are no statistical differences between the 2 mg/mL, 0.02 mg/mL, and control groups over the period studied. Furthermore, Alizarin red staining and CPC assays demonstrated that hSCAPs exposed to iRoot SP extract at 0.2 mg/mL generate more mineralized nodules and present higher calcium contents compared with the control group after 14 and 21 days (P < 0.01) (Fig. 3B, C), but no significant effects are observed at 3 and 7 days. Therefore, 0.2 mg/mL was selected to be the optimal concentration to measure the differentiation capacity of SCAPs in the following experiments.
Effect of iRoot SP on ALP and mineralization for hSCAPs. A ALP activity was assessed on days 3, 7, and 14. There is no significant difference in the ALP levels between the 2 mg/mL, 0.02 mg/mL, and control groups. The 0.2 mg/mL group presents the highest ALP activity. B Alizarin red staining shows that 0.2 mg/mL iRoot-SP-treated cells generate more mineralized nodules than those subjected to the control treatment. C The calcium contents of the iRoot-SP-treated cells are significantly higher than those of the control cells (as determined by CPC assay). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.005. Error bars: mean ± standard deviation
To further determine the effect of iRoot SP on the osteogenic differentiation of SCAPs, cells were treated with 0.2 mg/mL iRoot SP. The qRT-PCR results show that the mRNA expression levels for the iRoot SP group are significantly elevated compared with the control group at day 7 (P < 0.05). However, no significant changes in the expression of Runx2 and OCN are detected at day 3 (Fig. 4A). Meanwhile, the relative protein expression levels of the osteogenic markers are consistent with those of the genes (P < 0.01) (Fig. 4B, Additional file 1: Figure S1 and Fig. 4C). Collectively, these data indicate that 0.2 mg/mL iRoot SP enhances the osteogenic differentiation of hSCAPs.
Effects of iRoot SP on osteogenic differentiation in hSCAPs. A Relative expression levels of the osteogenic genes OCN, OSX, Runx2, and DSPP in hSCAPs normalized to the housekee** gene GAPDH. B Western blot results showing the upregulated protein levels of osteogenic markers in the 0.2 mg/mL iRoot SP group. GAPDH was used as a loading control. C Grayscale analyses of the results shown in (B). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.005. Error bars: mean ± standard deviation
Discussion
MSCs have wide application prospects in tissue-regenerative medicine. The hSCAPs used in this study are early MSCs present in develo** apical dental papilla tissues that exhibit great potential for tissue regeneration owing to their proliferation activity and pluripotency [6, 9]. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that, compared with other odontogenic stem cells under the same conditions, hSCAPs present a higher mineralized-tissue-formation rate and thus show promise for the treatment of bone defects [22].
Numerous biochemical and biophysical factors guide stem-cell regeneration in different ways [7]. Nano-bioceramic root canal filling materials directly contact periapical tissue, isolating inflammatory environments and inhibiting microbial invasion, thus promoting the healing of damaged apical tissues [23]. Accordingly, the treatment of periapical diseases calls for root-canal-filling materials that provide appropriate microenvironments conducive to effective root-canal disinfection and the proliferation and differentiation of stem cells [19, 24].
iRoot SP is an injectable, pre-mixed bioceramic root-canal sealer with excellent sealing properties and antimicrobial activity [21]. Most studies on iRoot SP have focused on its feasibility as a root-canal-repair material. For instance, Zaki et al. found that the hydroxyapatite generated by iRoot SP can be used as a scaffold that accepts osteoblasts, and that bone tissue treated with iRoot SP reaches a state of almost complete healing within two months [25]. Thus, stem-cell therapies based on a combination of nanomaterials and stem-cell biology show promise for tissue repair in the clinic [26]. iRoot SP may be used as a potential regulator of hSCAP activity and osteogenic differentiation to improve the extracellular environment so as to better promote the regeneration and healing of periapical bone defects. Accordingly, on the basis of previous research results and preliminary data [27, 28], different concentrations of iRoot SP extract were selected for investigation in the present study.
Biomaterials for tissue engineering should exhibit excellent cytocompatibility and support cell growth and proliferation because cytotoxic biomaterials can cause cellular degeneration and delay wound healing [29]. In this study, the effects of iRoot SP on the proliferation of hSCAPs on the 1st, 3rd, and 5th day after treatment were evaluated by CCK-8 assays. The results showed that there are differences in the proliferation of hSCAPs treated with different concentrations of the extract. Lower concentrations of iRoot SP extract have no significant negative effects on cell proliferation, while the extract improves cell proliferation at 0.2 mg/mL.
Previous studies have demonstrated the relationship between cell biological behavior and calcium concentration [30]. An appropriate amount of calcium leached from the iRoot SP facilitates cell proliferation by activating mitochondrial matrix dehydrogenases [31]. However, iRoot SP at high concentrations inhibits the proliferation of hSCAPs. However, these findings are different from those reported by Zhang et al., who observed that iRoot SP has no cytotoxic effects after curing for 24 h [32]. The cytotoxic effects of iRoot SP may be explained by its high surface pH, which cause denaturation of adjacent cells and culture medium proteins. These inconsistencies may be due to the different setting time and stimulation modes applied for the test materials in our study [33].
Cell migration plays an important role in tissue regenerative and repair processes as it allows more cells to be recruited for repairing damaged sites [34]. In this study, wound-healing assays were used to detect the migration of hSCAPs treated with iRoot SP extract at three concentrations after 12 h. The results indicated that low concentrations promote cell migration, with the migration ability for the 0.2 mg/mL group being higher than those of the other groups. This result is in agreement with that of a previous study, which showed that iRoot BP Plus promotes dental pulp cell migration and pulp repair by activating FGFR-mediated signaling pathways, upregulating the expression of focal adhesion molecules and promoting stress-fiber assembly [35]. It has also been reported that the formation of a hydroxyapatite layer on the surface of a filling material promotes the recruitment of MSCs, leading to highly active tissue repair and/or regeneration [36].
As a functional marker enzyme, ALP is involved in the formation of mineralized tissues such as teeth and bone and is considered to be an early marker of osteogenic differentiation in odontogenic stem cells [37]. The results showed that 0.2 mg/mL iRoot SP extract significantly increases the ALP activity of hSCAPs, and Alizarin red staining and semi-quantitative CPC analysis also demonstrated that the calcium matrix produced by cells increases significantly under treatment at this optimal concentration. OCN, Runx2, OSX, DSPP are characteristic markers of osteogenic differentiation [37, 38]. Our results revealed that treatment of hSCAPs with 0.2 mg/mL iRoot SP extract creates a suitable microenvironment for periapical bone regeneration and upregulates the expression of osteogenesis-related genes and proteins. This result is consistent with previous findings indicating that iRoot SP upregulates the gene and protein expression of osteogenic-related factors in MG63 cells [18]. Chang et al. found that iRoot SP promote the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stromal cells (PDLSCs) by activating integrin receptors and downstream signaling molecules [20].
Related studies have demonstrated that the silicon and calcium ions released by iRoot SP during hydration and solidification may be the main active components of the material, and that their bioactivities affect cellular response [39]. The release of non-polar ions induces a series of biological reactions in MSCs, thus inducing tissue repair and regeneration [40]. It has been shown that MTA induces BMP-2 expression and calcification in human periodontal ligament cells through CaSR interactions, which are activated by the gradual release of calcium [41]. Another study demonstrated that silicon ions have a dual action, promoting osteoblasts and inhibiting osteoclasts [42]. The inorganic ions released by bioceramic materials have been identified as important signaling molecules and regulators that control numerous cellular activities that maintain the homeostasis of bones [43].
It should be noted that the present study has several limitations. First, the concentrations of the ionic products from iRoot SP were not determined. Furthermore, the signal transduction pathways of iRoot-SP-induced osteogenic differentiation in hSCAPs was not investigated. Additionally, osteogenic differentiation has a particular time profile, so longer observation periods may be needed to understand the fluctuation of the expression of osteogenesis-related factors during the complete process.
Conclusions
iRoot SP is a promising calcium-silicate-based biocompatible material with potential application value in periapical bone regeneration. Our results demonstrate that iRoot SP extract at 0.2 mg/mL enhances hSCAP proliferation, migration, and osteogenic differentiation. Overall, this study provides valuable information for the further study of the mechanisms of bioceramic-mediated periapical bone repair.